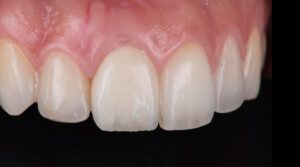
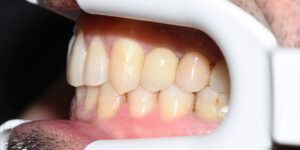
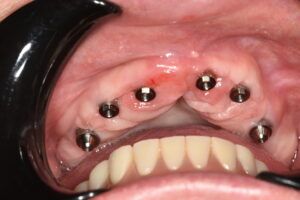
Introduction
Increase in keratinized gum in posterior sectors: Although there is still controversy surrounding the role of keratinized mucous membranes around implants, there are more and more studies that observe a correlation between the absence of an adequate band of keratinized gum and different pathologies in the tissues around implants in the medium to long term (greater inflammation, bleeding upon probing, recession and even greater crestal bone loss).
There are studies that justify prior periimplant mucogingival treatment, simultaneous or subsequent to placing the dental implants when a lack of this tissue is detected, with the aim of optimizing the width and thickness of the keratinized mucous membranes and avoiding exposing the implant to adverse conditions. But to do so, like teeth, there are no uniform criteria, although free gingival grafts associated with an apical repositioning flap are considered the gold standard when the purpose of the surgery is to increase the keratinized tissue. Increase in keratinized.
The detailed study of the case and the clinical experience are going to be deciding factors in the treatment plan of the case, making it predictable in the long term, as shown in the case below.
Case presentation
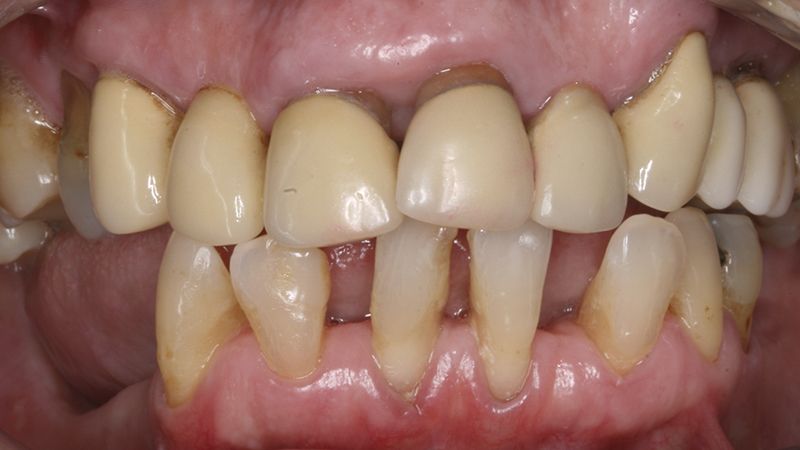
A female patient, aged 62 years, with no medical history of interest, only controlled hypertension, attended the clinic intending to replace her lower removable prosthesis with a fixed restoration.
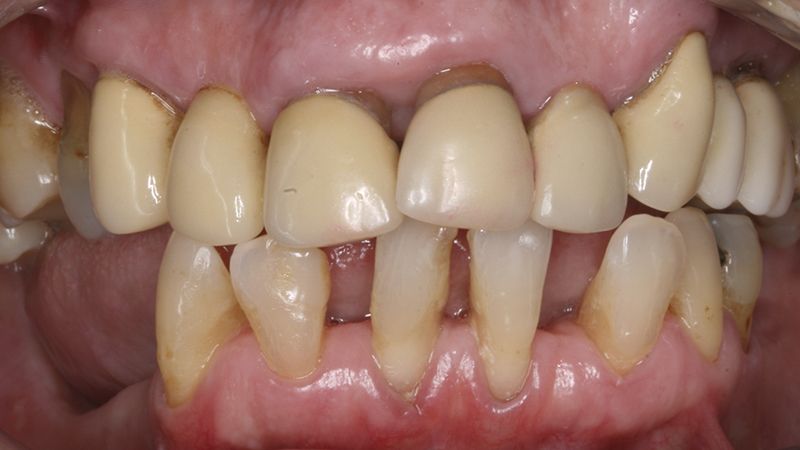
After an exhaustive examination, observing the distribution of the teeth and bite presented, the patient was offered an orthodontic treatment first to align the teeth and distribute the spaces properly, to then be able to place four dental implants in the posterior edentulate areas.
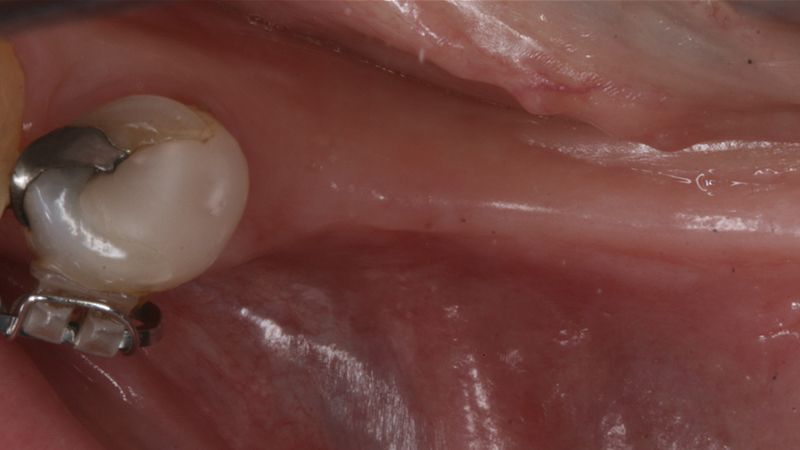
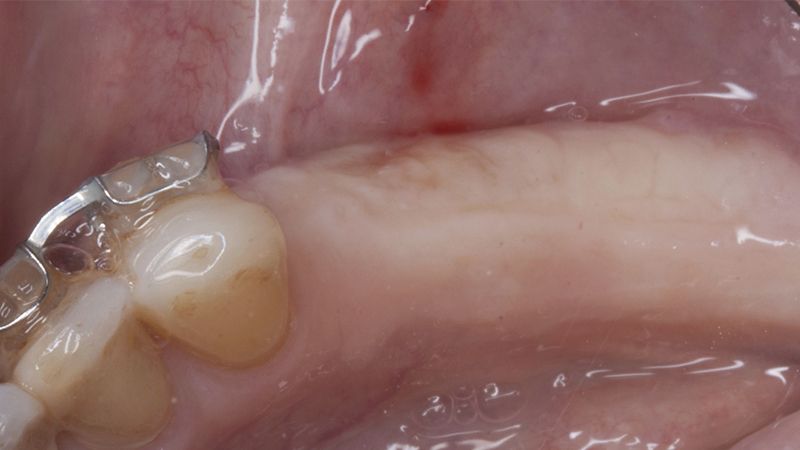
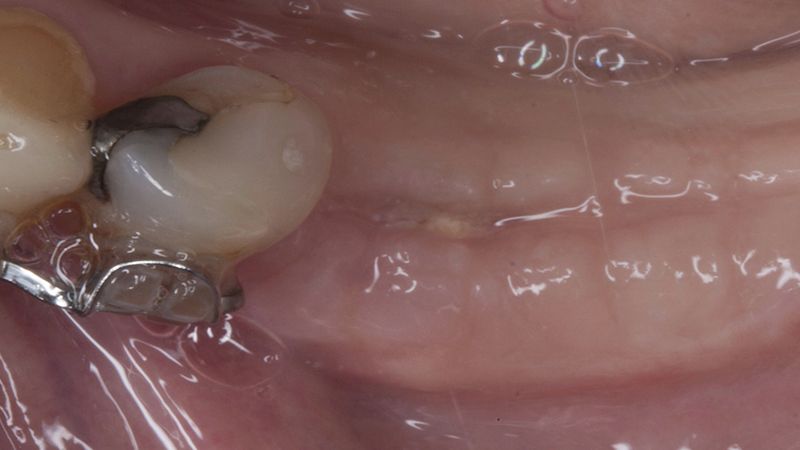
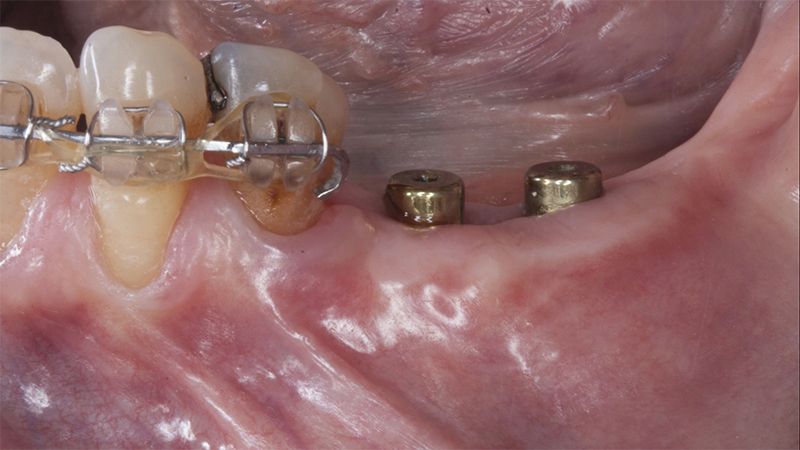
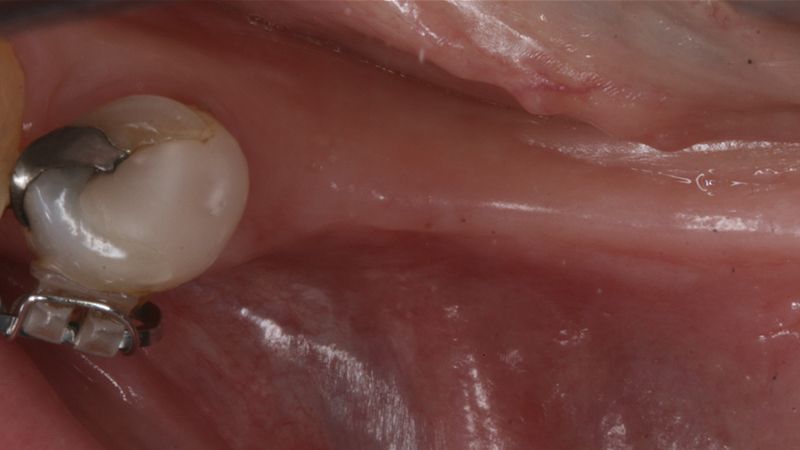
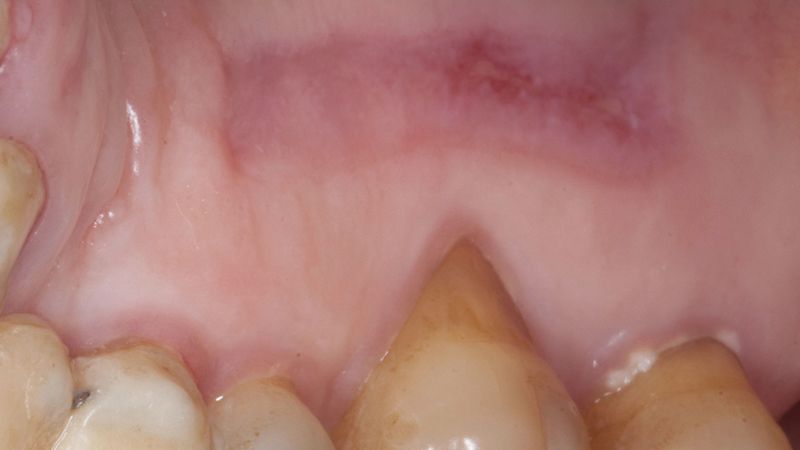
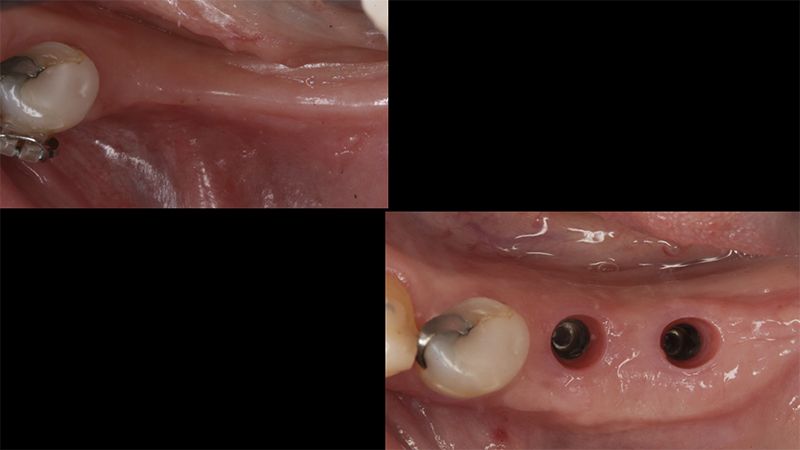
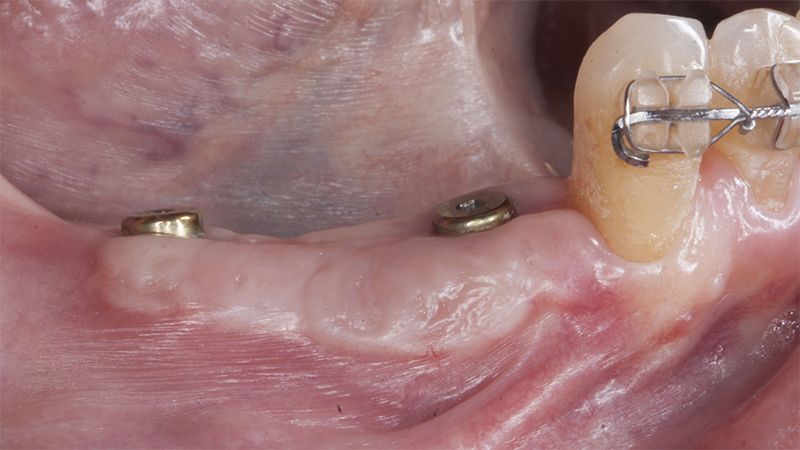
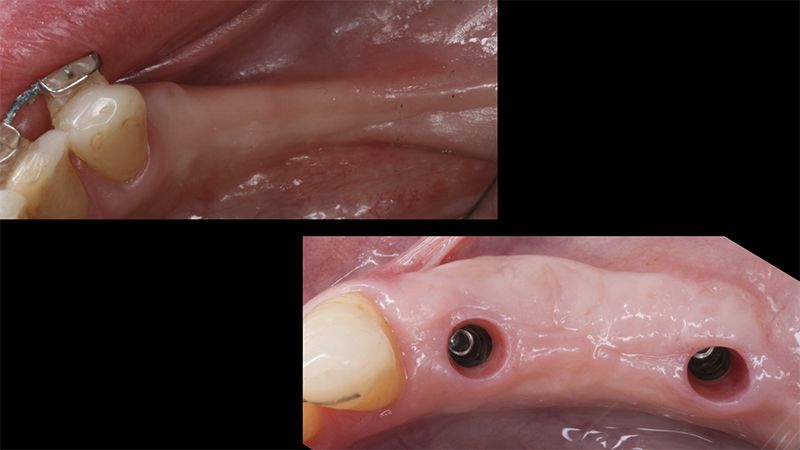
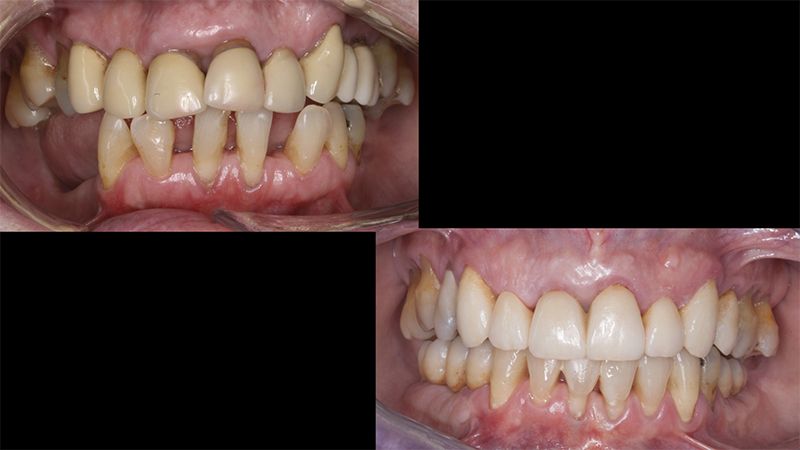
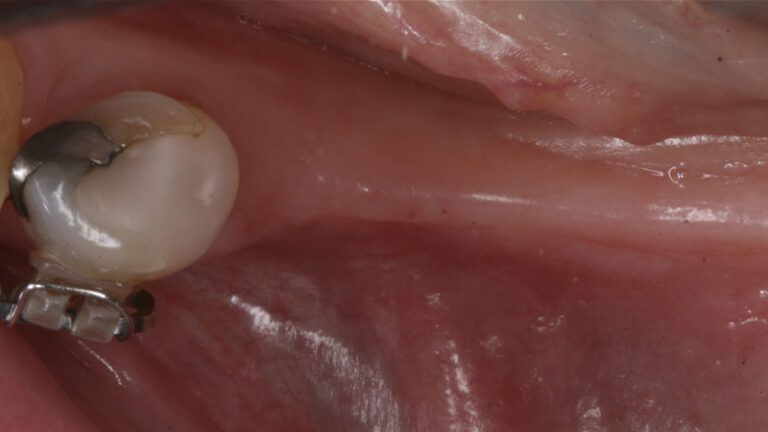
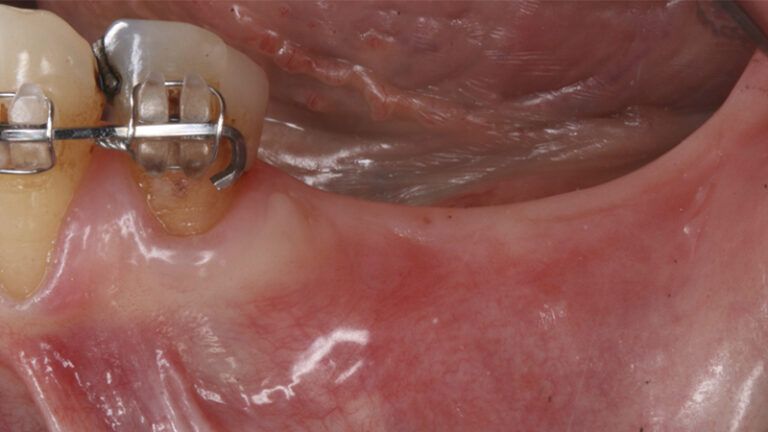
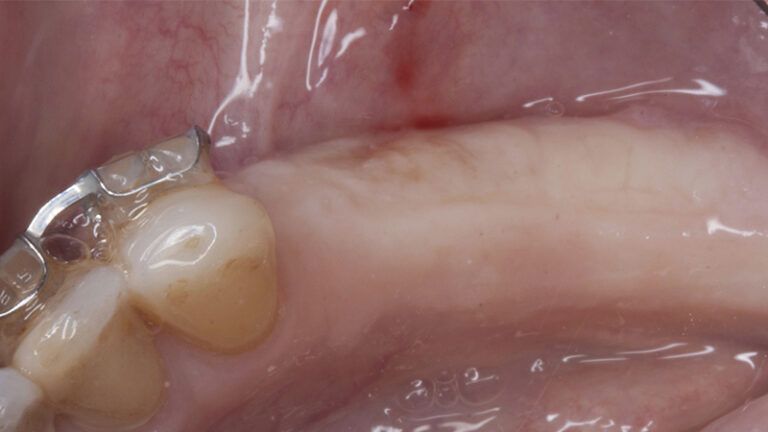
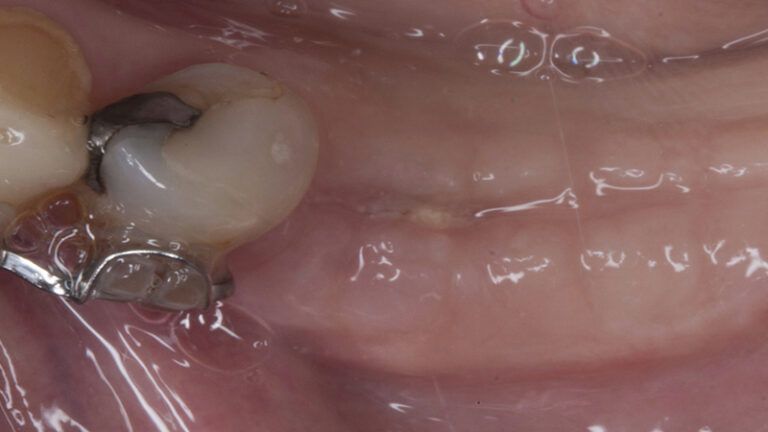
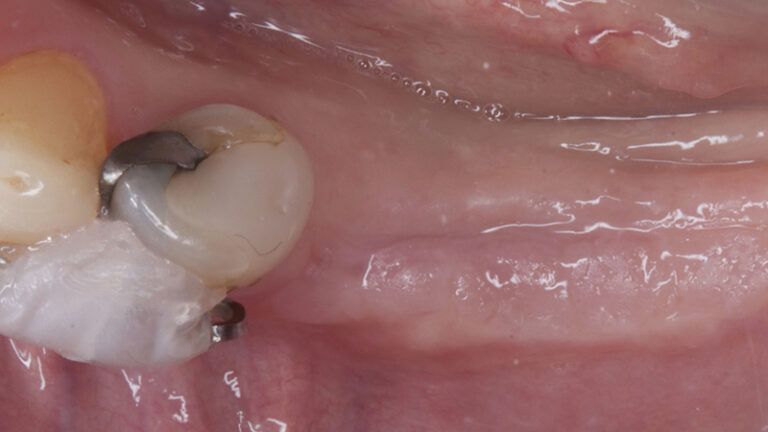
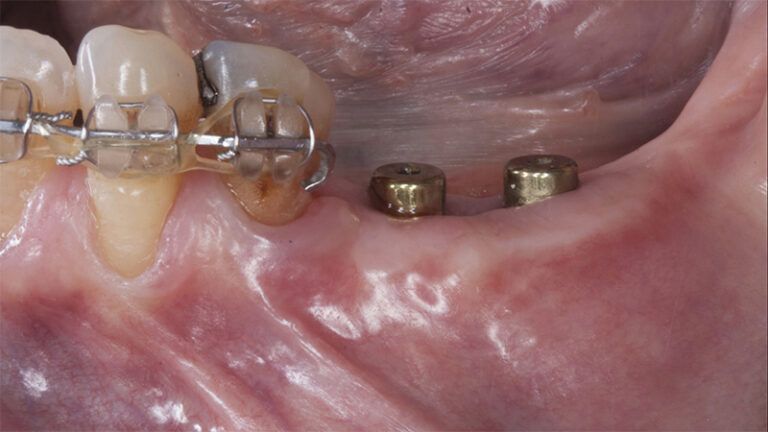
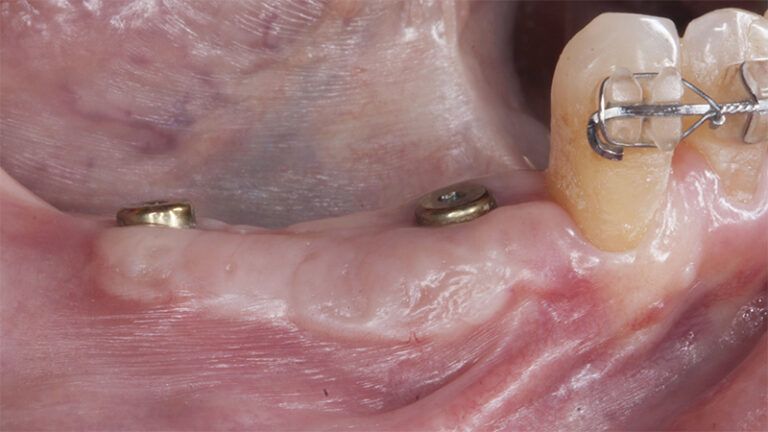
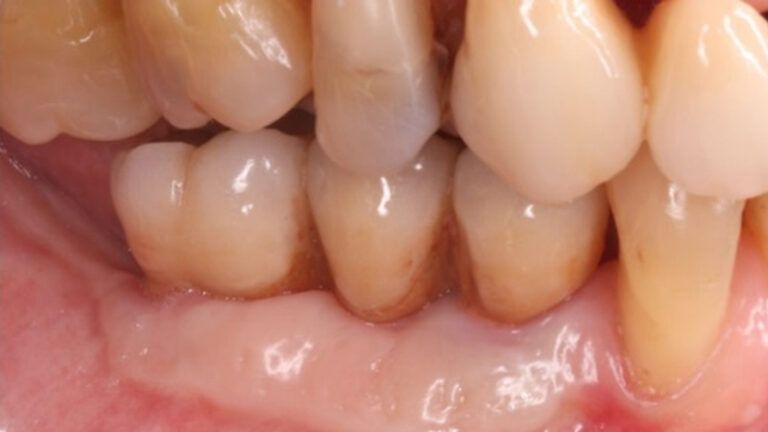
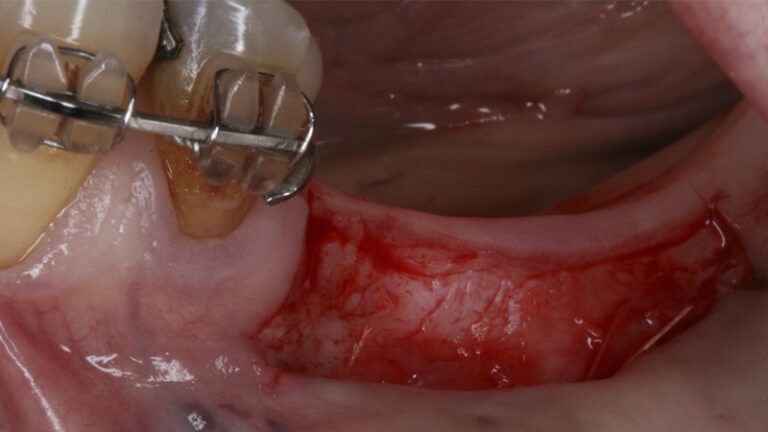
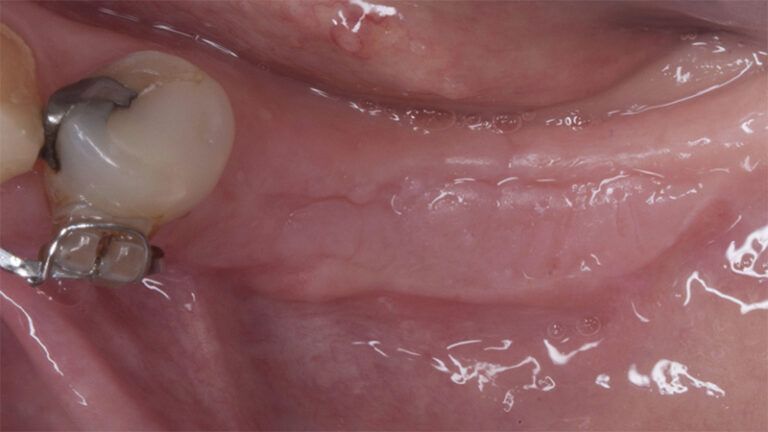
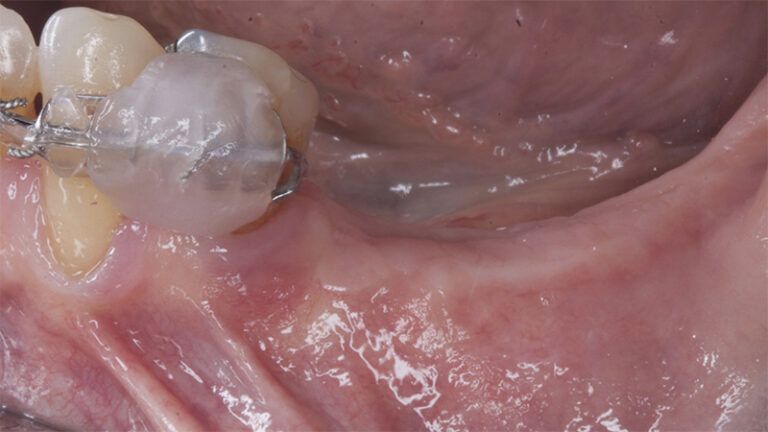
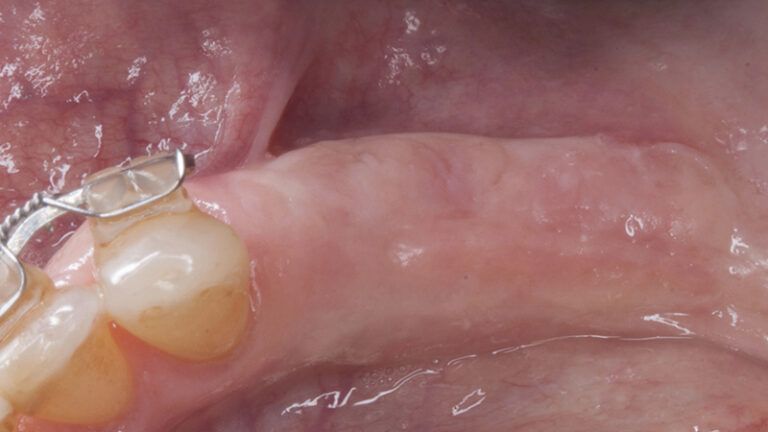
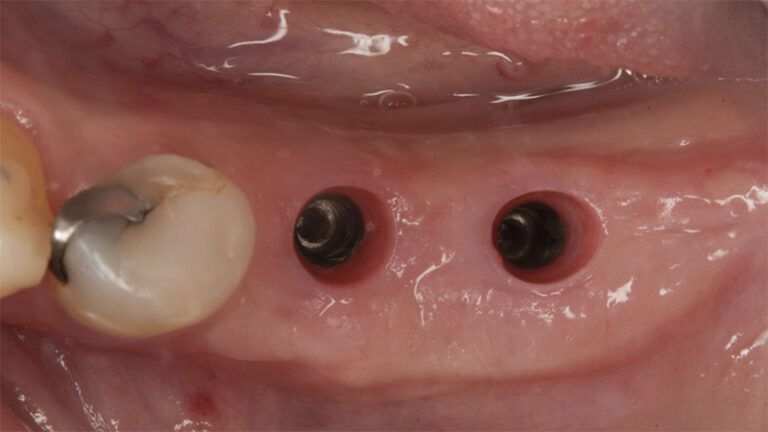
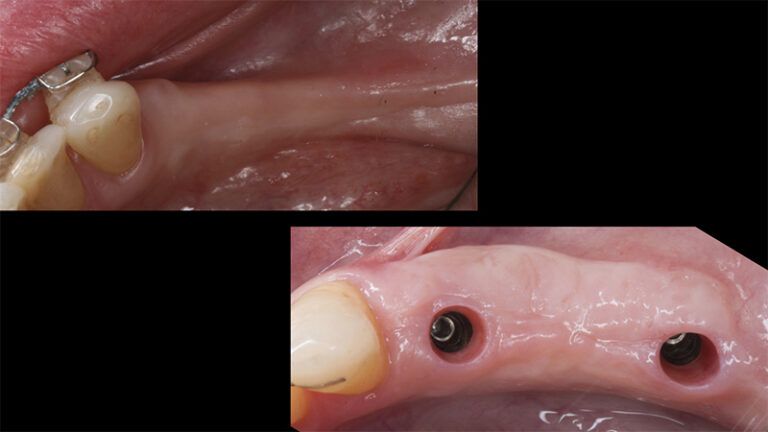
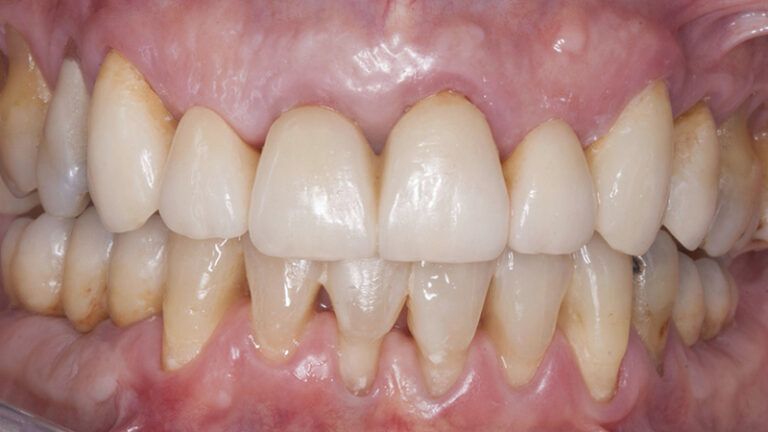
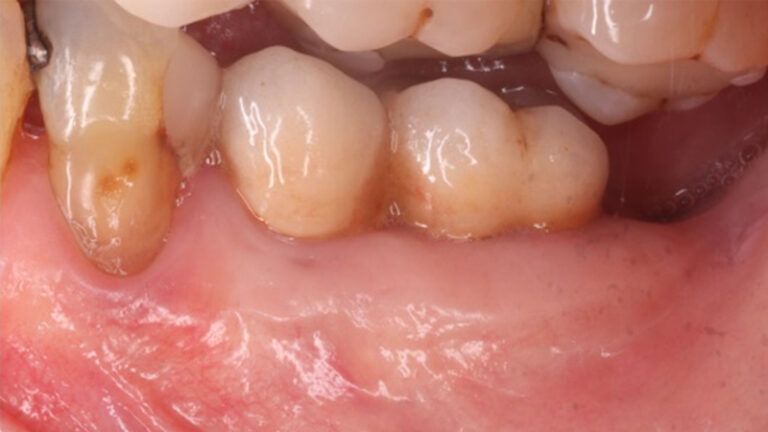
During the orthodontics stage and the planning of the dental implants, there was found to be insufficient keratinized gum in the vestibular area of the two lower quadrants, which could affect the stability of the long-term treatment.
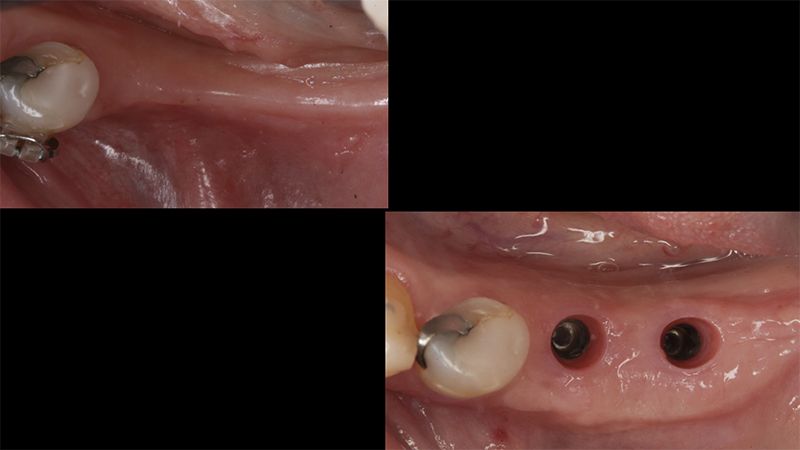
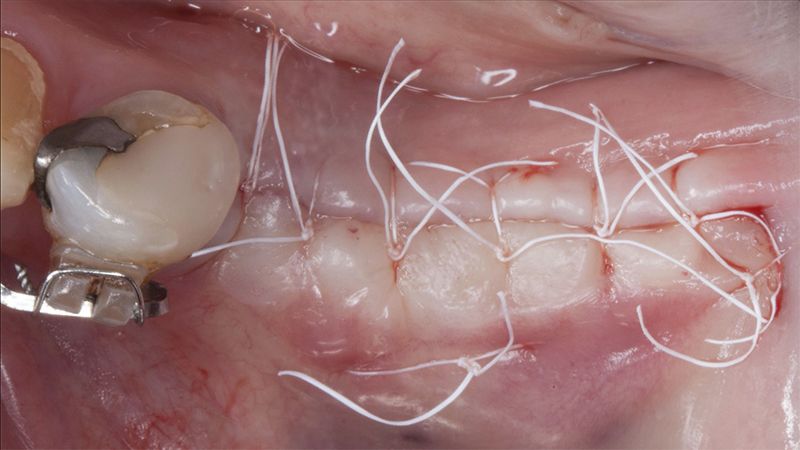
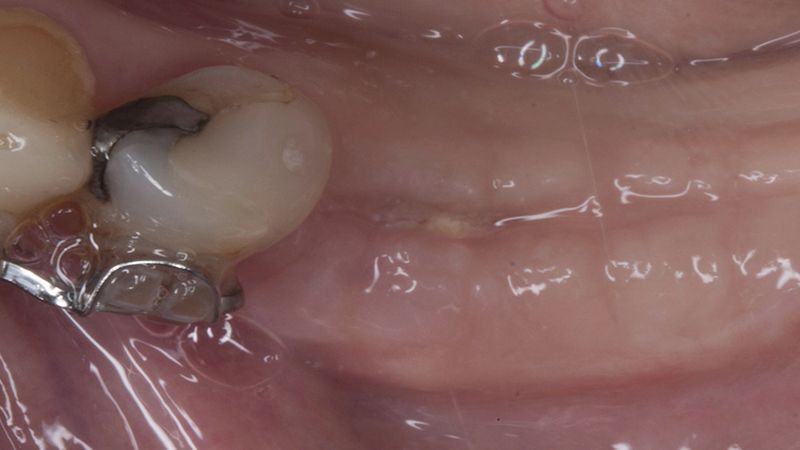
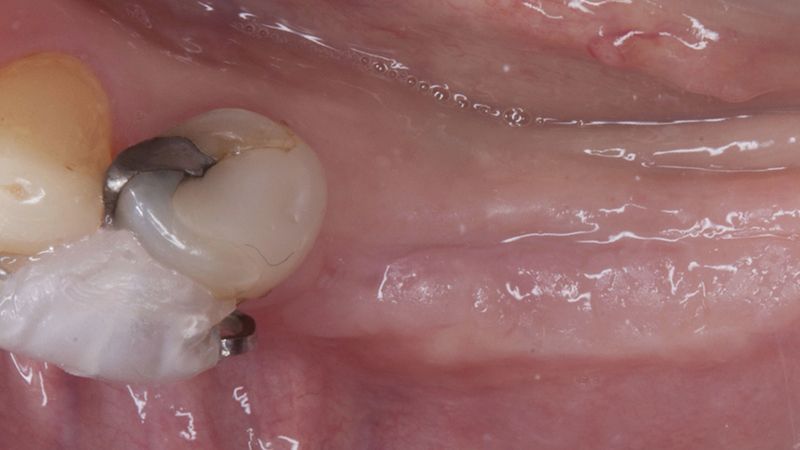
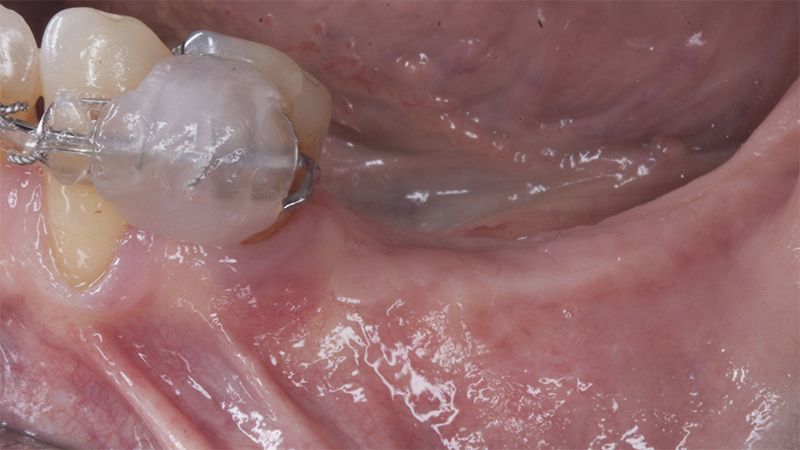
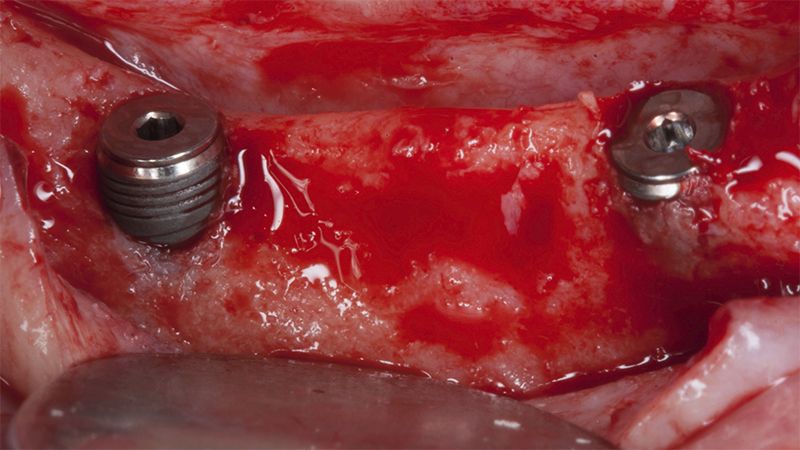
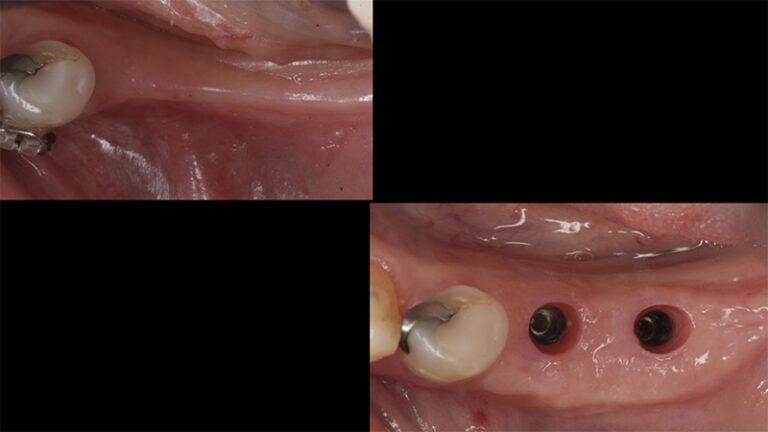
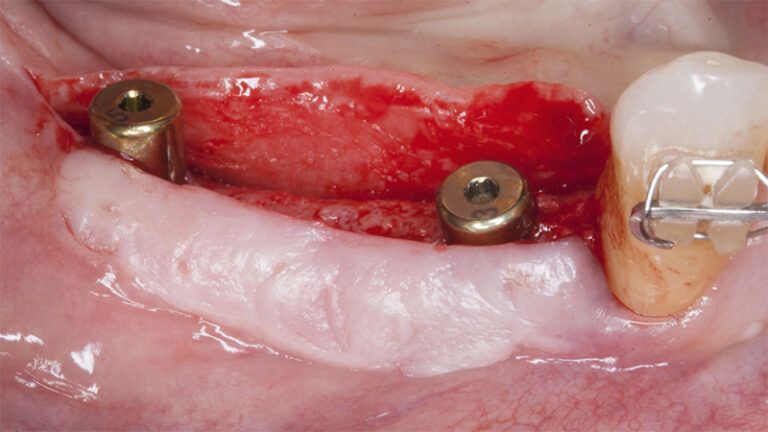
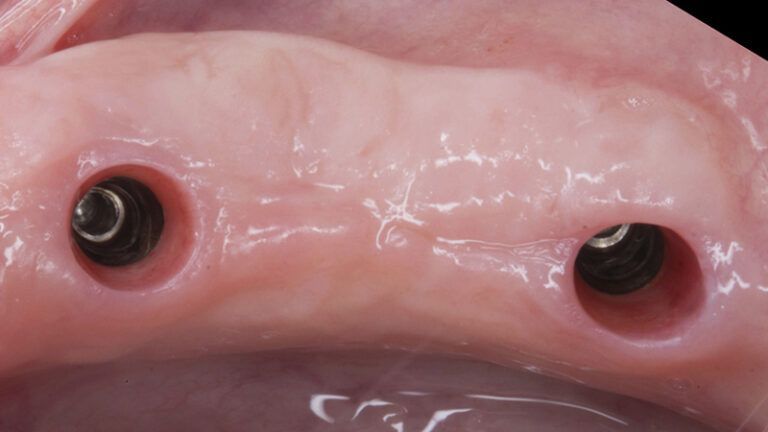
Initial situation of the implant area Initial situation of the implant area
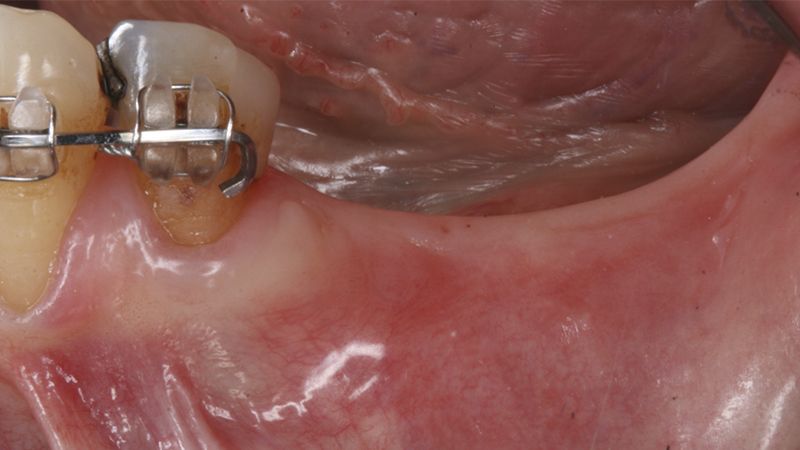
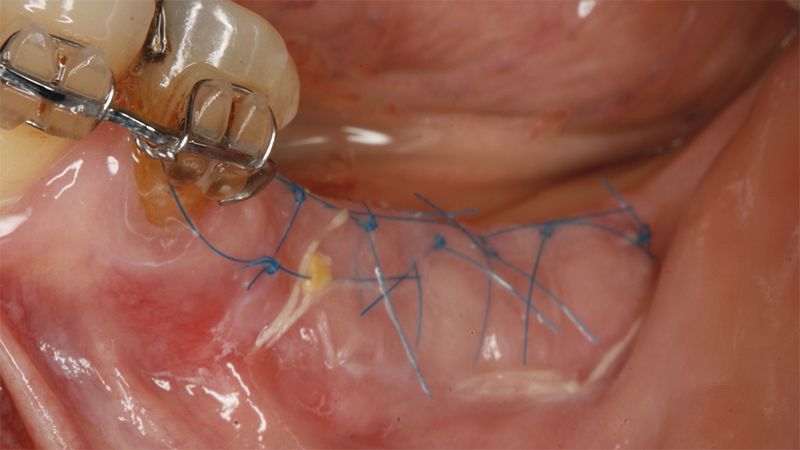
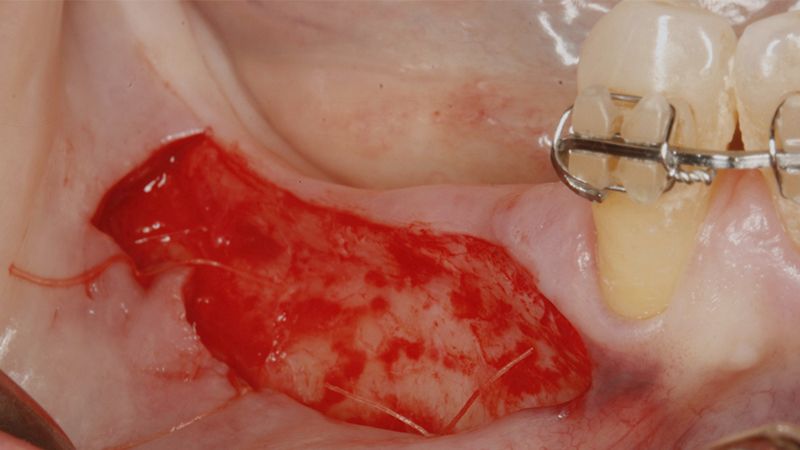
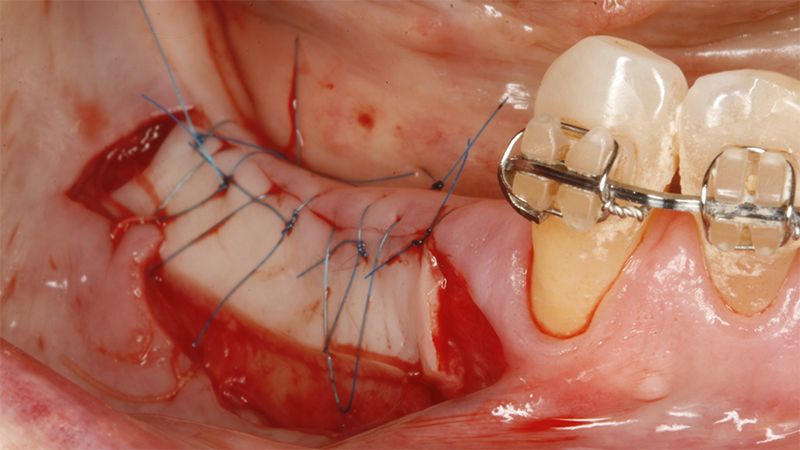
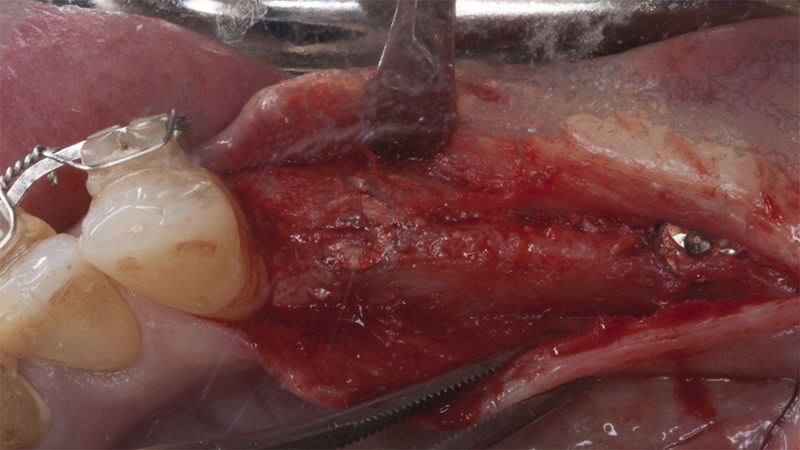
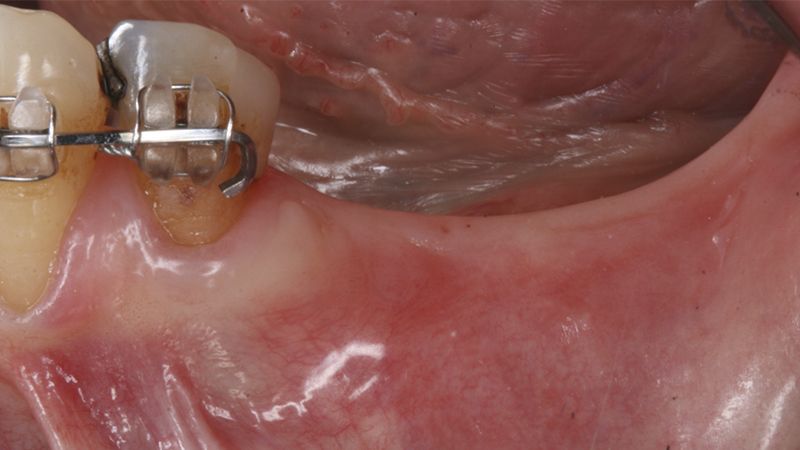
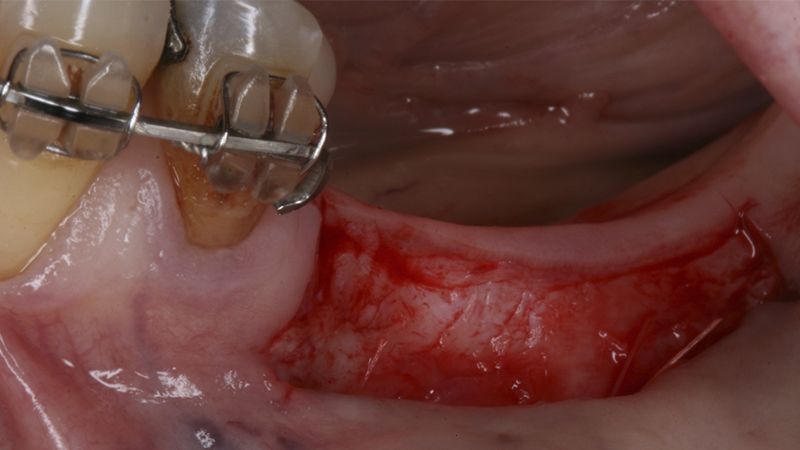
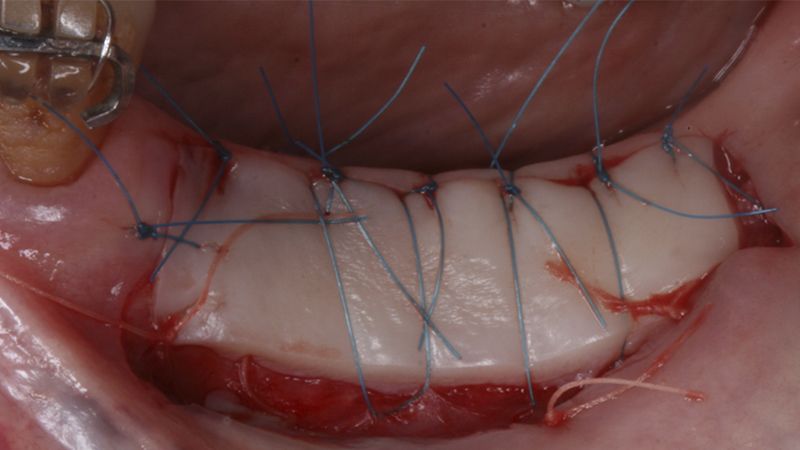
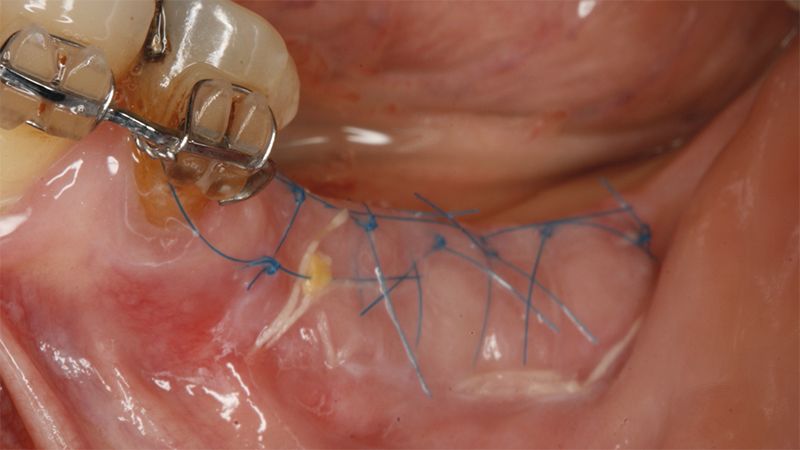
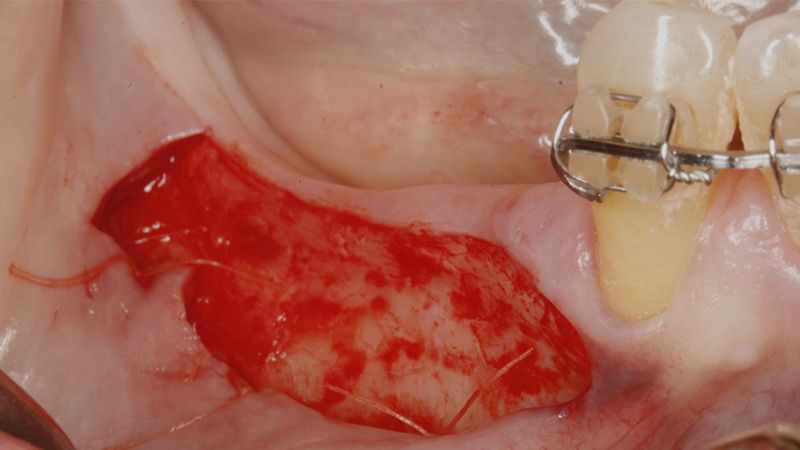
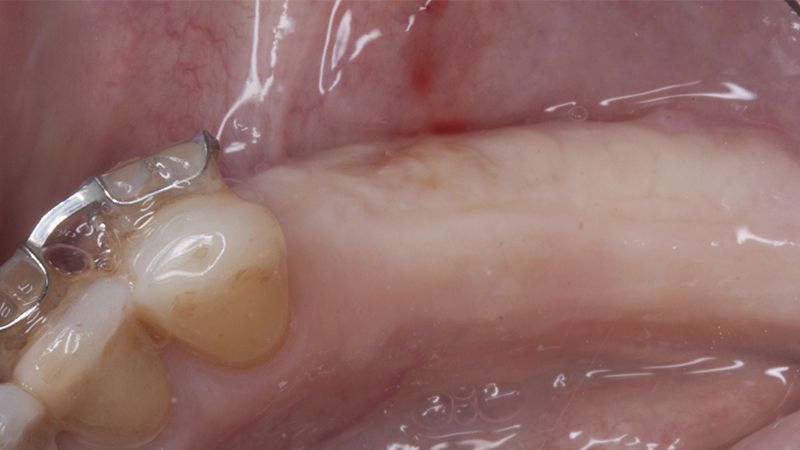
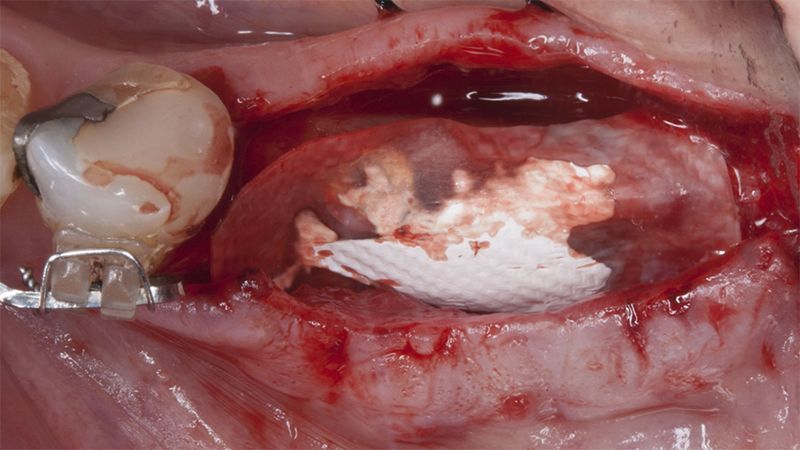
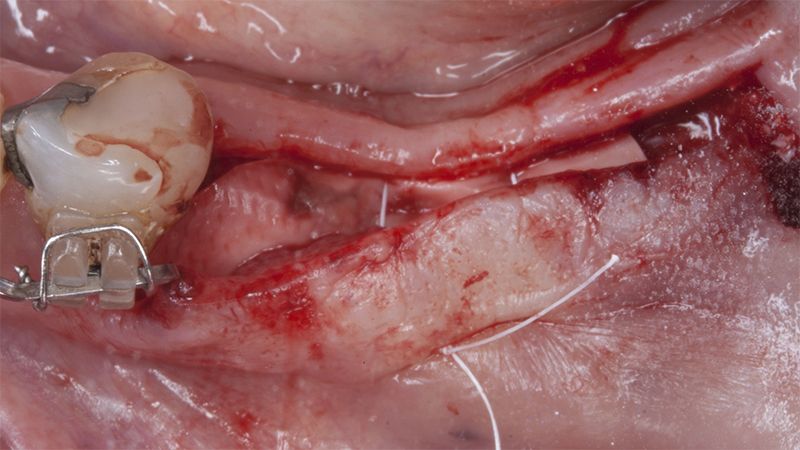
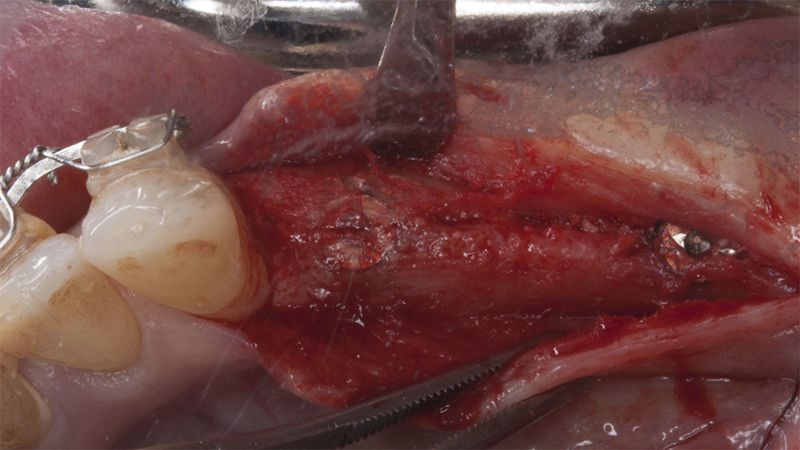
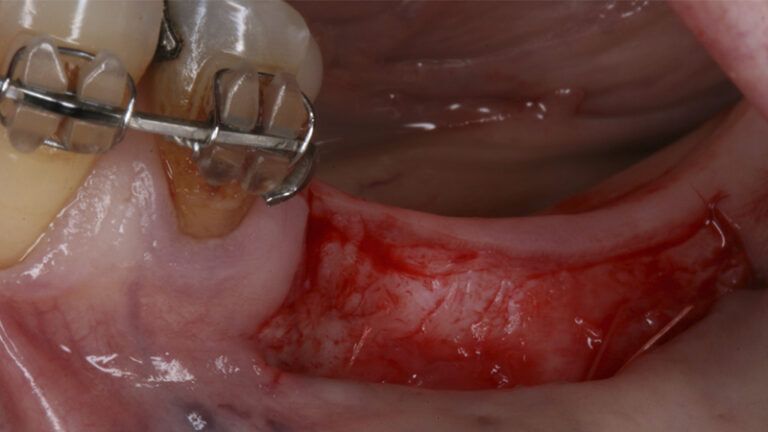
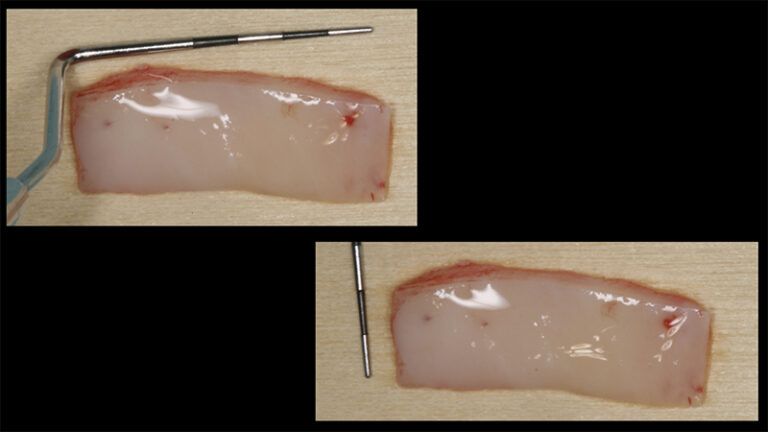
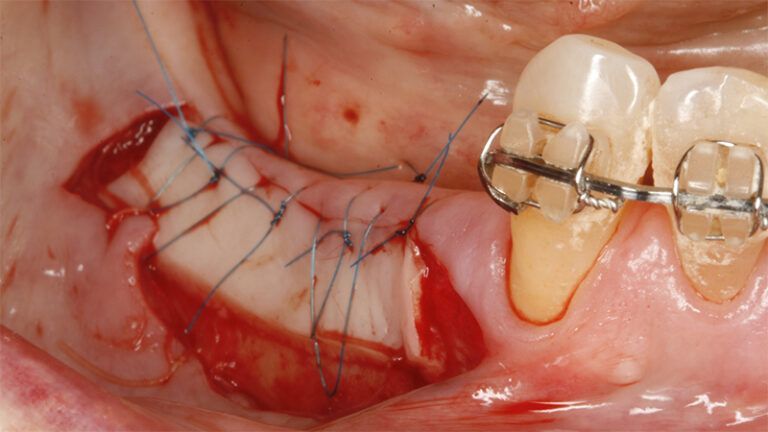
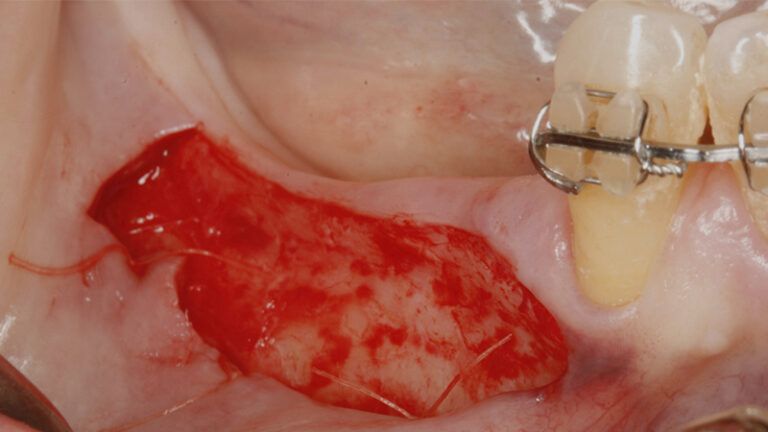
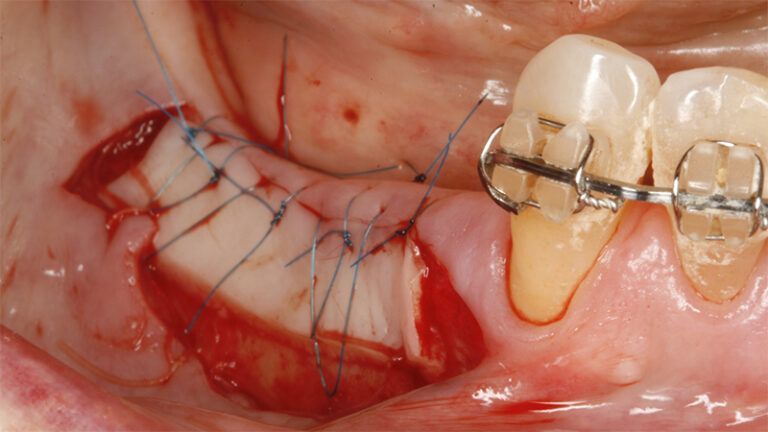
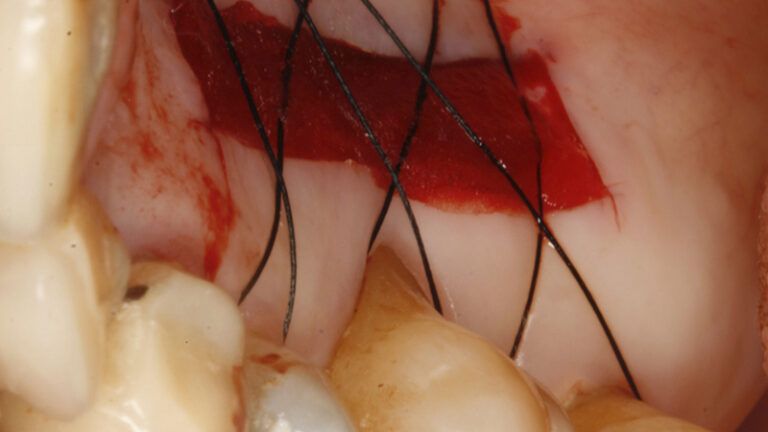
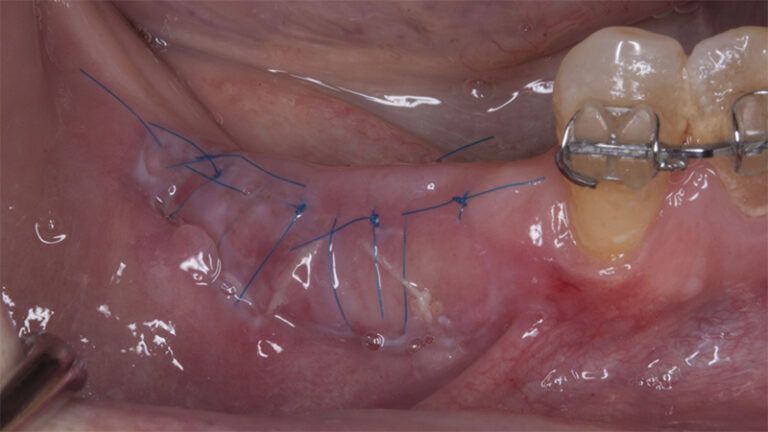
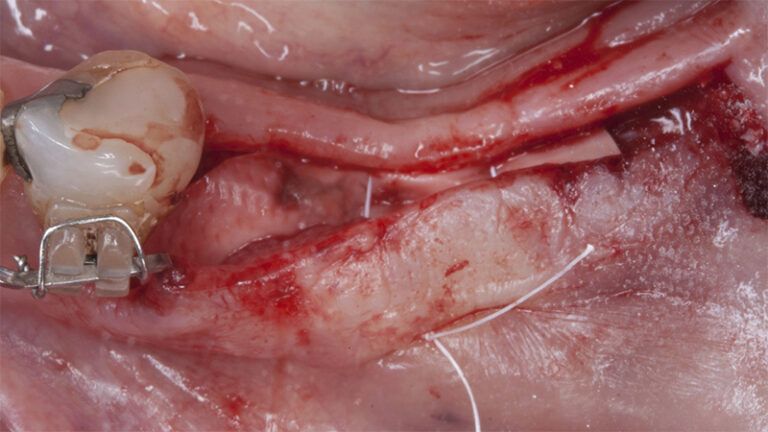
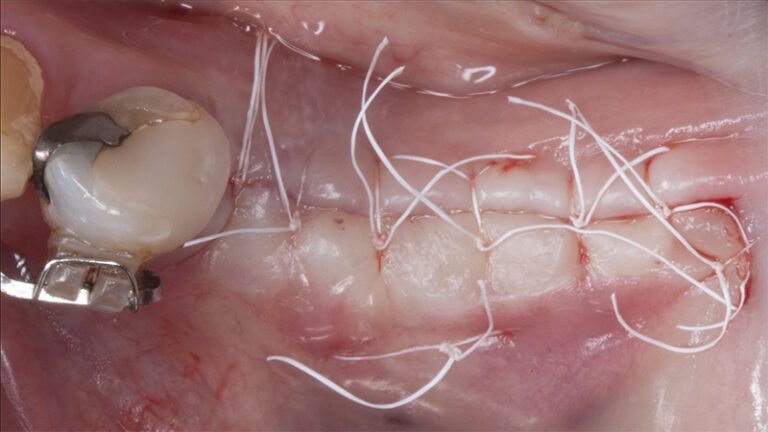
It was decided to make two free gingival grafts (FGG), prior to the implant surgery, to increase the band of keratinized mucous membrane in the two posterior areas to facilitate the prosthetics procedures and the subsequent maintenance of the implants.
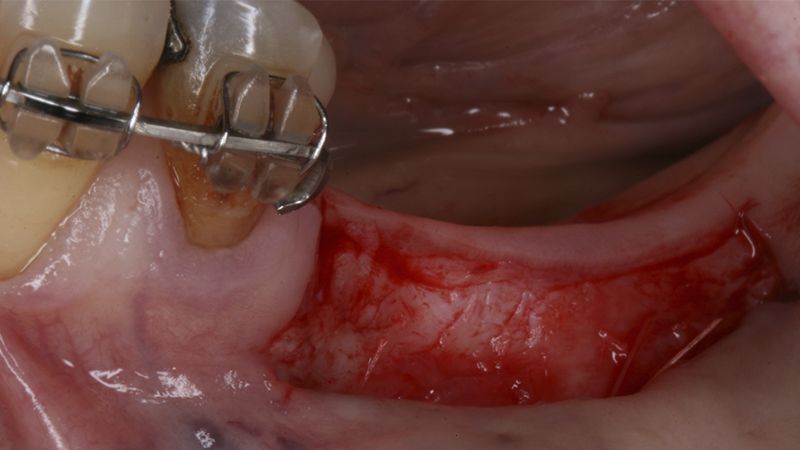
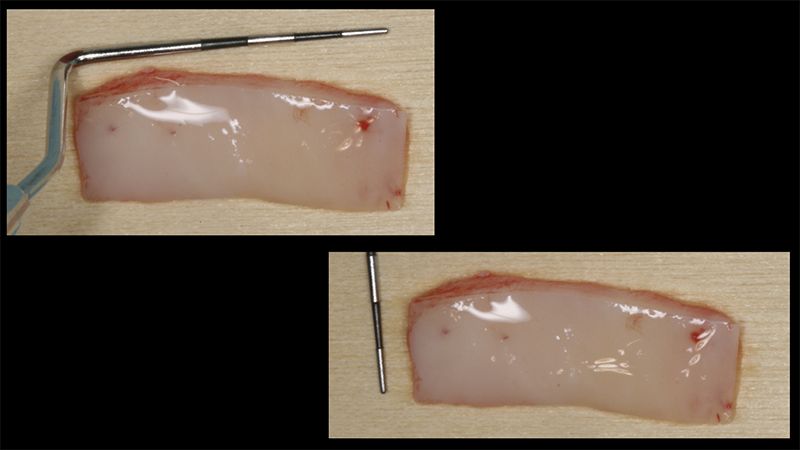
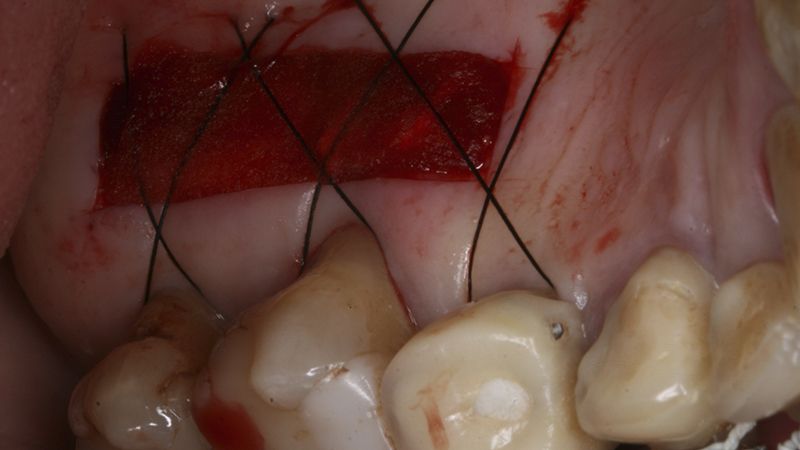
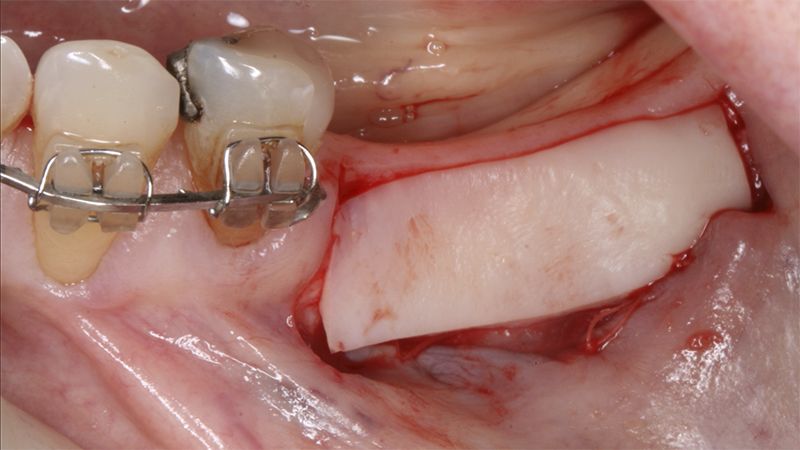
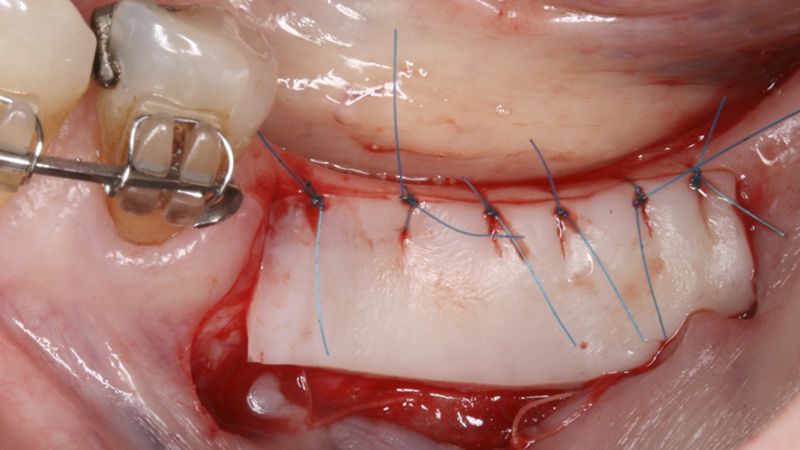
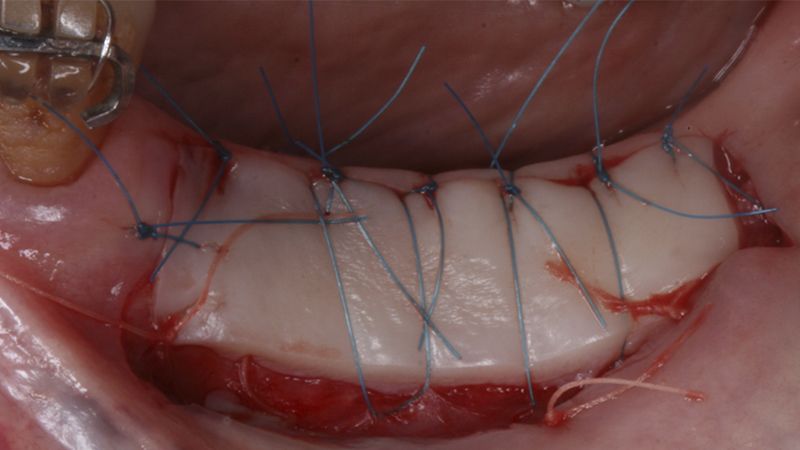
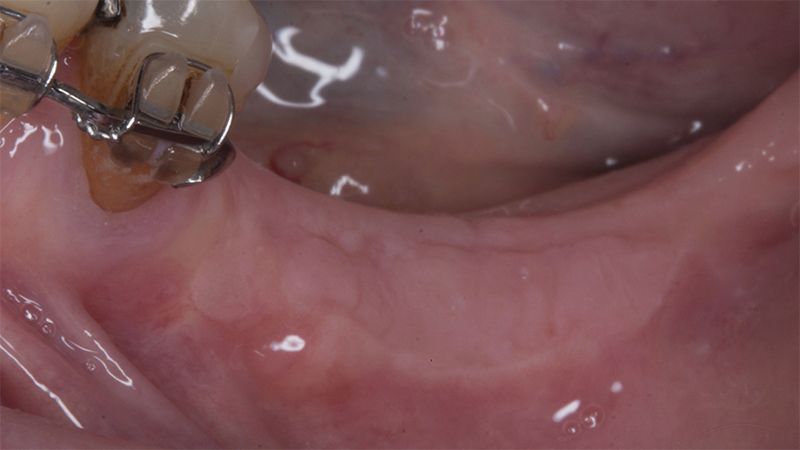
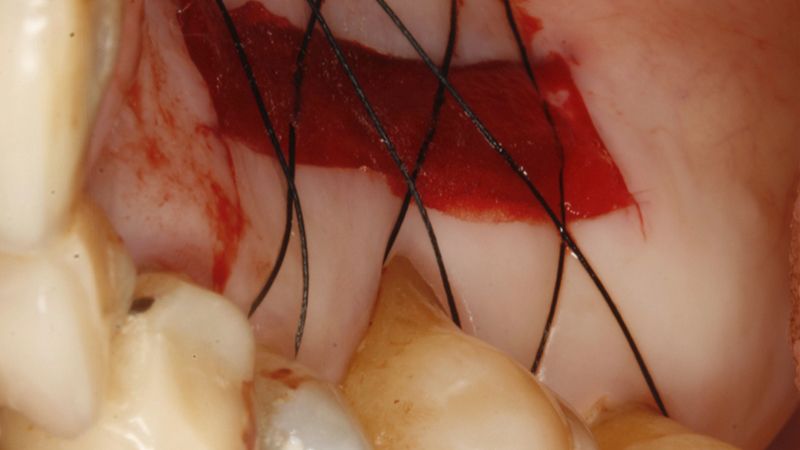
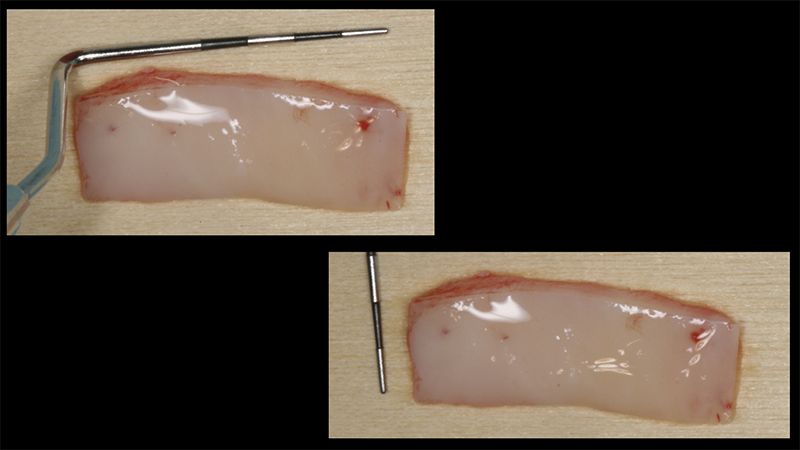
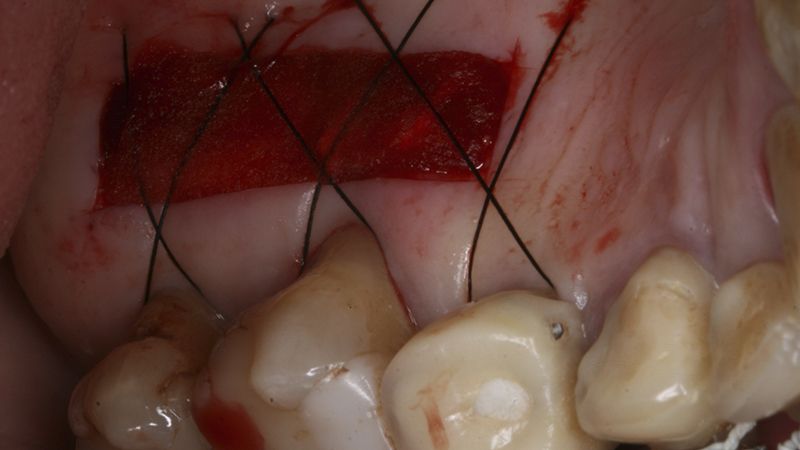
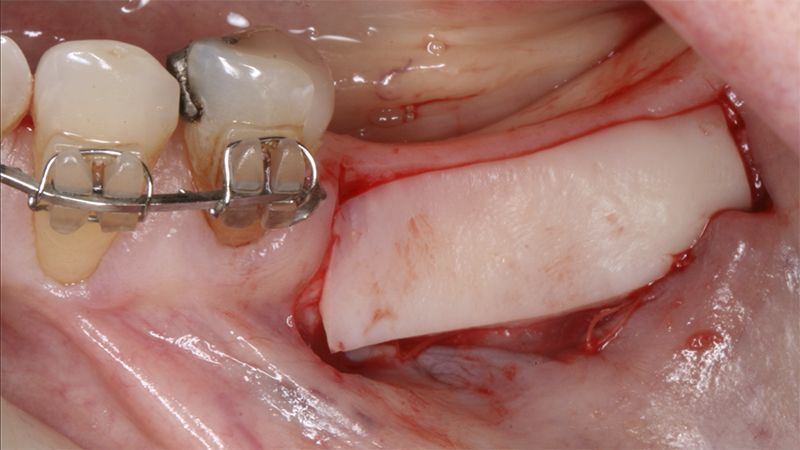
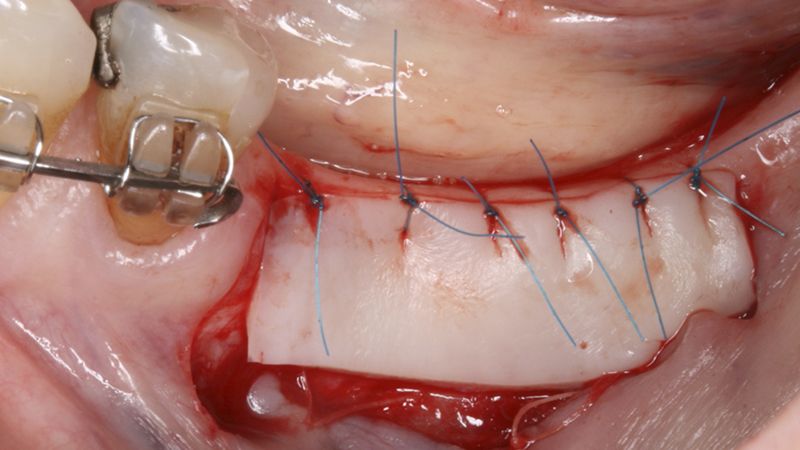
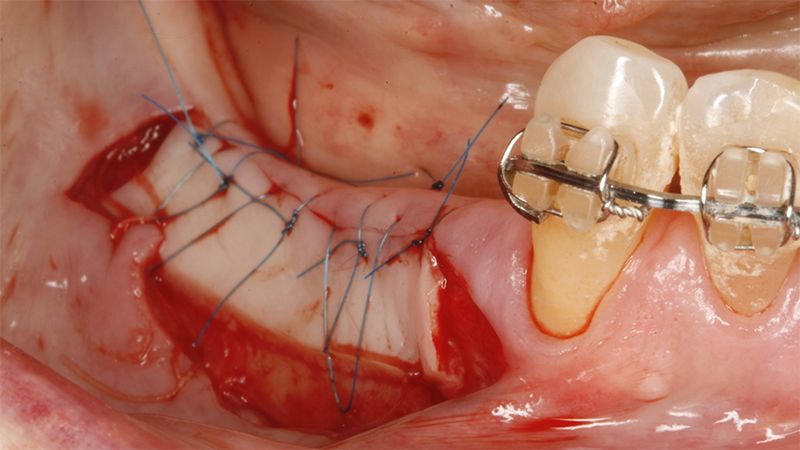
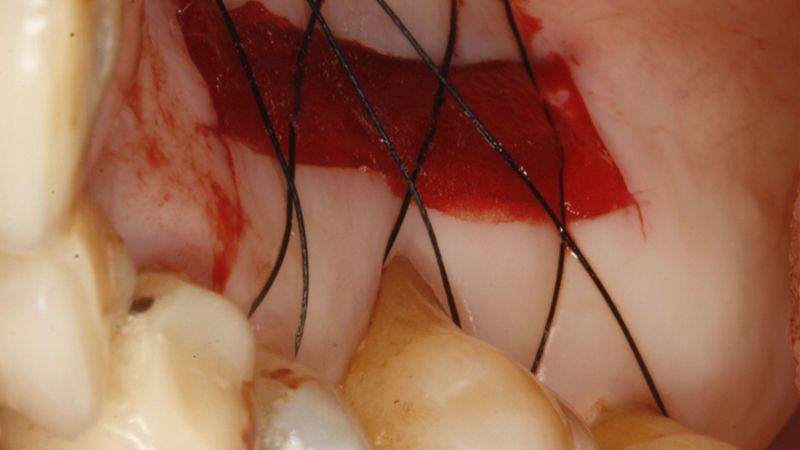
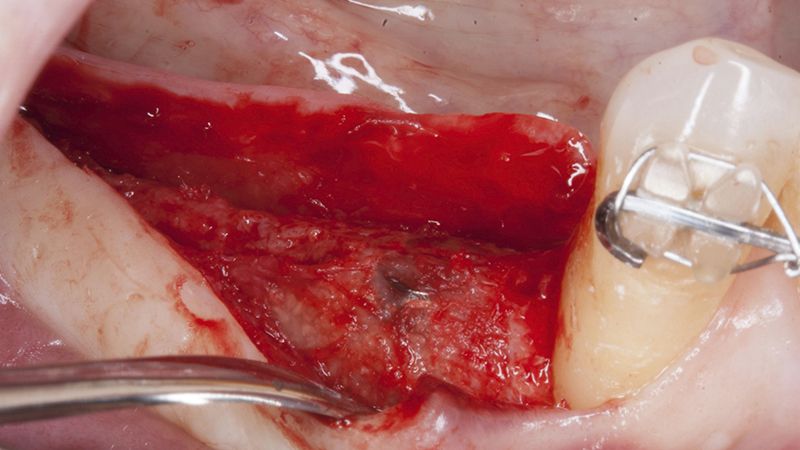
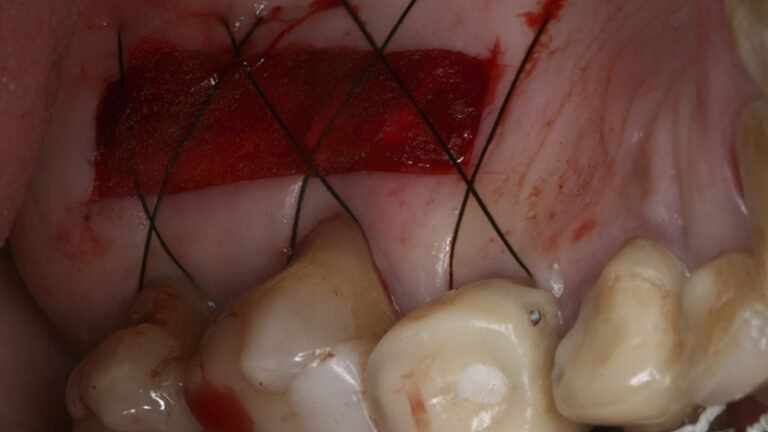
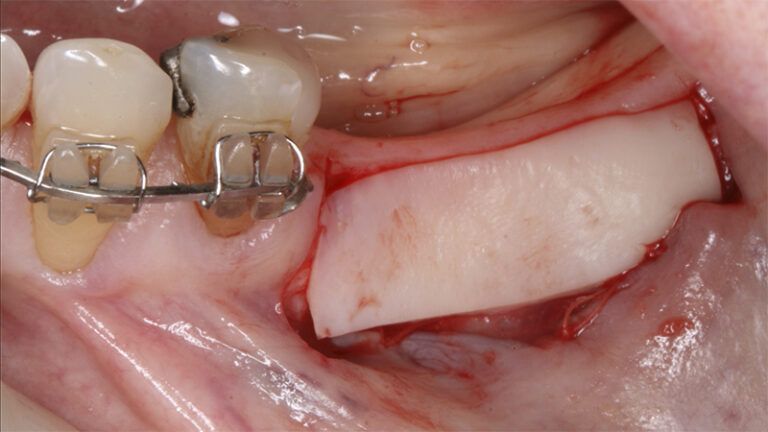
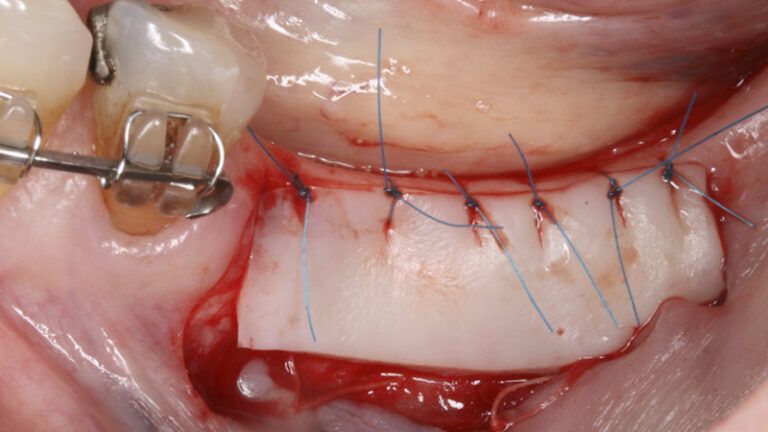
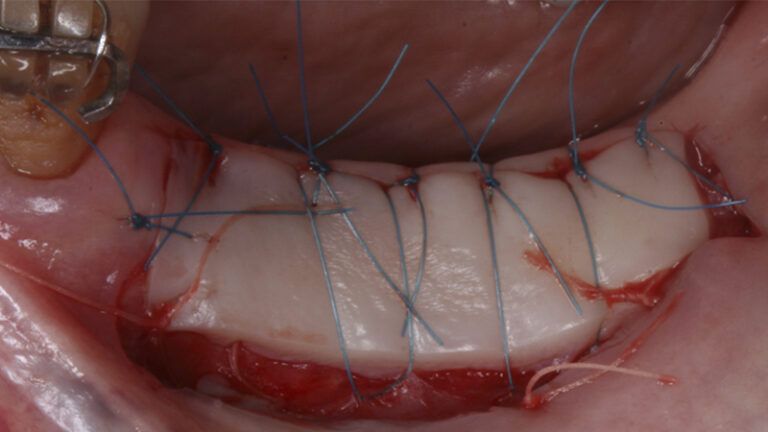
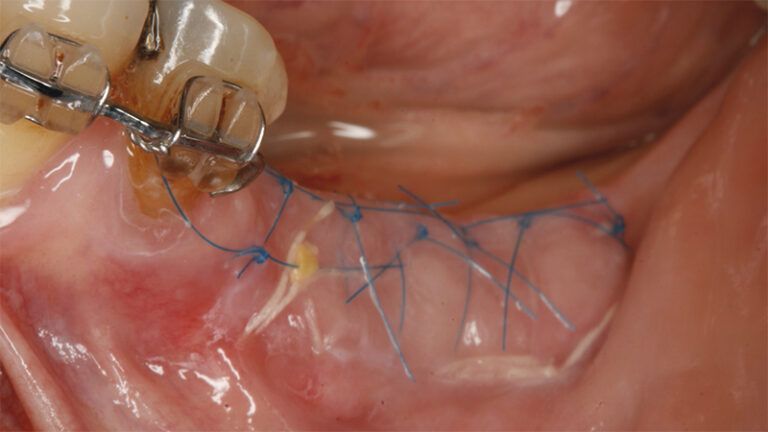
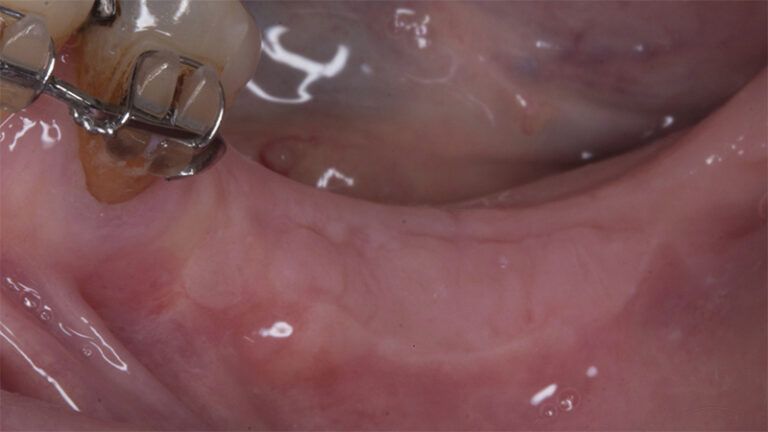
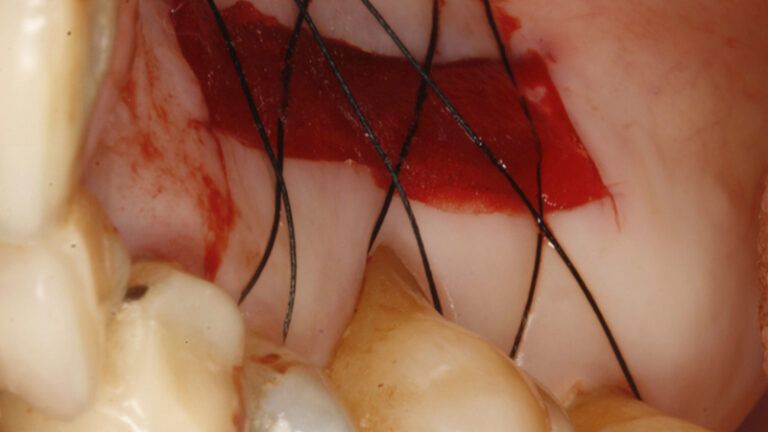
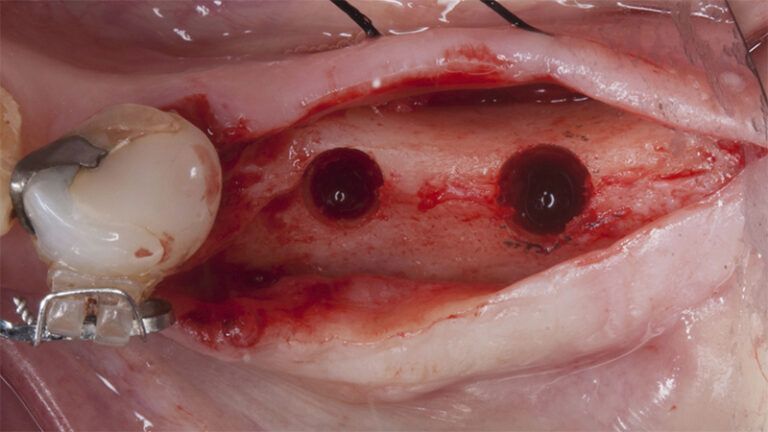
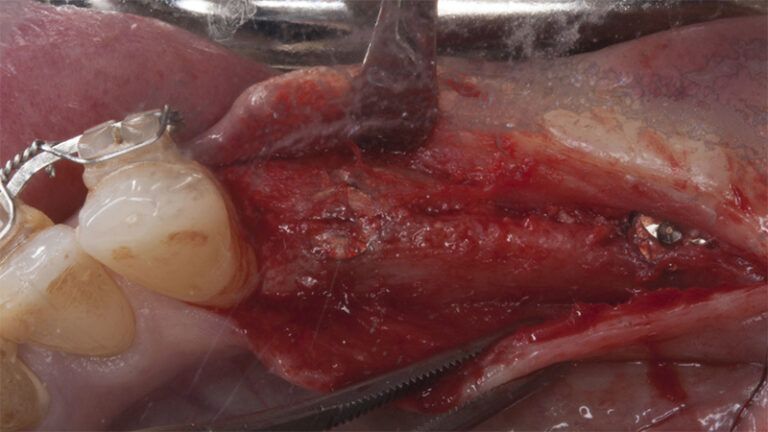
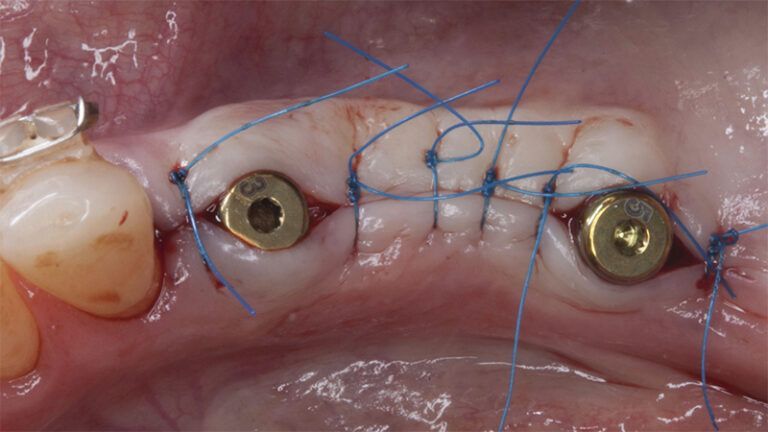
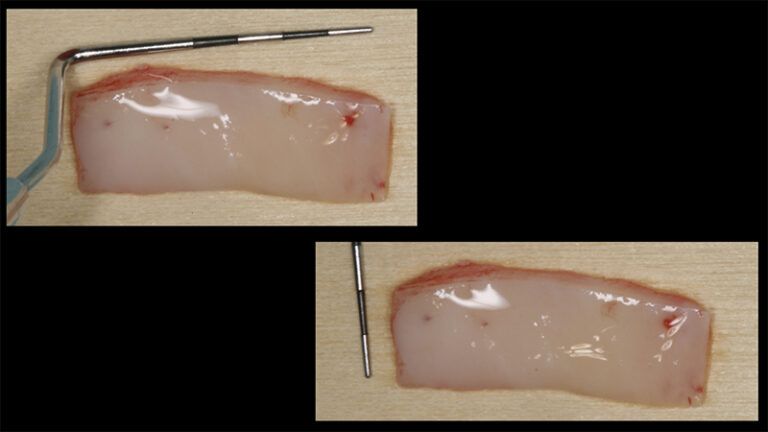
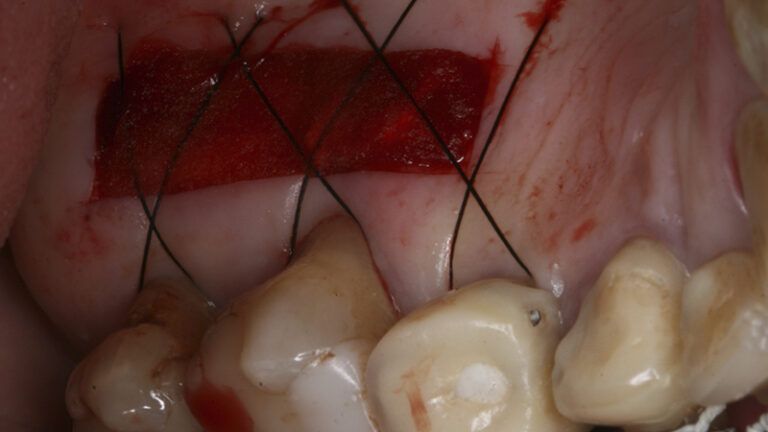
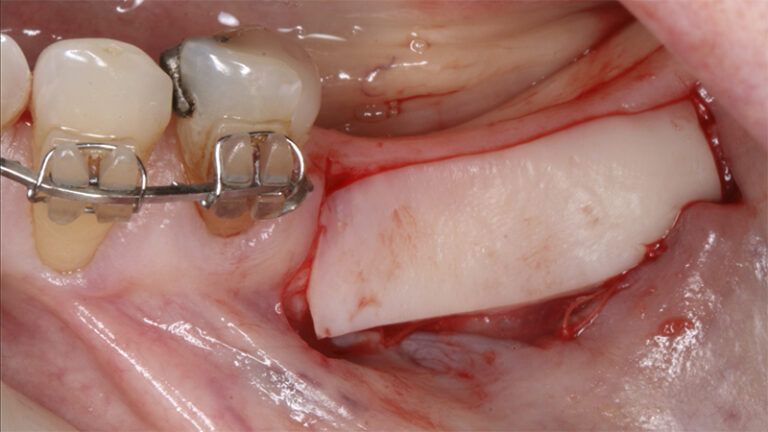
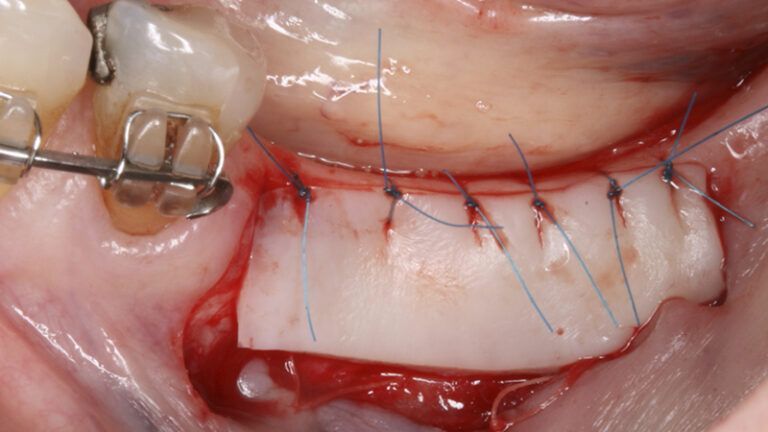
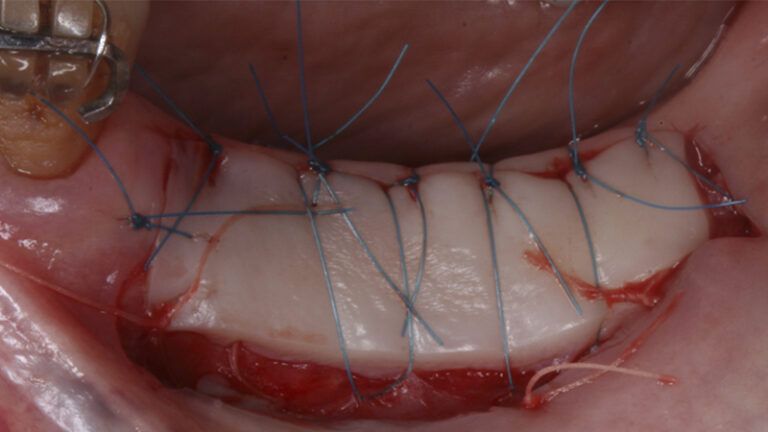
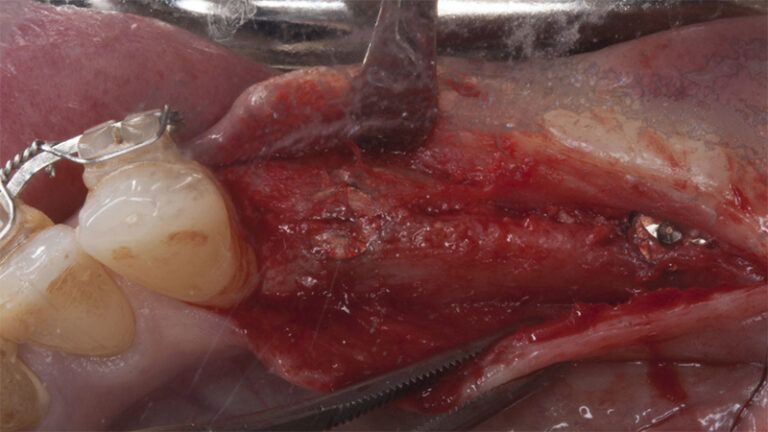
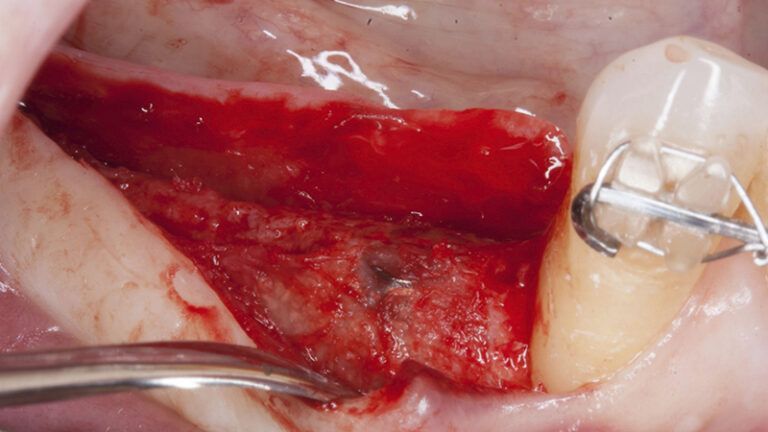
Preparation of the recipient bed for the graft in the 3rd quadrant Obtaining the free gingival graft of 20x7mm, with an approximate thickness of 1.5mm Details of the treatment of the donor area of the palate with hemostatic collagen sponges and cross sutures Checking the graft and its dimensions in the recipient bed Stabilizing the graft with simple stitches and compression sutures with 6-0 monofilament Stabilizing the graft with simple stitches and compression sutures with 6-0 monofilament Healing 15 days after surgery Lateral view of the complete revascularization and integration of the graft in the bed after 8 weeks Occlusal view of the keratinized tissue gained after 8 weeks
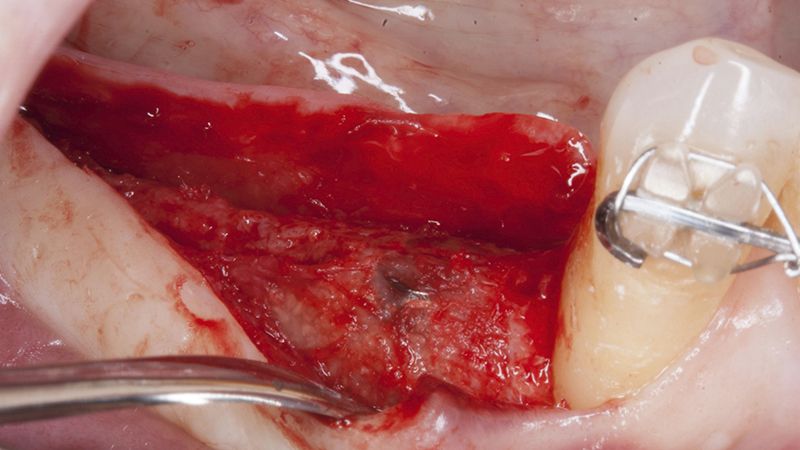
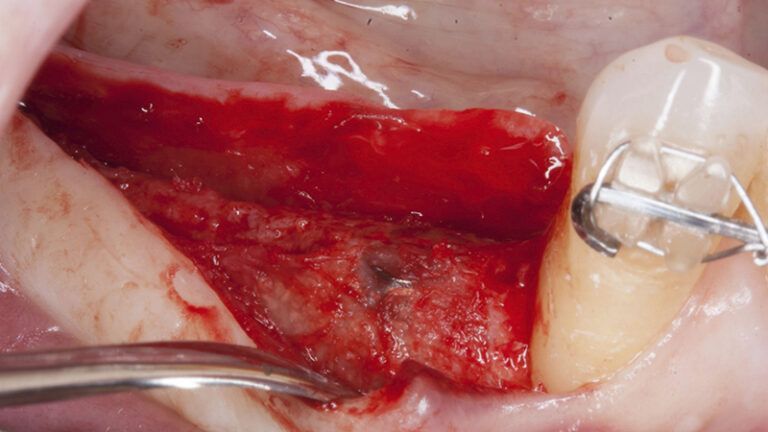
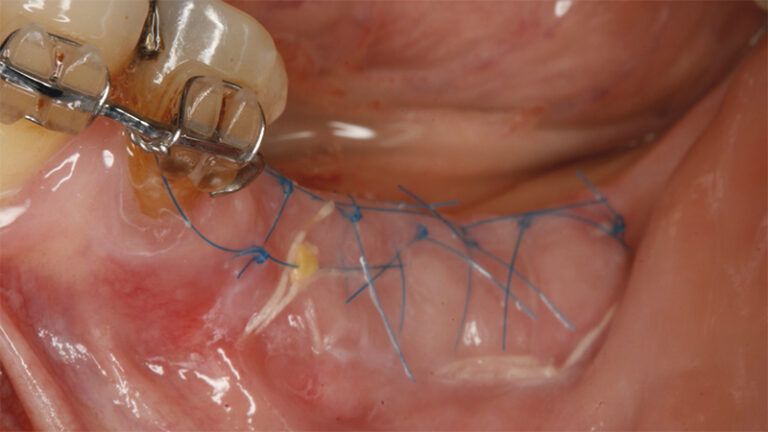
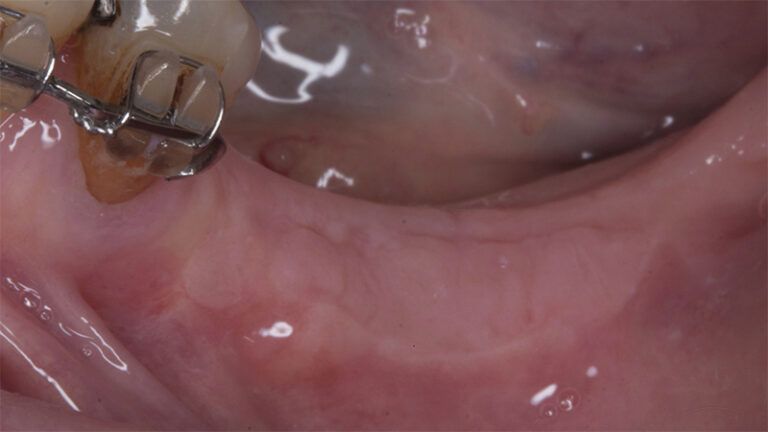
Details of the recipient bed of the graft in the 4th quadrant Stabilization and suture of the graft Details of the donor area Healing of the graft after 15 days Healing of the graft after 15 days Details of the increase in the band of keratinized gum after 8 weeks
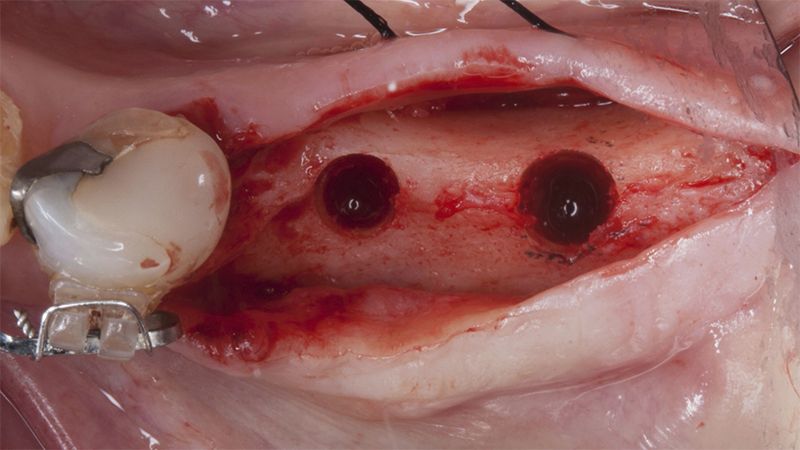
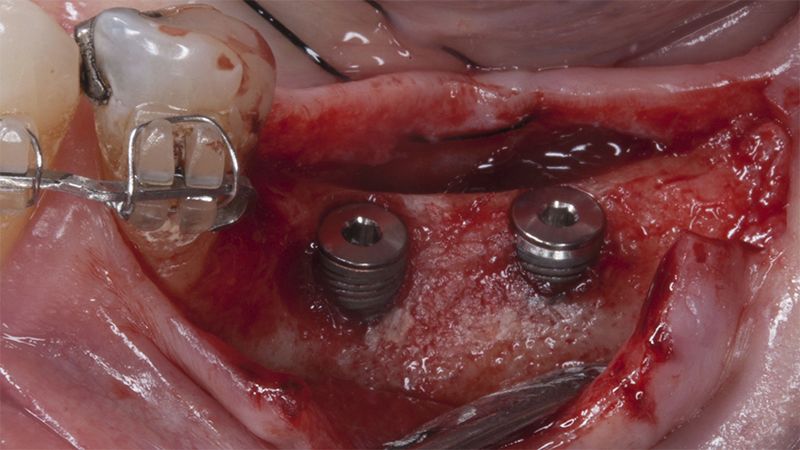
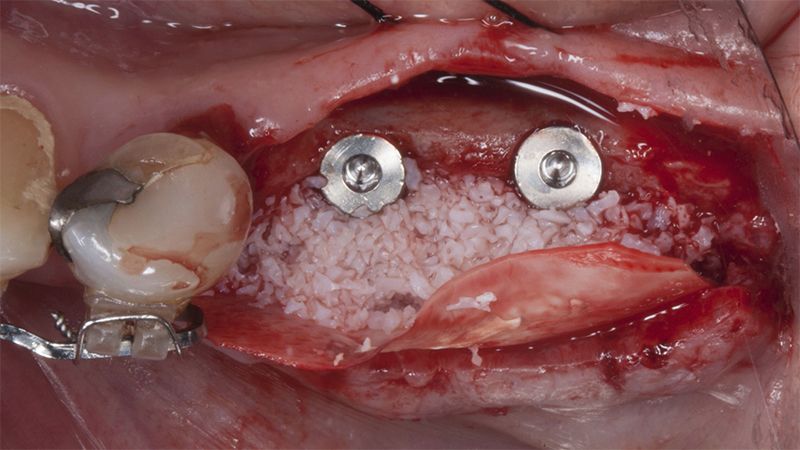
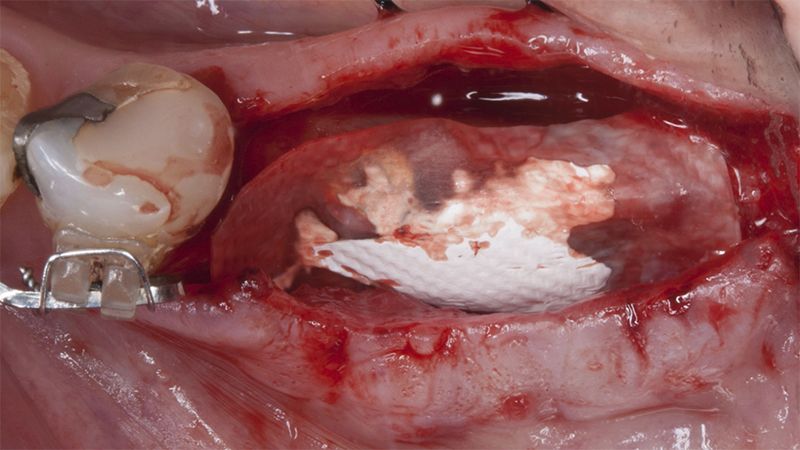
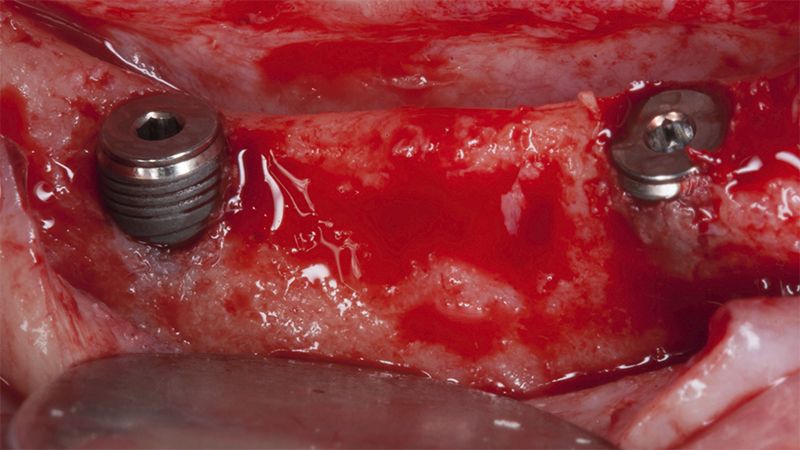
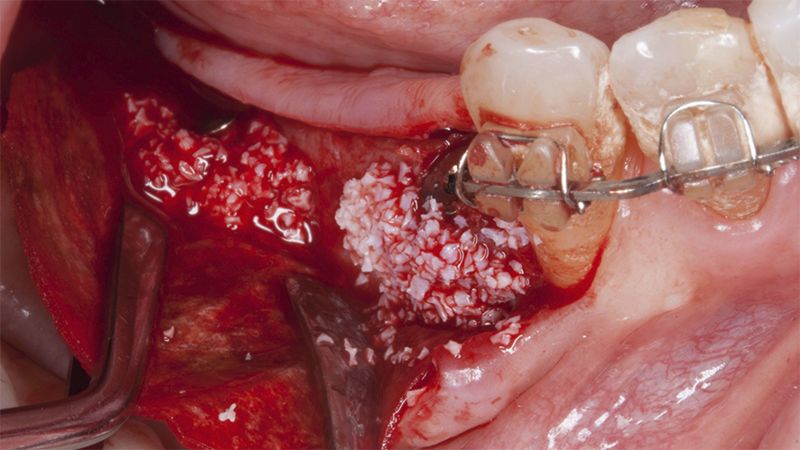
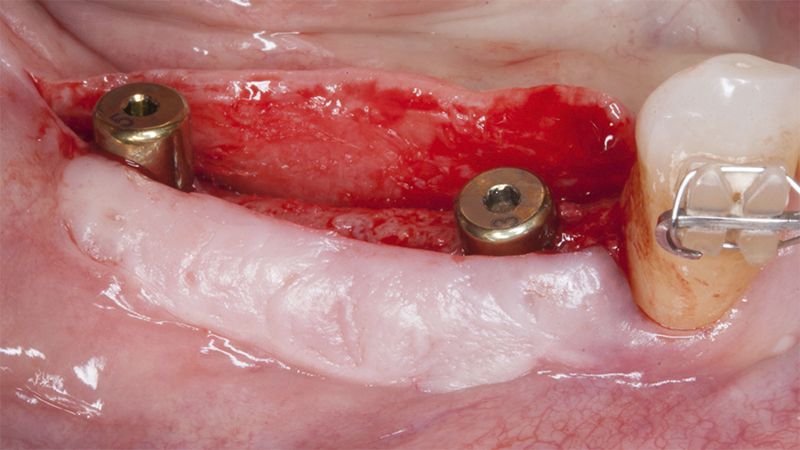
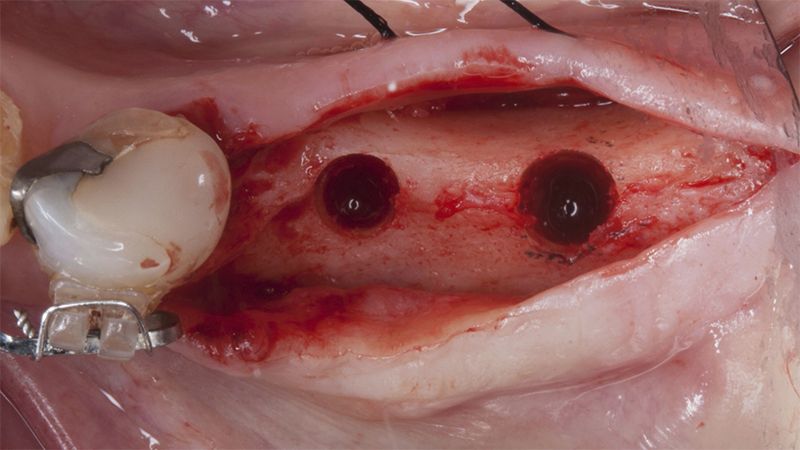
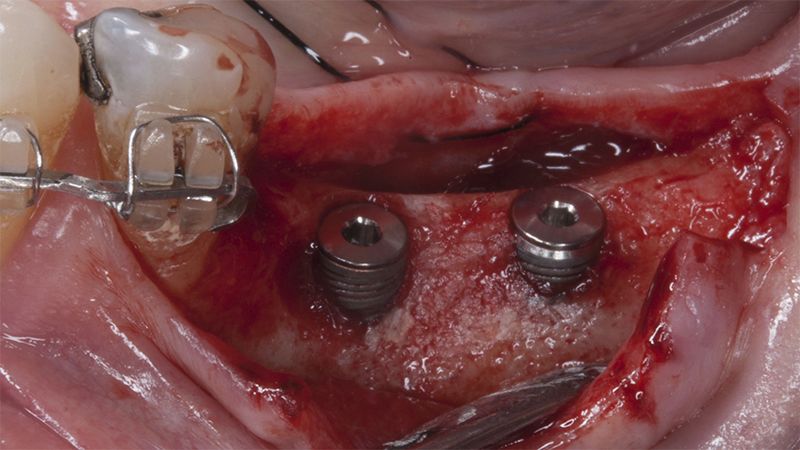
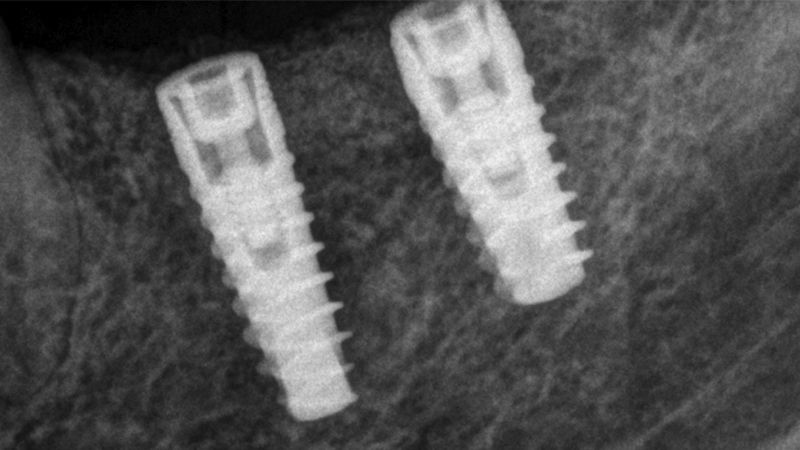
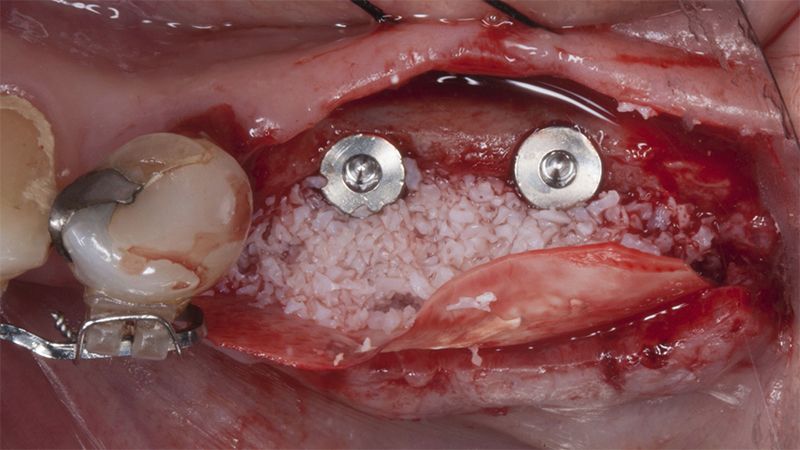
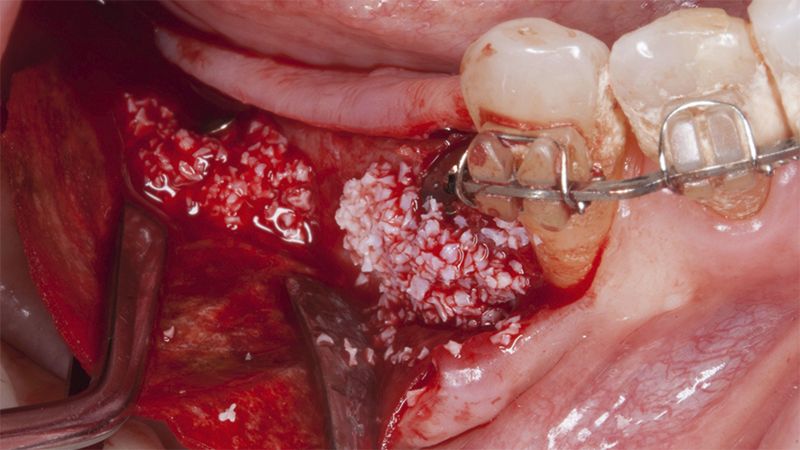
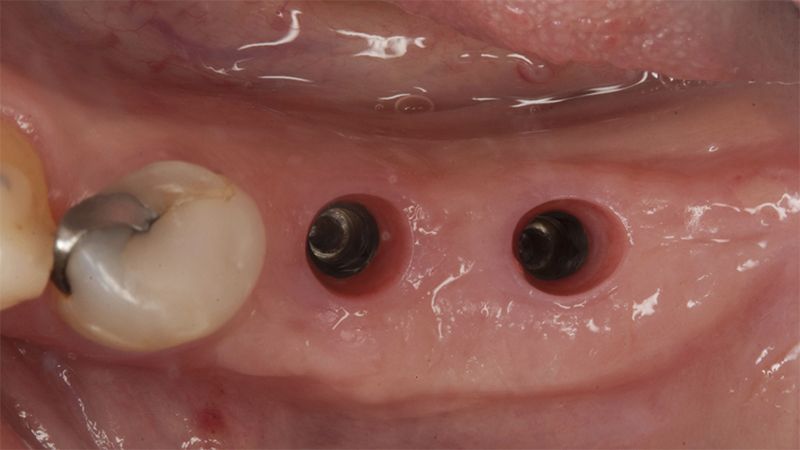
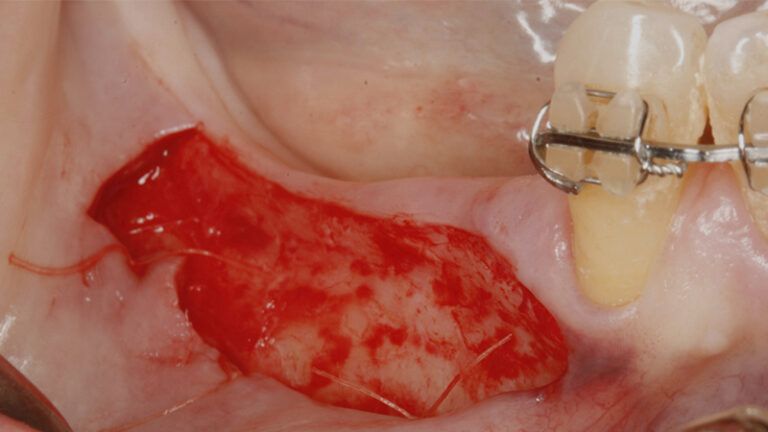
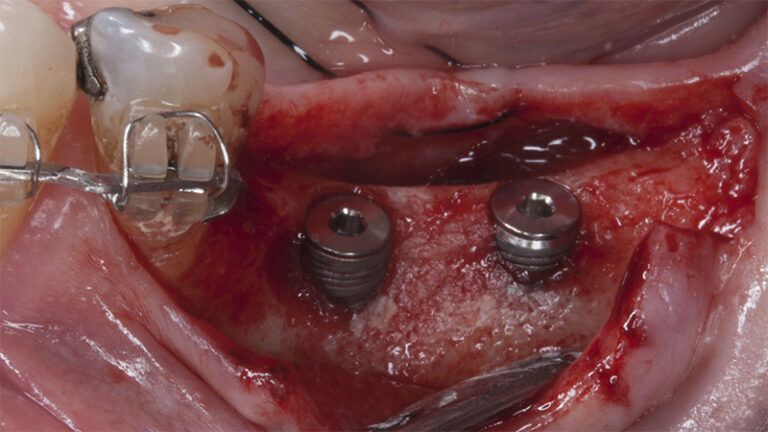
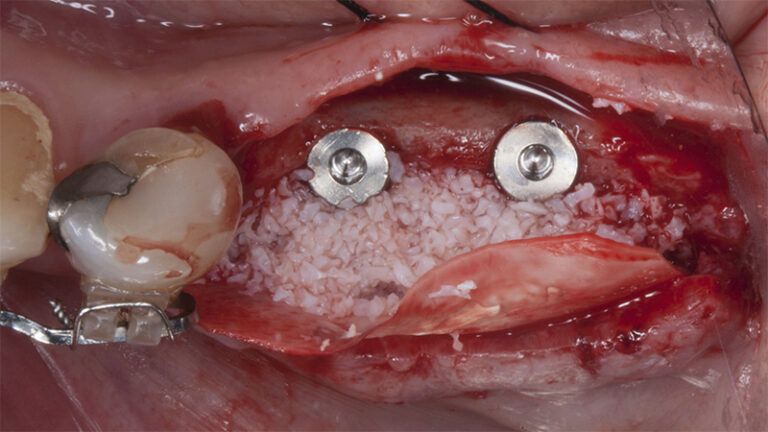
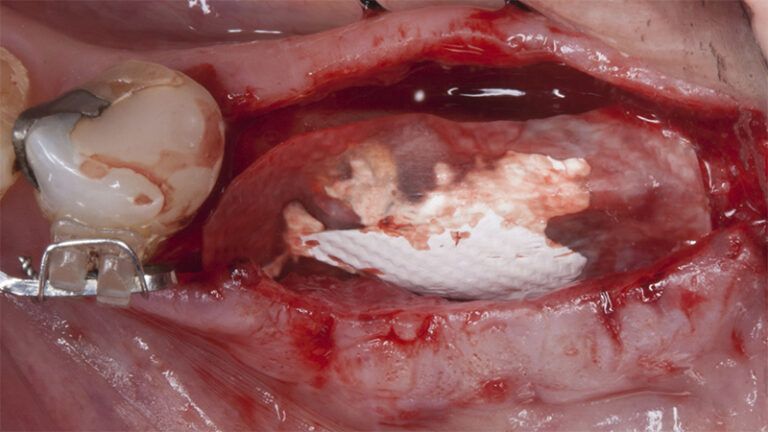
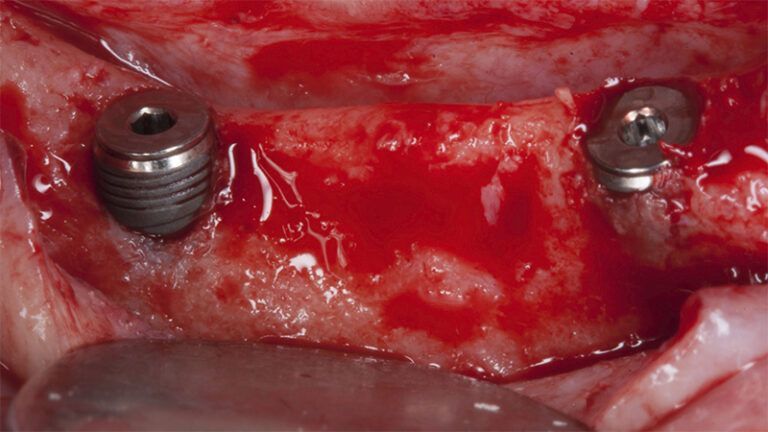
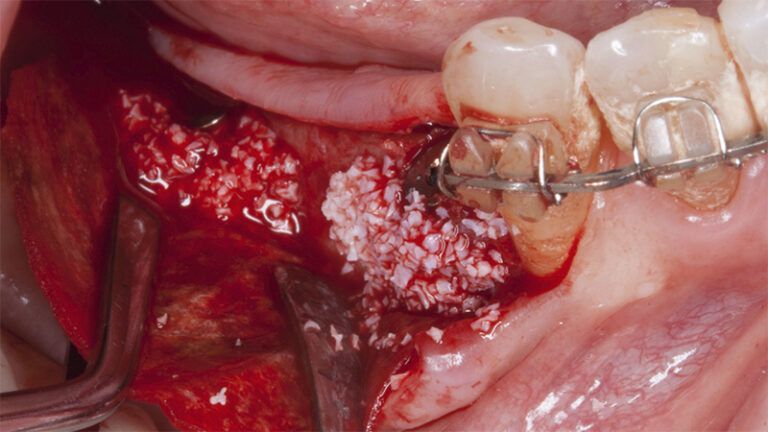
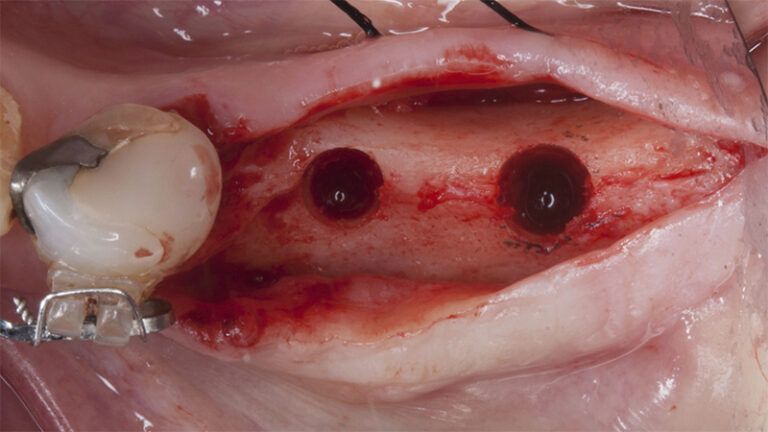
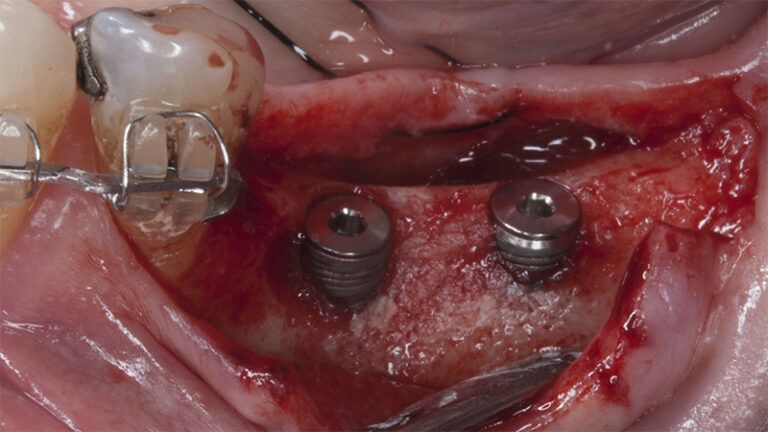
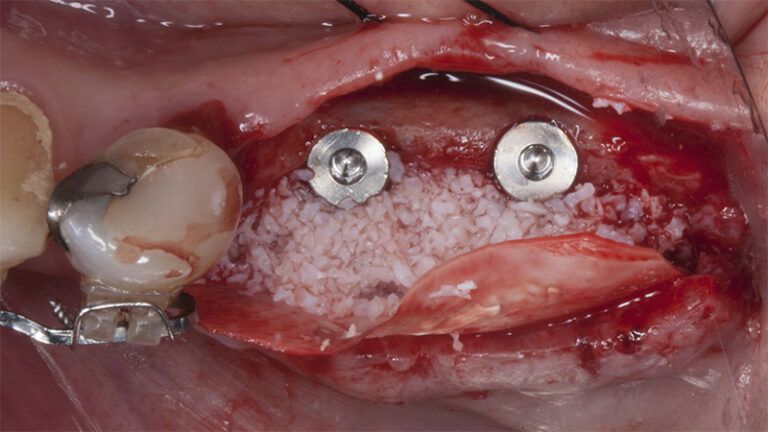
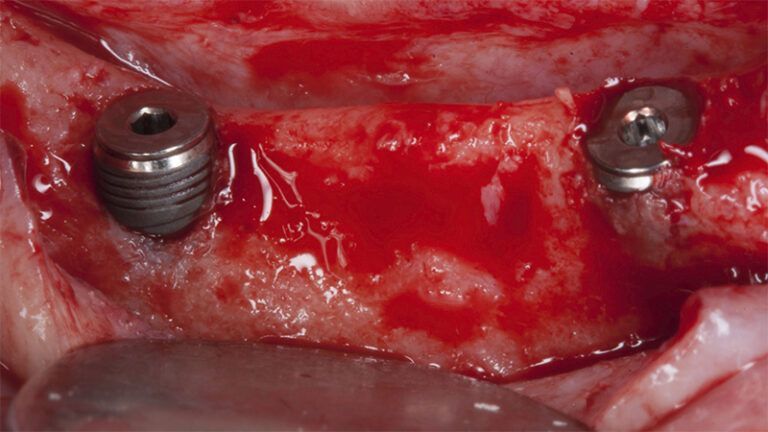
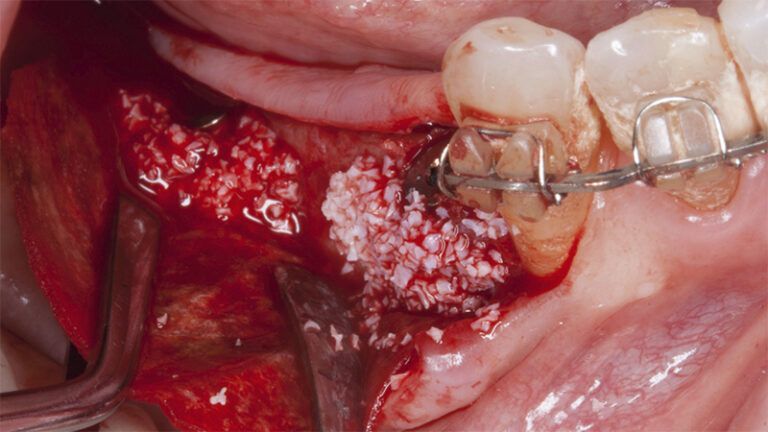
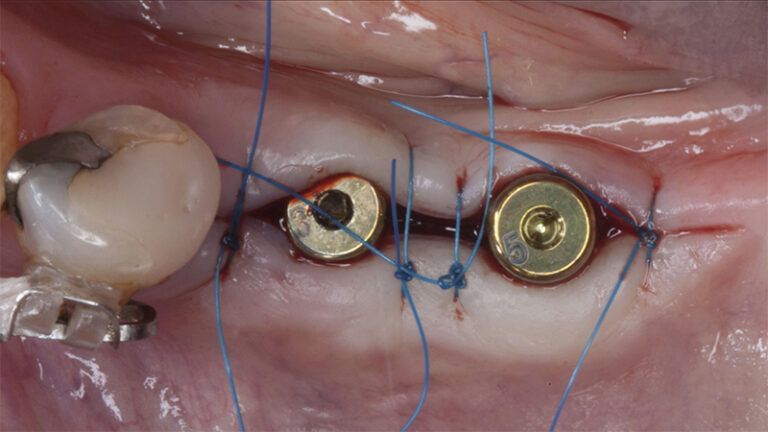
After an 8-week healing period, two submerged Avinent Biomimetic Ocean CC implants of 3.5×11.5 and 4.0×10 were placed in positions 35 and 36 respectively, with simultaneous regeneration of the vestibular part with xenografts and reabsorbable membranes.
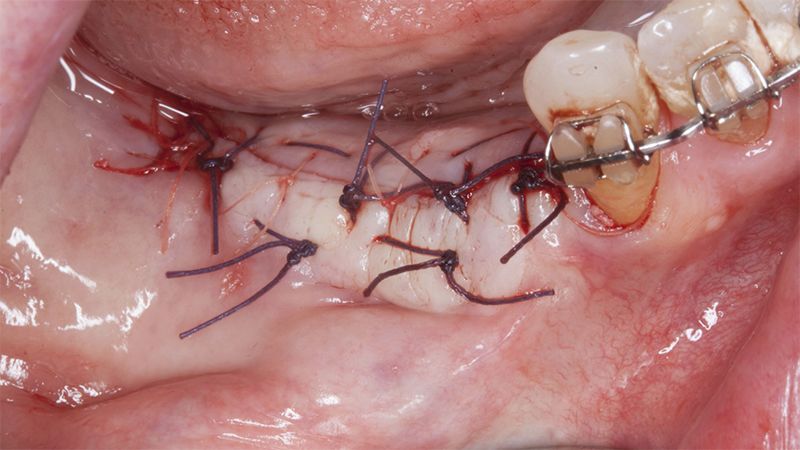
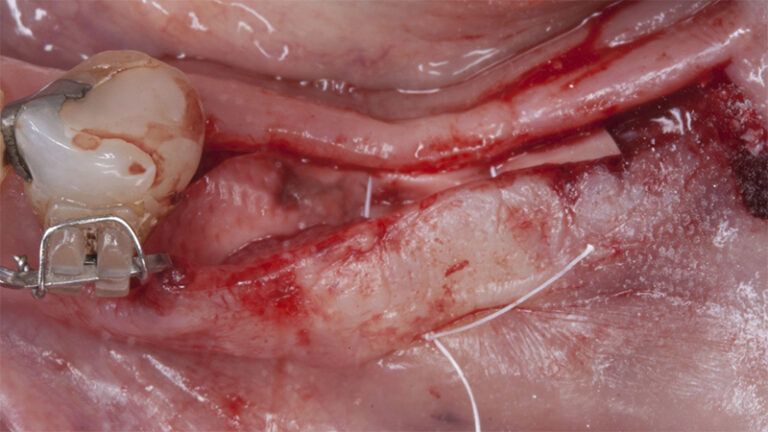
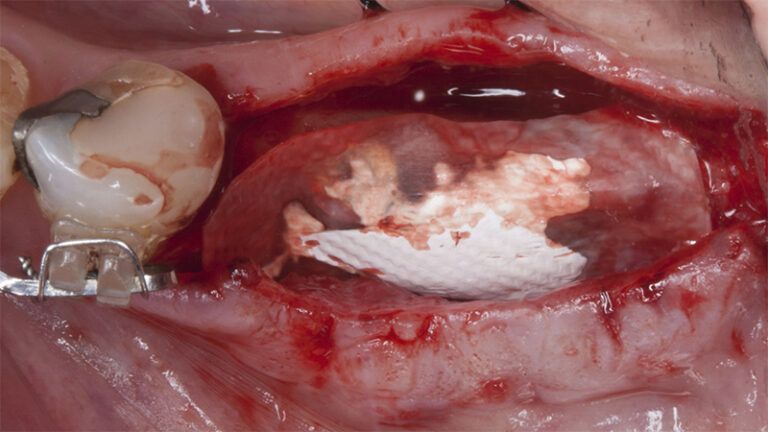
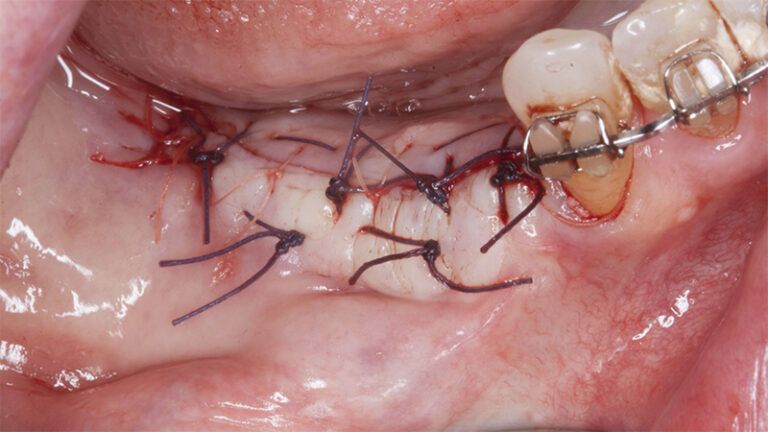
Placement sequence of the Avinent Biomimetic CC implants Placement sequence of the Avinent Biomimetic CC implants Placement sequence of the Avinent Biomimetic CC implants Guided bone regeneration simultaneous to implant placement Guided bone regeneration simultaneous to implant placement Complete closure of the tissues after the bone regeneration Healing after 15 days
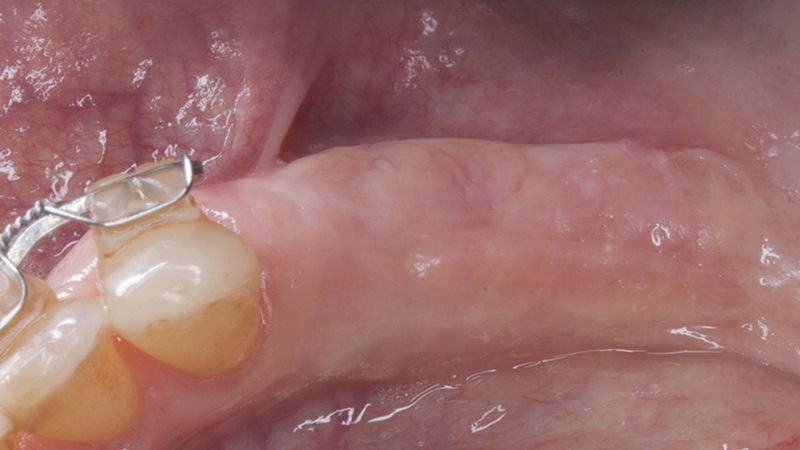
Healing after 15 daysOcclusal view of the volume gained after 4 months Lateral view of the tissues after 4 months
In this surgical session the same procedure of placing the submerged implants with healing caps in the other quadrant, placing two Avinent Biomimetic Ocean CC implants of 3.5×11.5 and 4.0×10 in positions 44 and 46 respectively and regenerating the vestibular area with xenografts and reabsorbable membranes.
Placement of the implants in the 4th quadrant with simultaneous regeneration
Placement of the implants in the 4th quadrant with simultaneous regenerationSuture of the flaps without tension Details of the volume regenerated
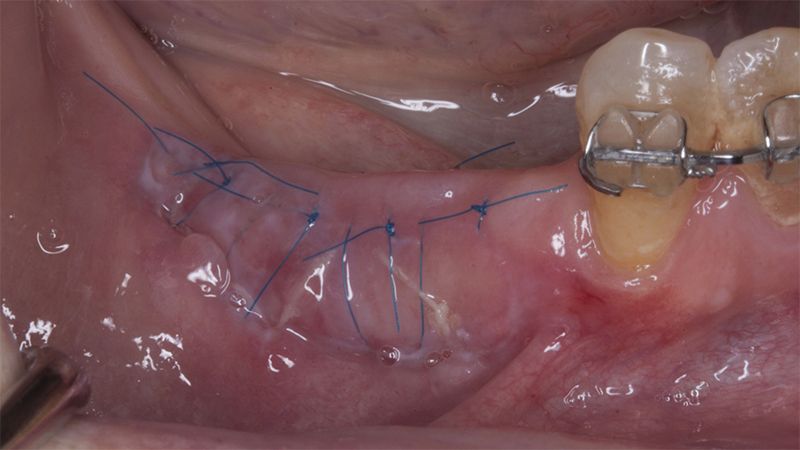
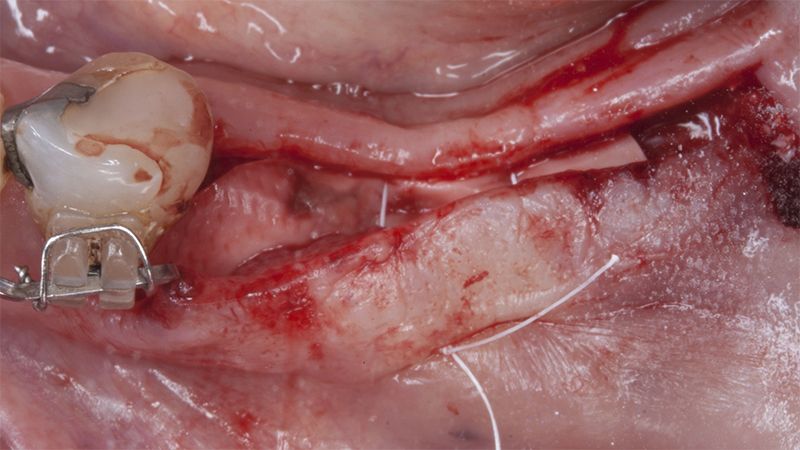
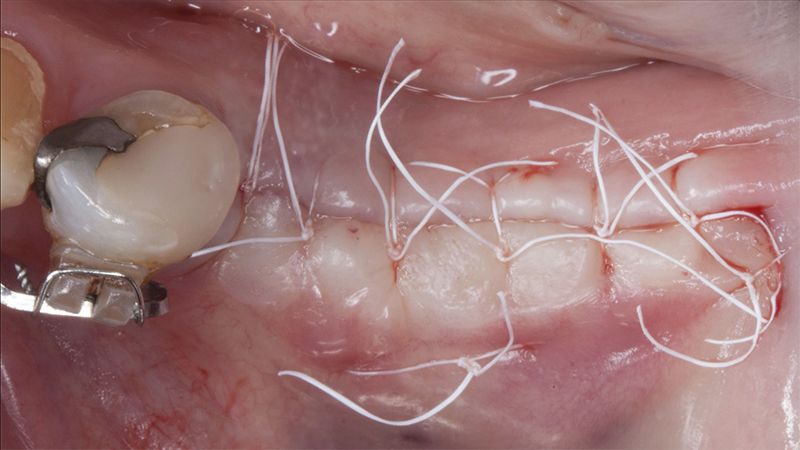
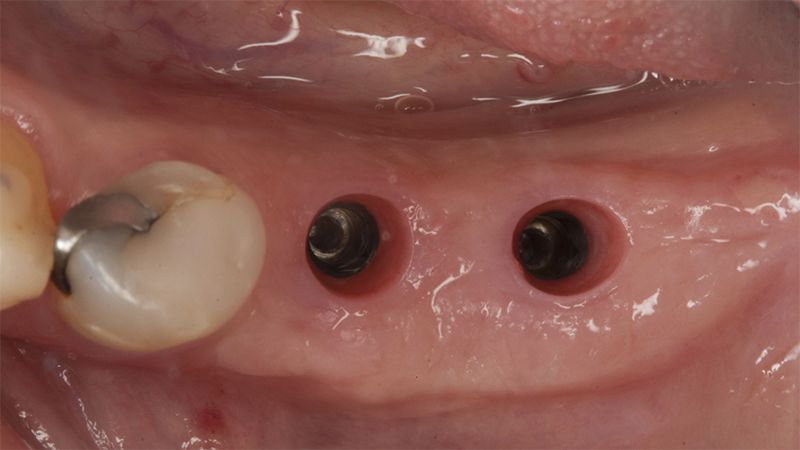
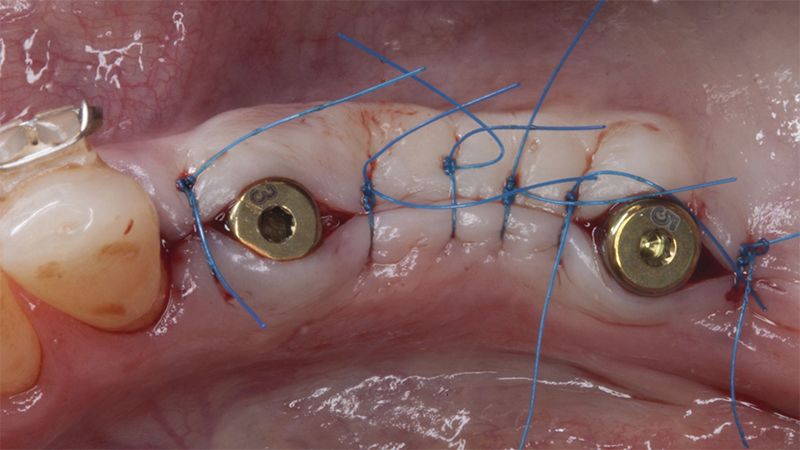
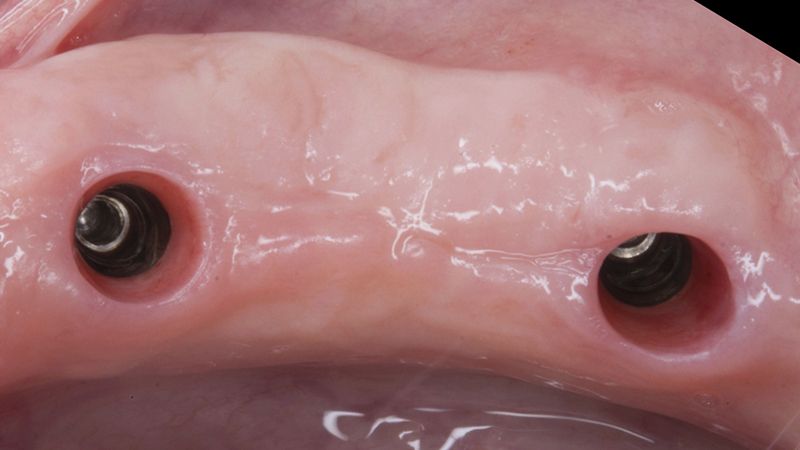
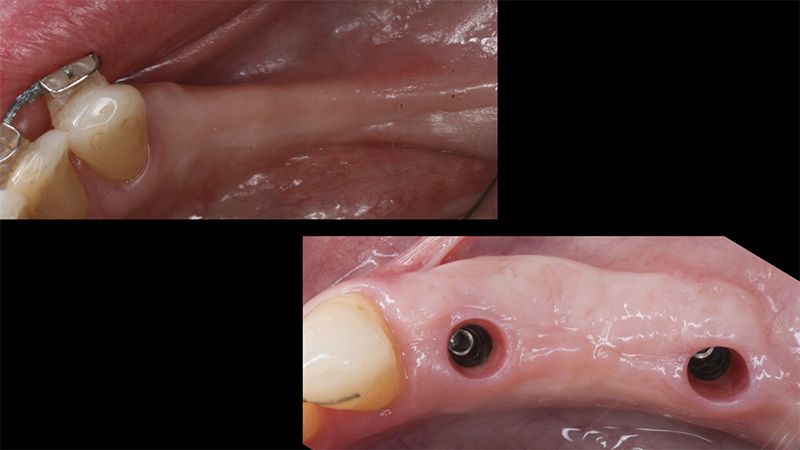
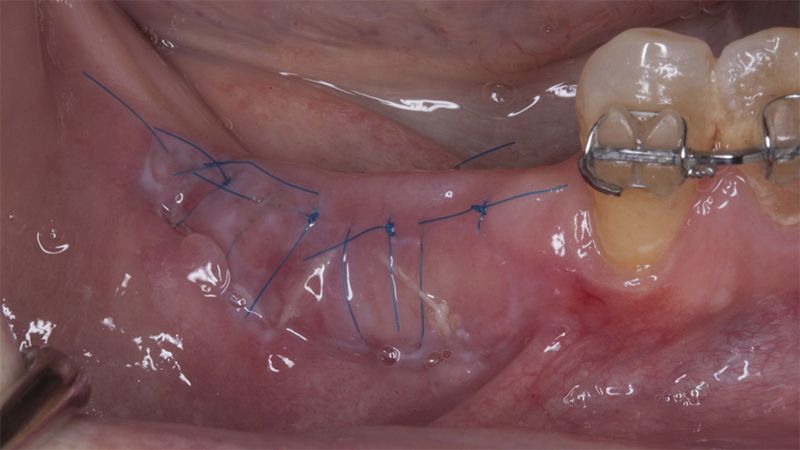
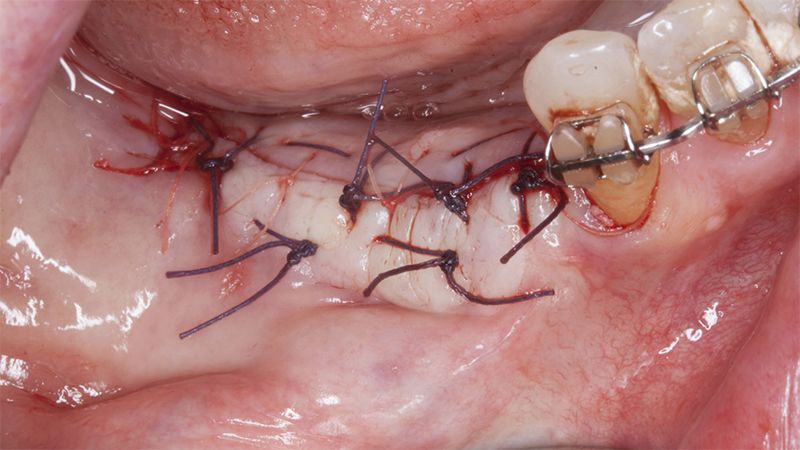
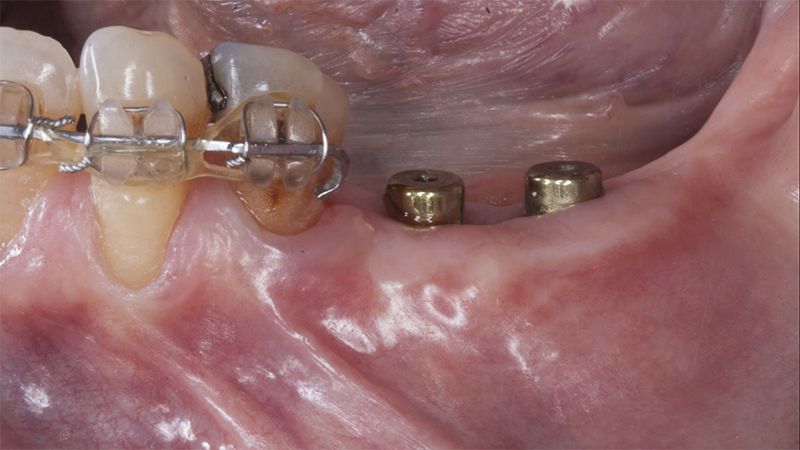
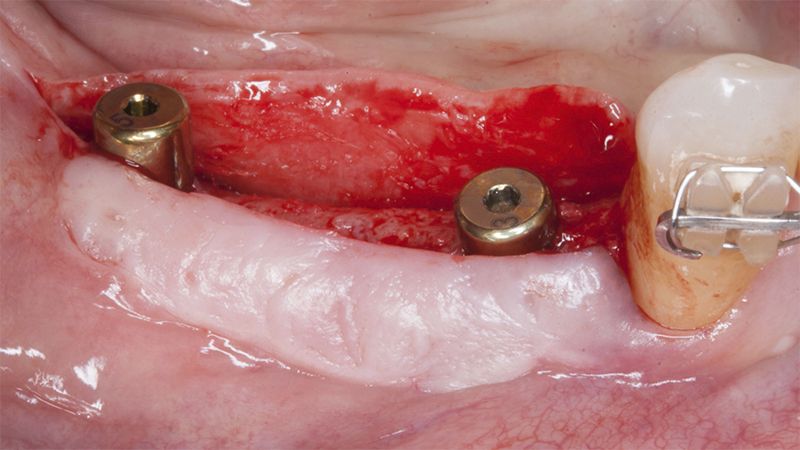
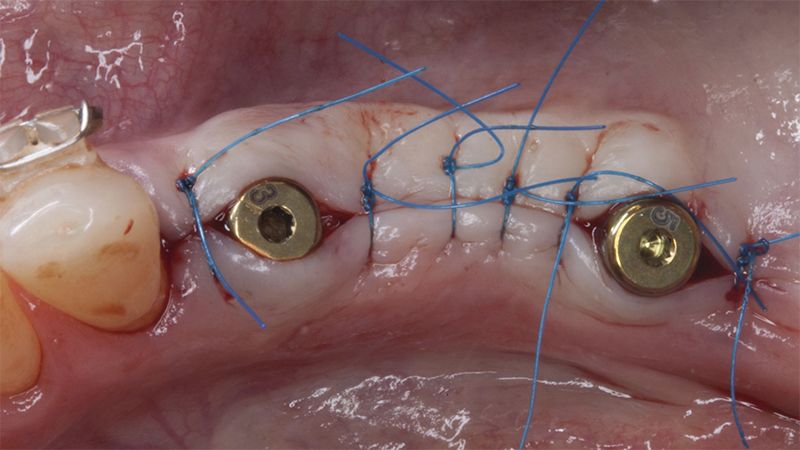
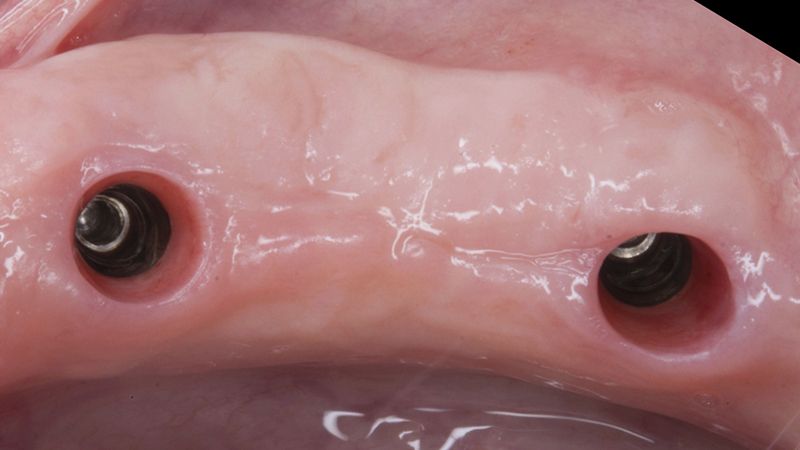
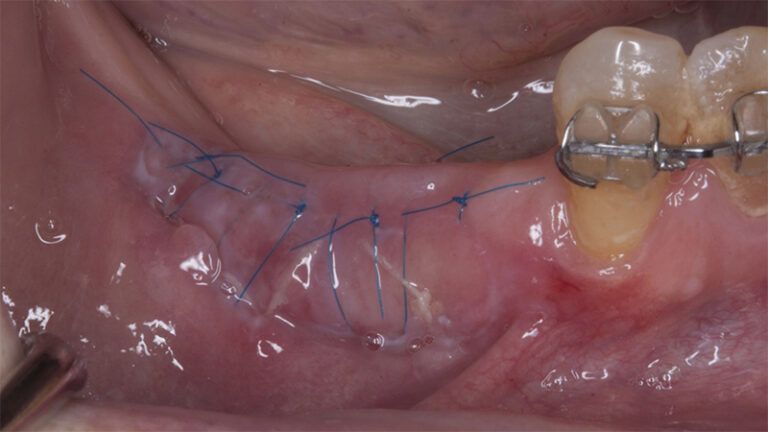
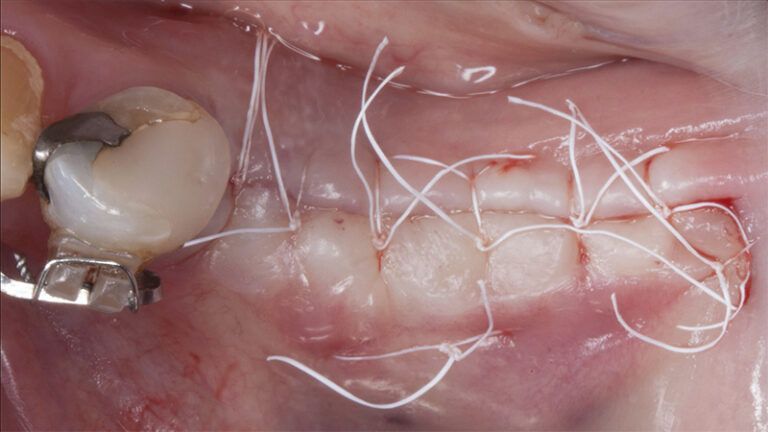
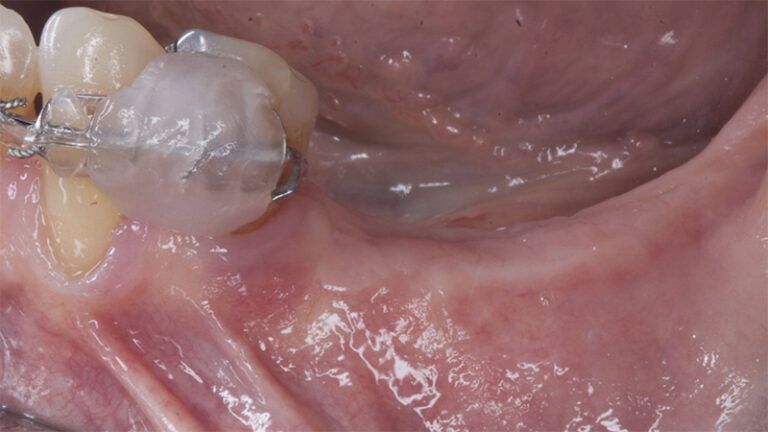
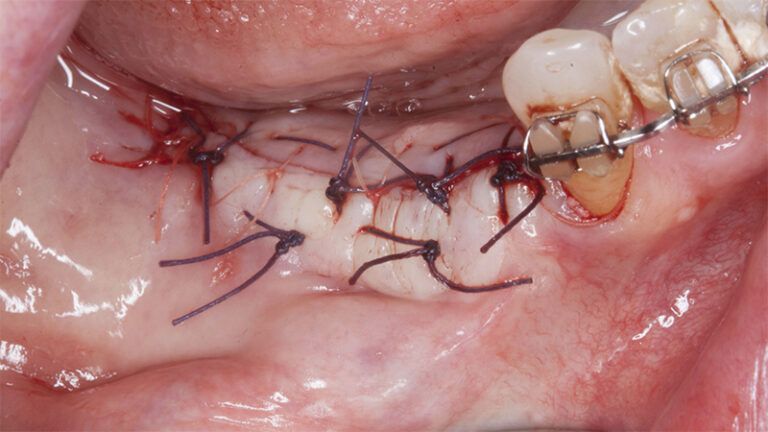
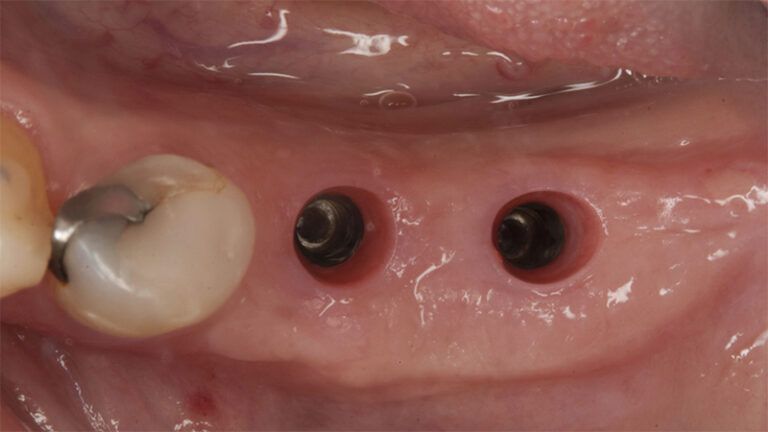
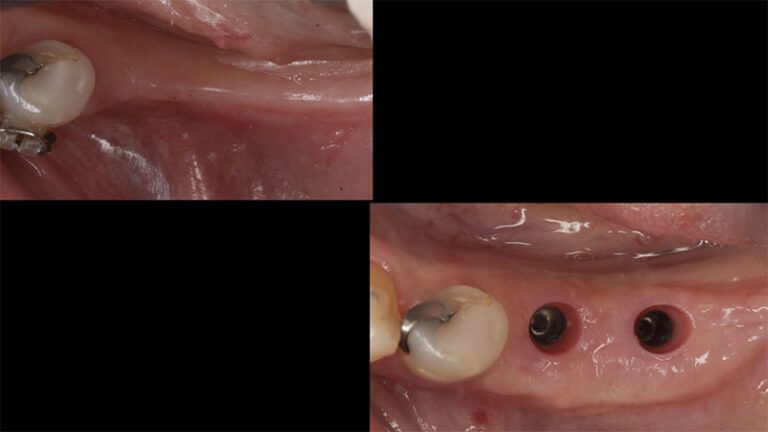
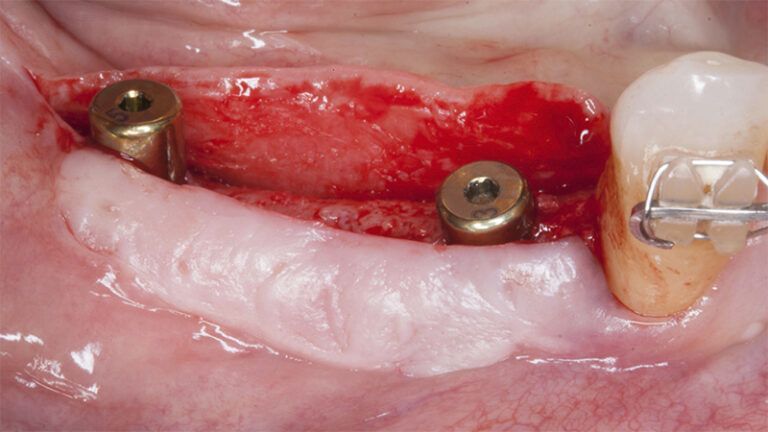
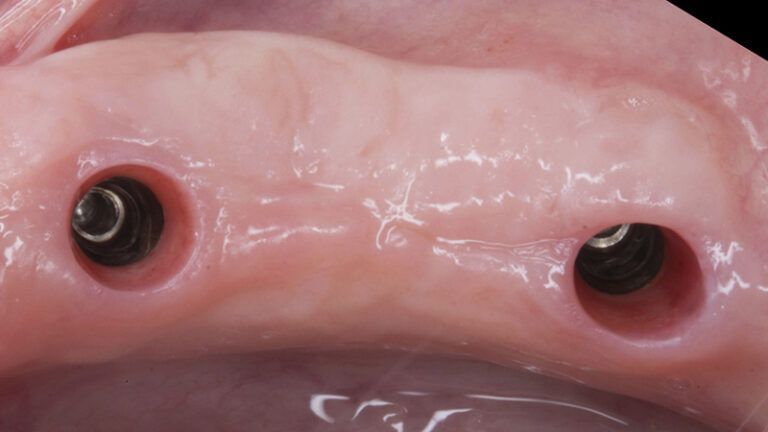
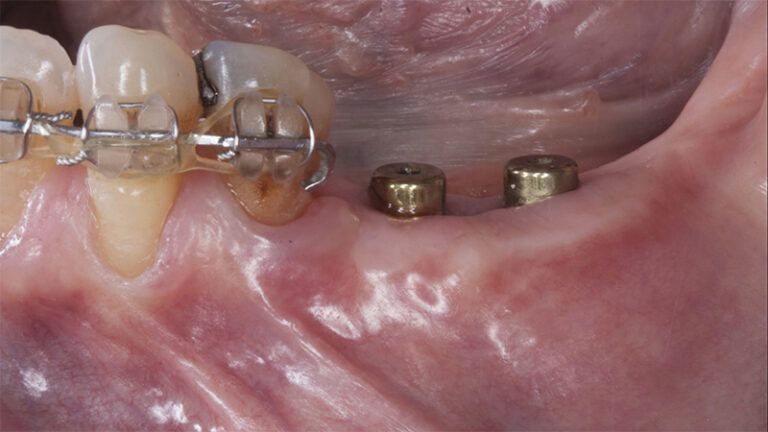
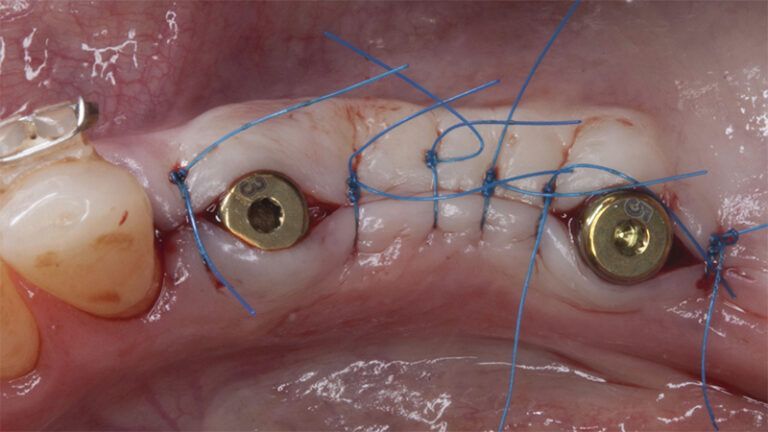
Five months after the bone regeneration, the second phase of the surgery was performed on the four implants simultaneously, placing healing abutments and suturing to shape the tissues. In this surgery the keratinized tissue was divided in the middle so that the implants had a good band of keratinized tissue on both the vestibular and the lingual side.
Placement of the healing abutments 5 months after the guided bone regeneration Placement of the healing abutments 5 months after the guided bone regeneration Healing after 15 days
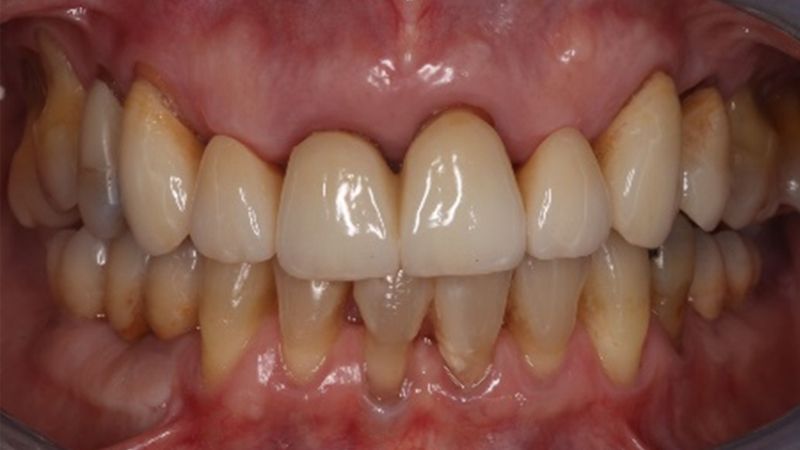
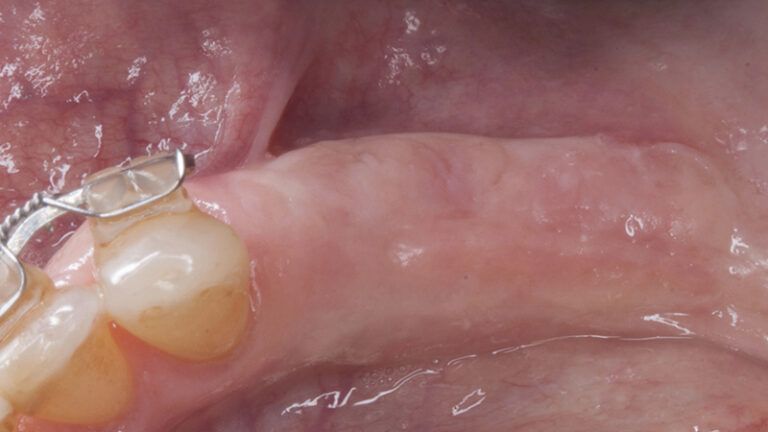
Initial situation and final appearance of the periimplant tissues Initial situation and final appearance of the periimplant tissues
Reentry in the 4th quadrant after the regeneration Reentry in the 4th quadrant after the regeneration Placement of the healing abutments in the second phase Placement of the healing abutments in the second phase Suture of the flaps in the second surgery Healing after 15 days
Initial and final appearance of the periimplant tissues Initial and final appearance of the periimplant tissues
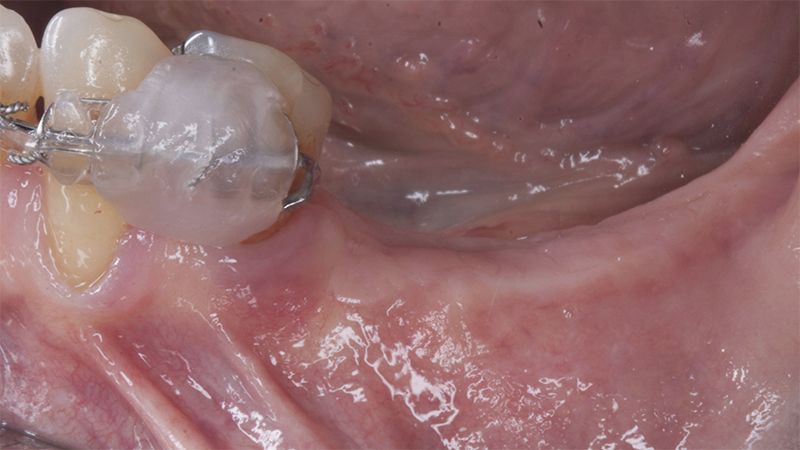
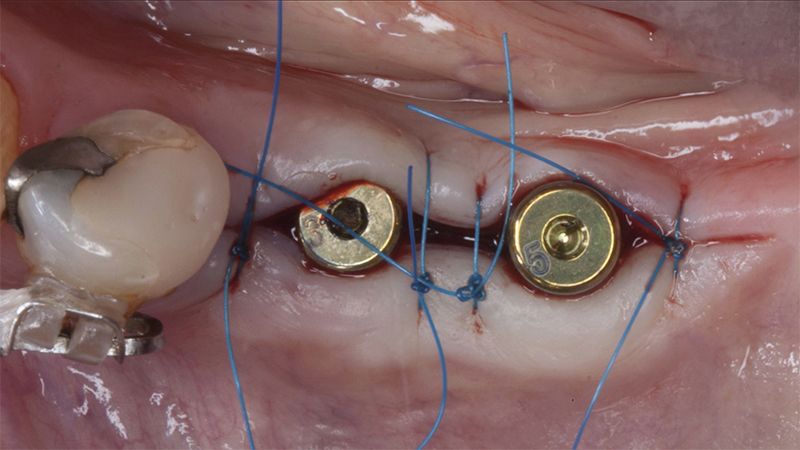
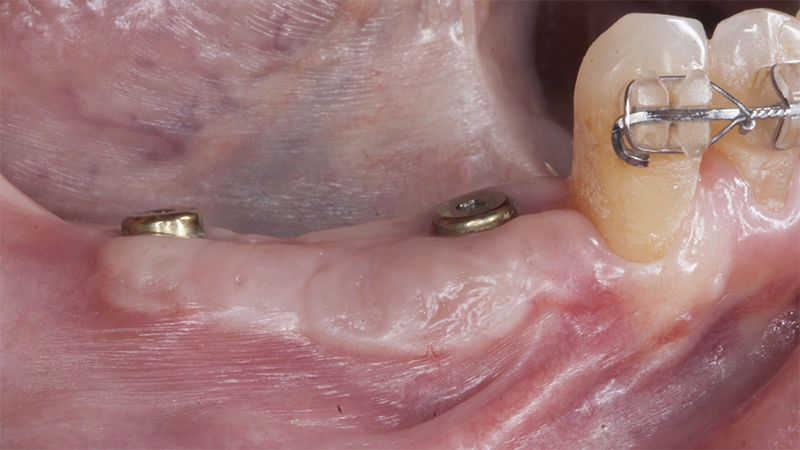
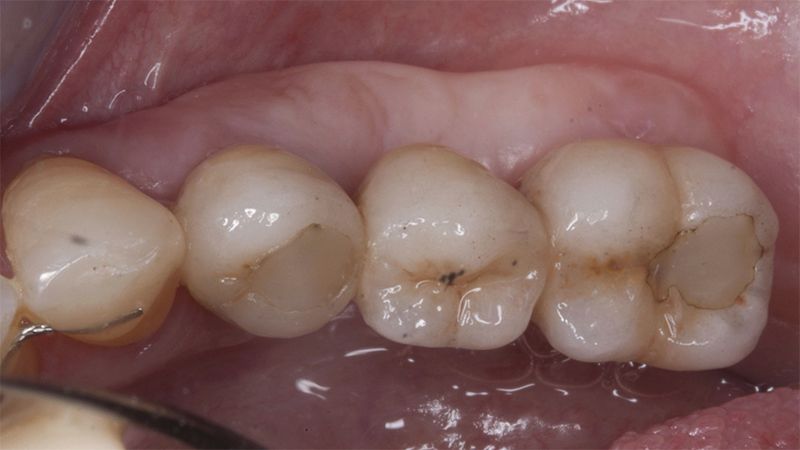
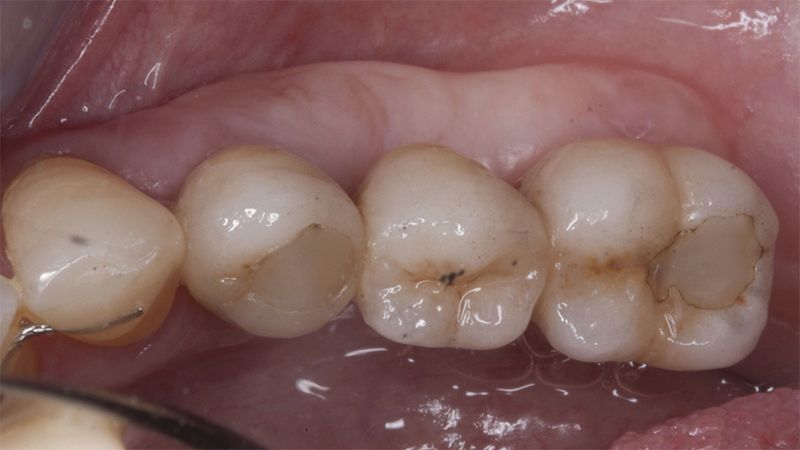
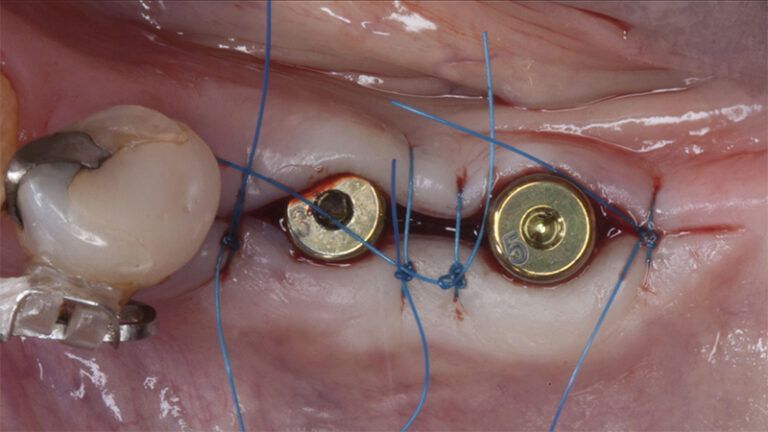
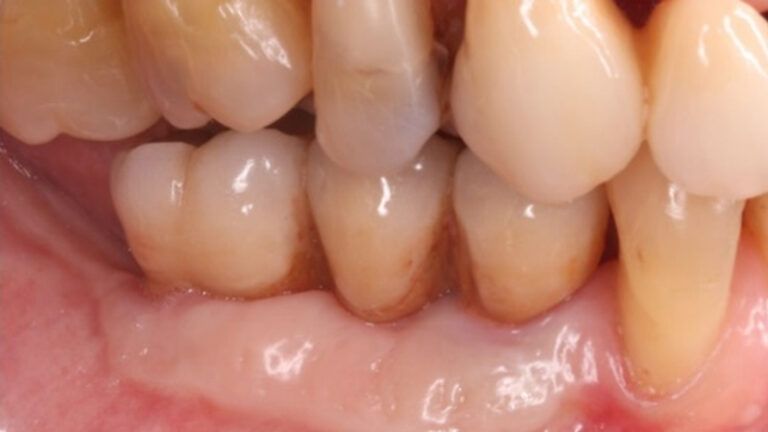
Once when the orthodontic treatment had finished, the patient was given a restoration with two splinted implant-supported metal-ceramic crowns in positions 35 and 36 and with a fixed implant-supported bridge of 44 from 46, also in metal and ceramic.
Fit of crowns 35 and 36 Definitive prosthesis in the mouth Definitive prosthesis in the mouth
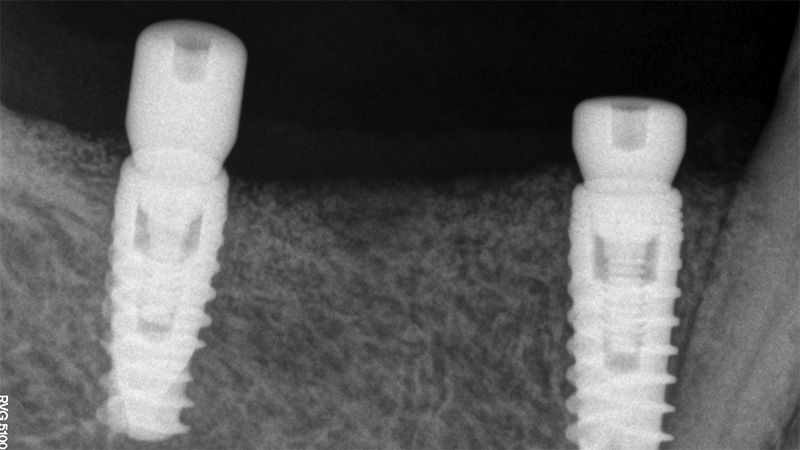
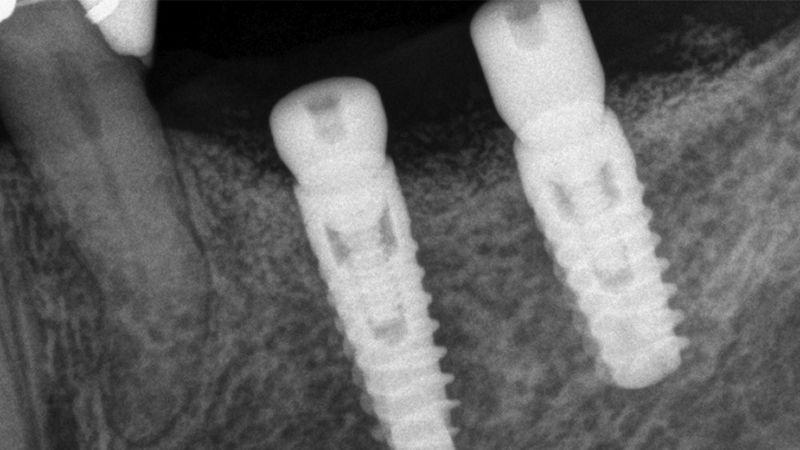
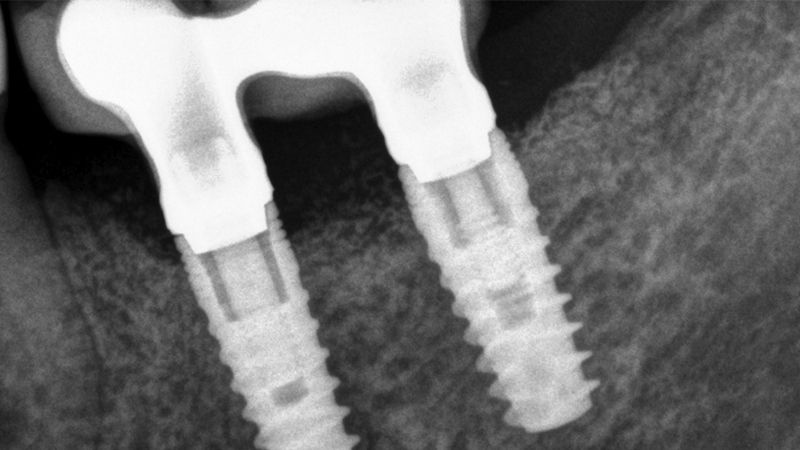
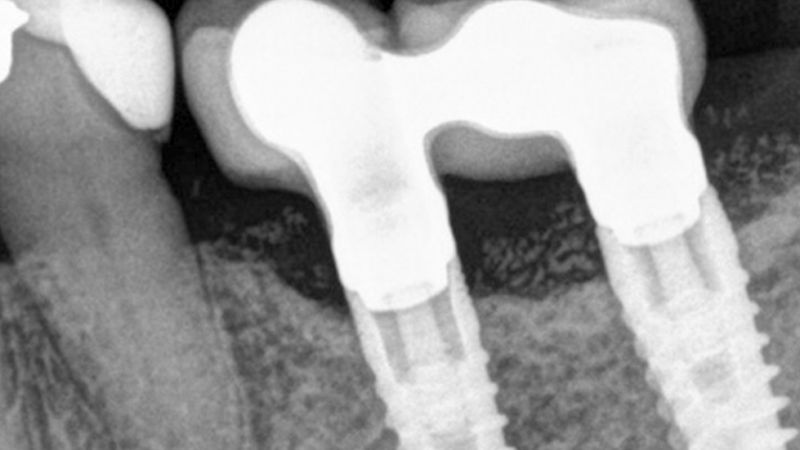
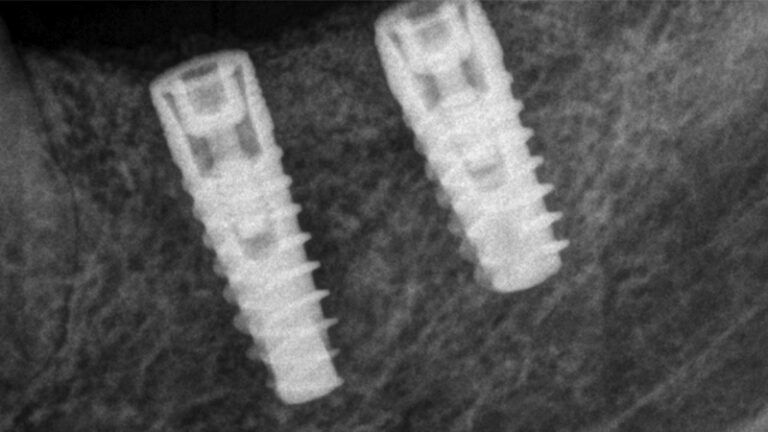
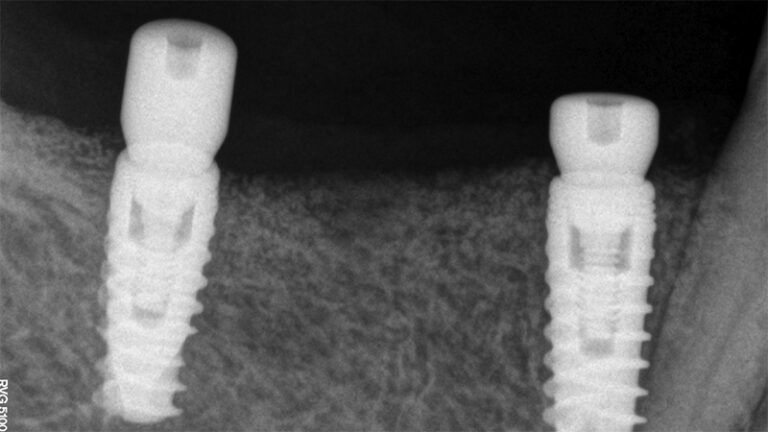
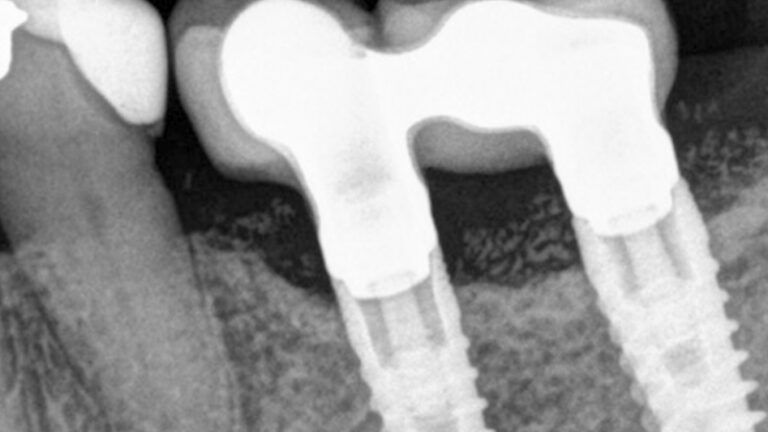
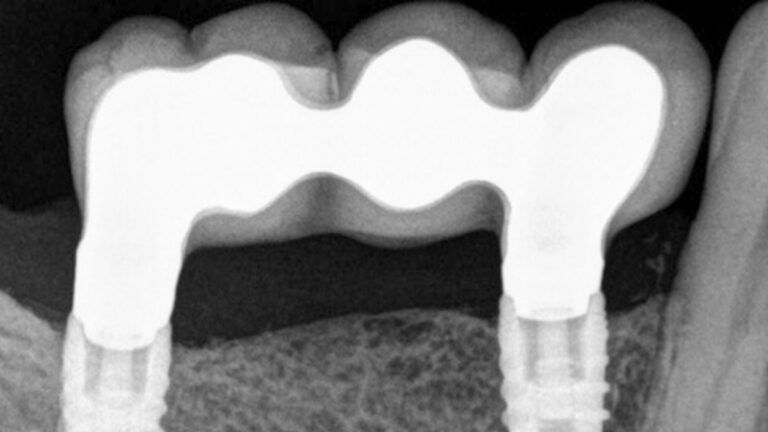
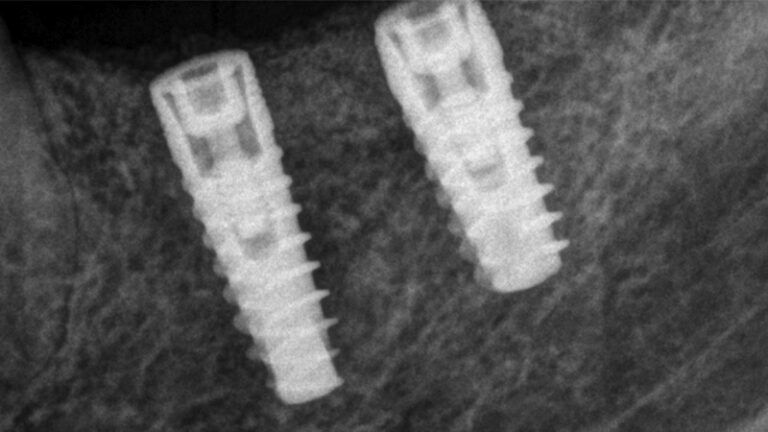
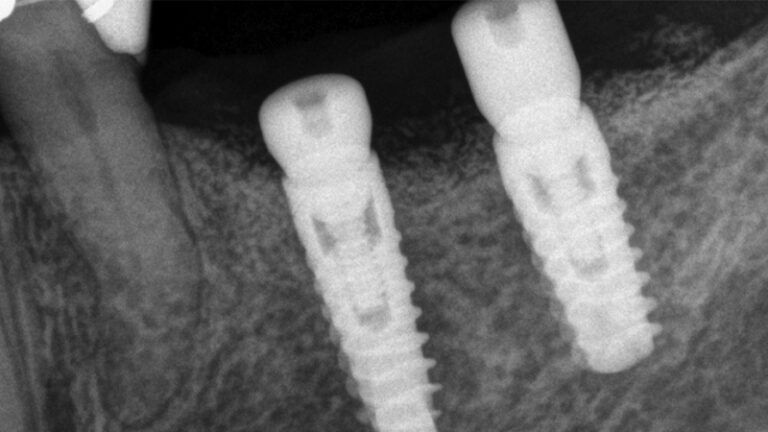
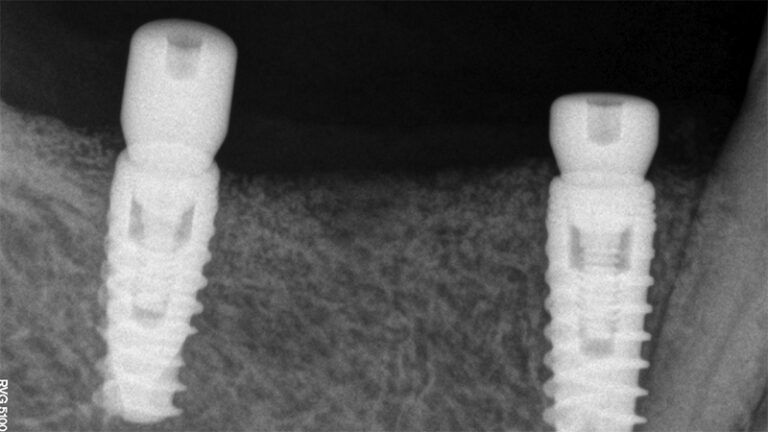
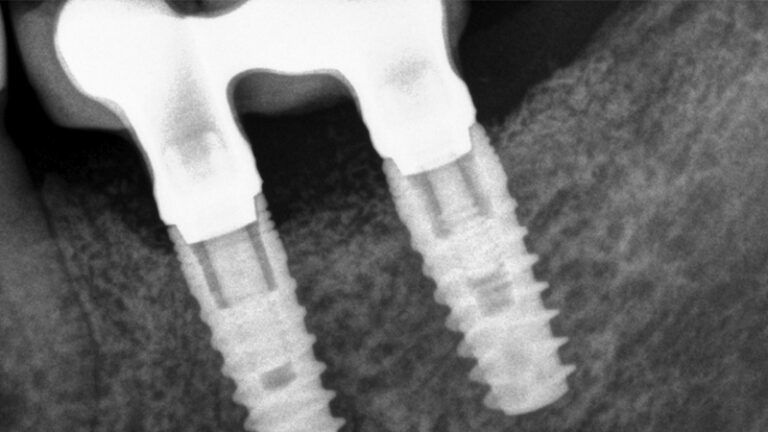
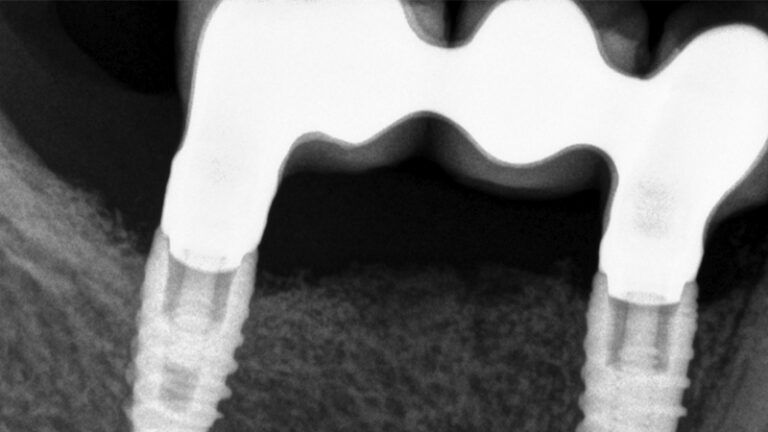
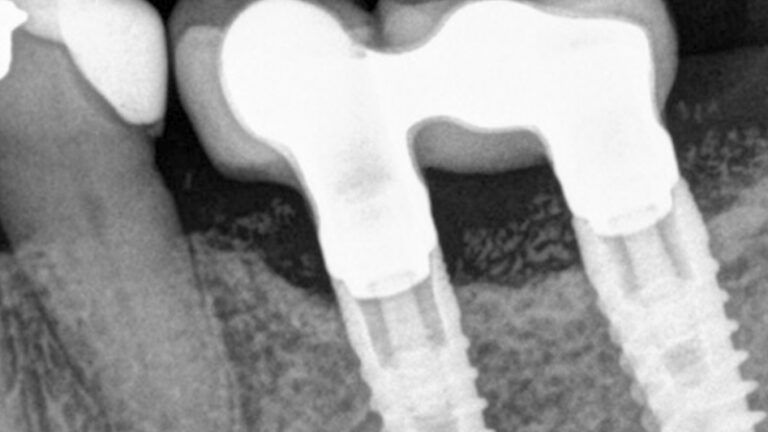
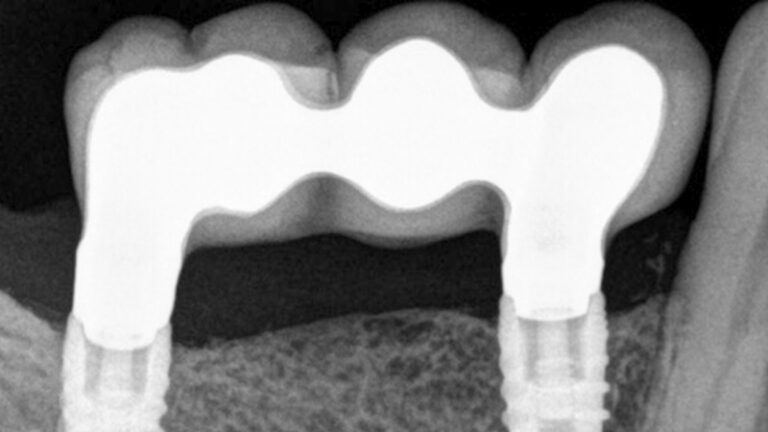
X-ray image of the prosthetic load Metal-ceramic prosthesis in the mouth Metal-ceramic prosthesis in the mouth
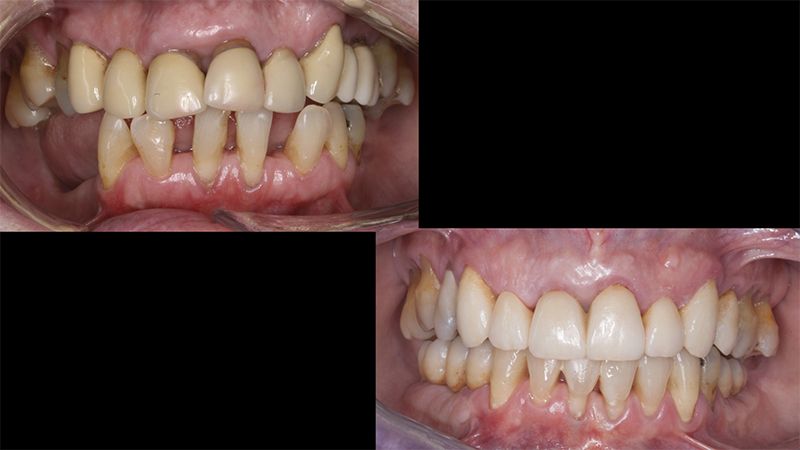
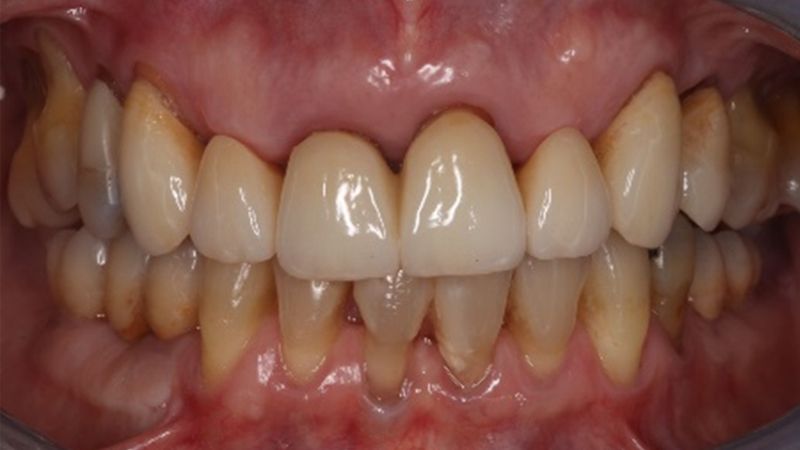
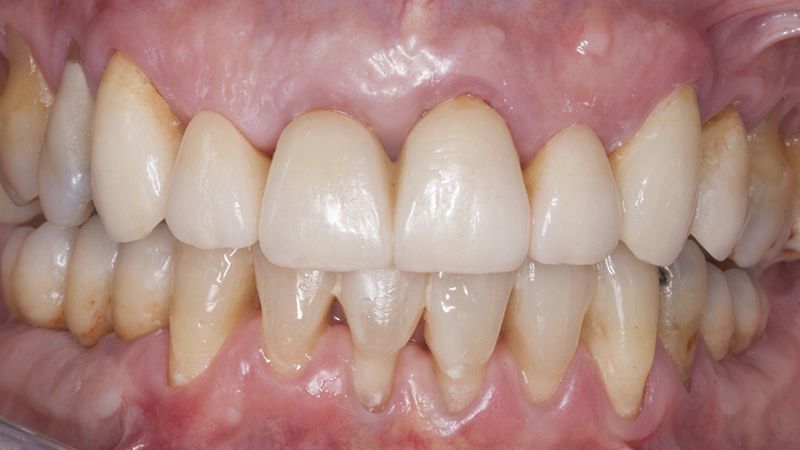
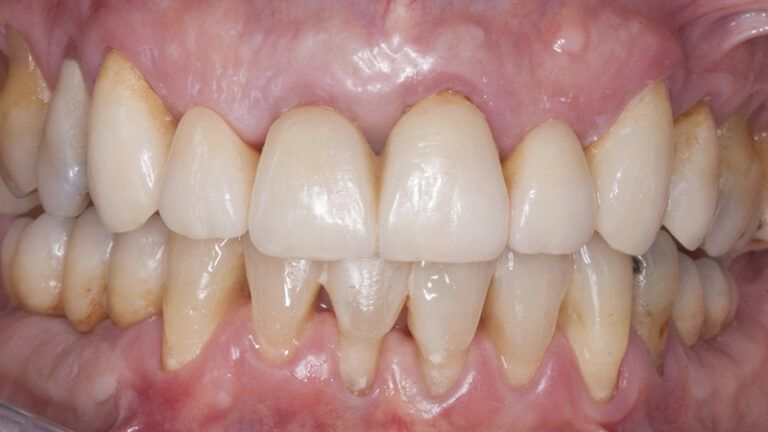
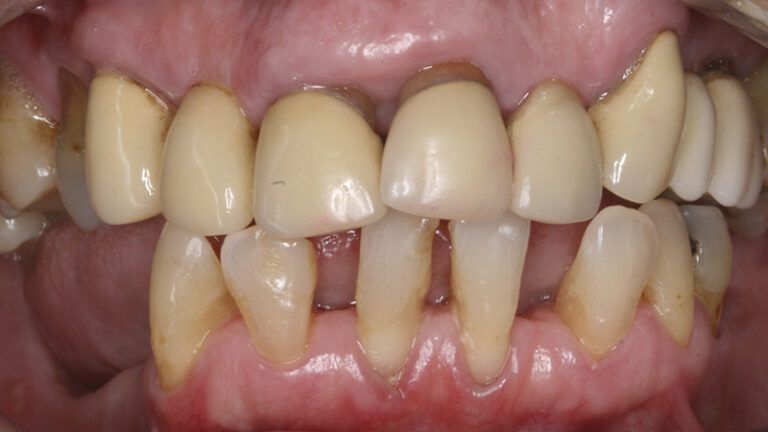
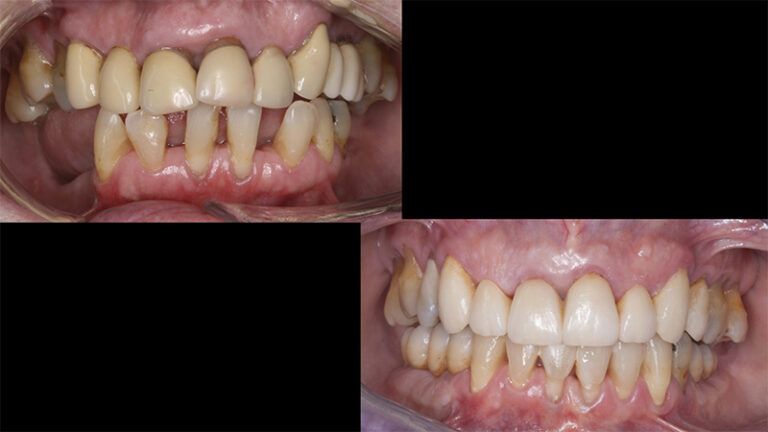
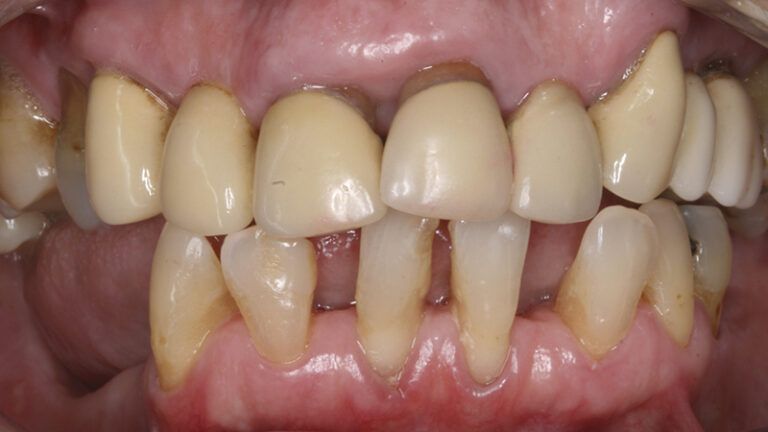
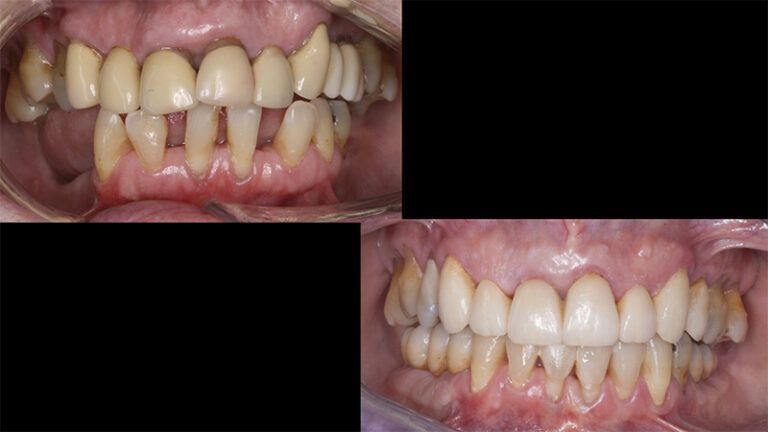
Finally, as the patient’s expectations to replace her lower removable prosthesis for a fixed solution were fulfilled, she decided to change the upper bridges for a more aesthetic overall result.
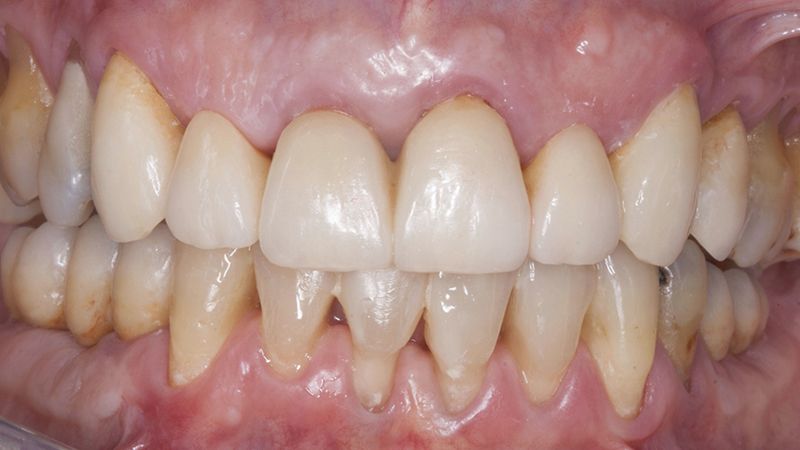
Initial and final images of the patient
Final image of the rehabilitated case
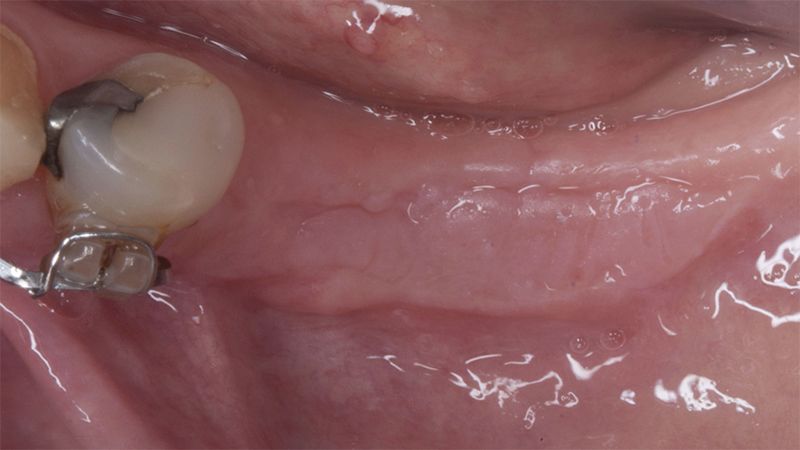
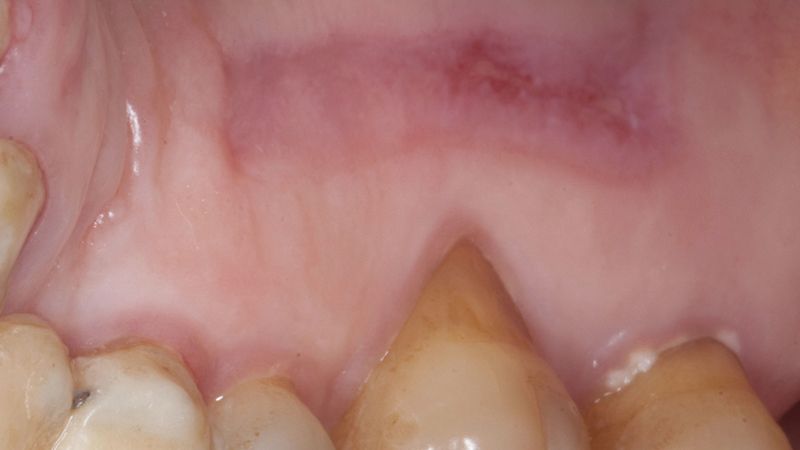
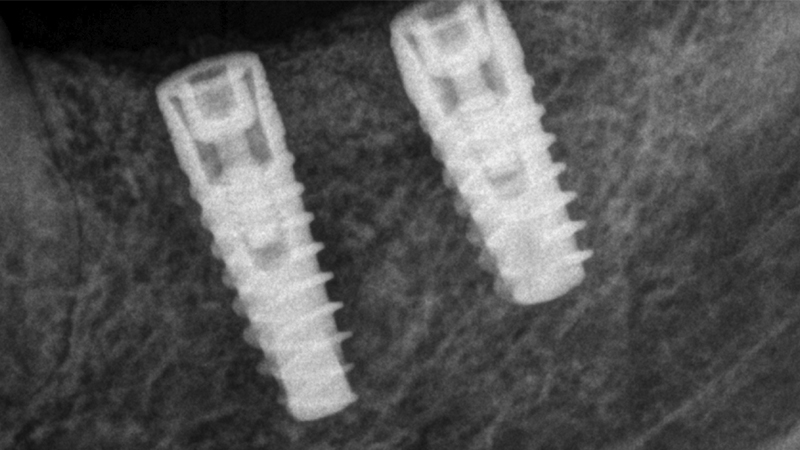
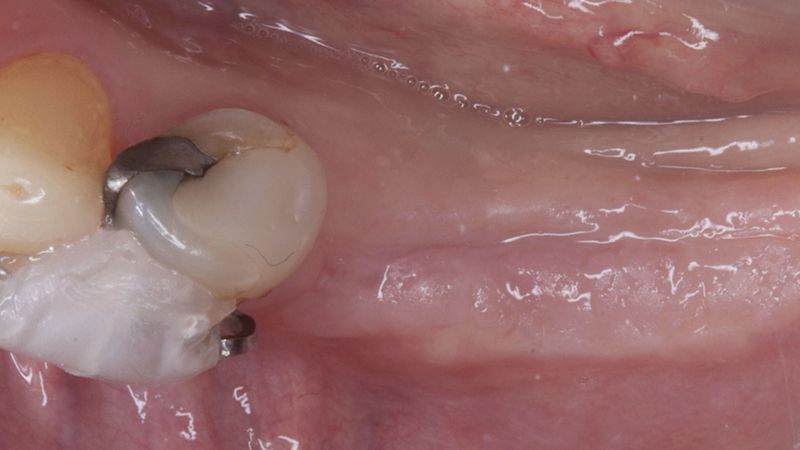
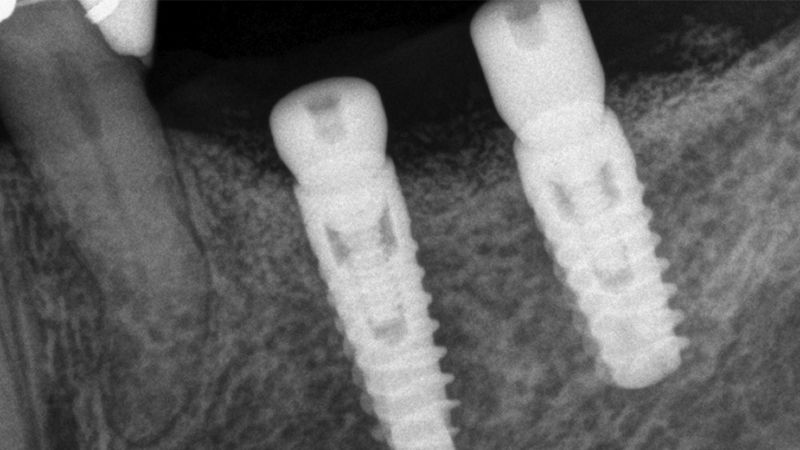
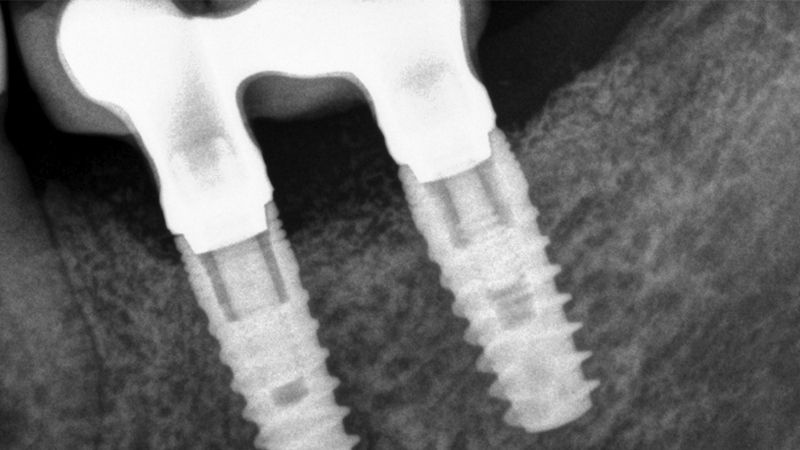
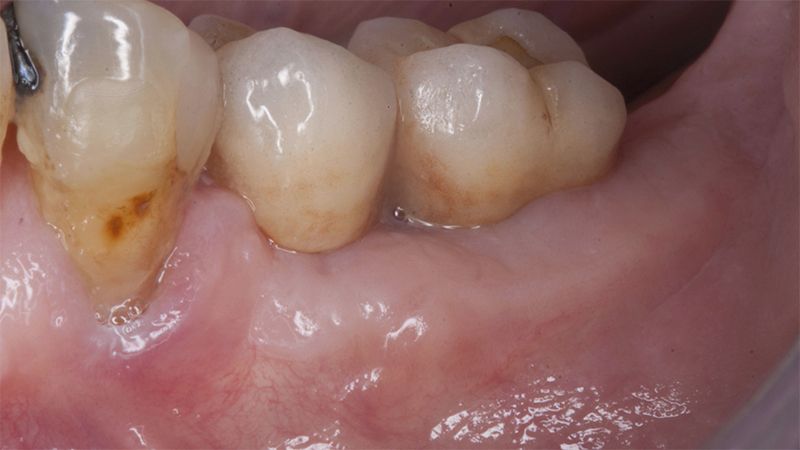
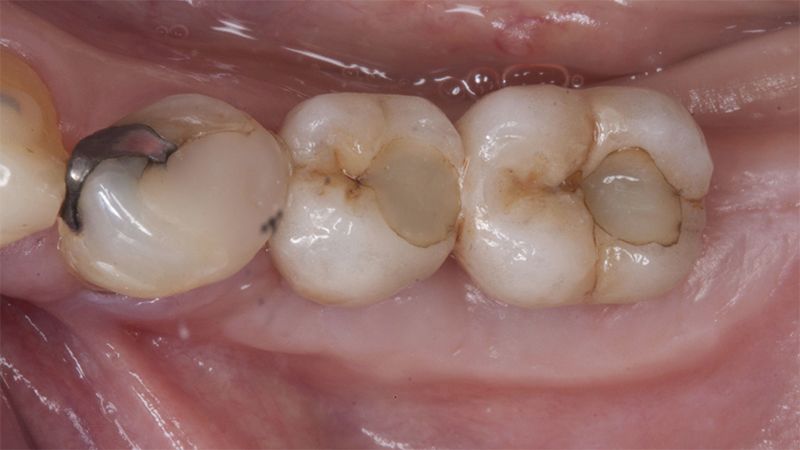
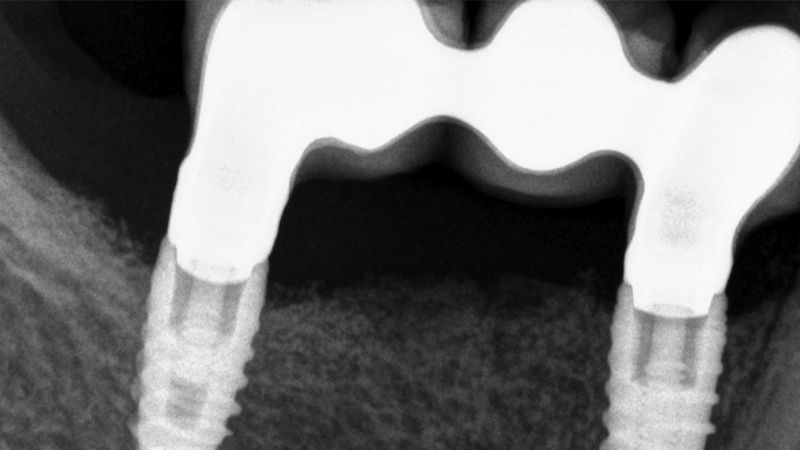
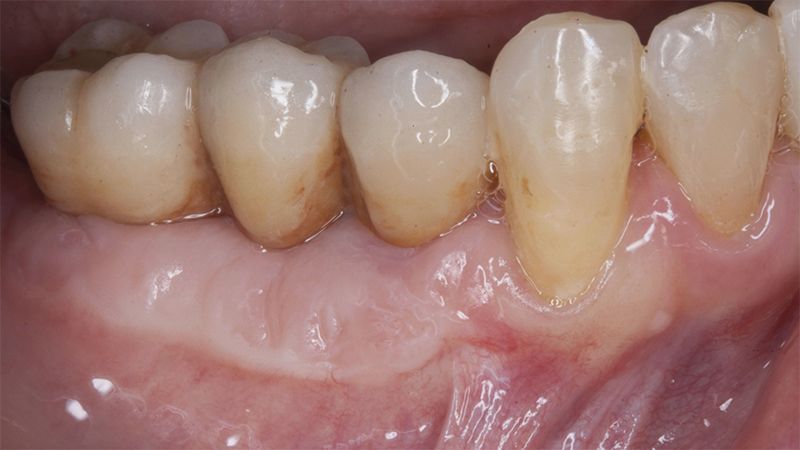
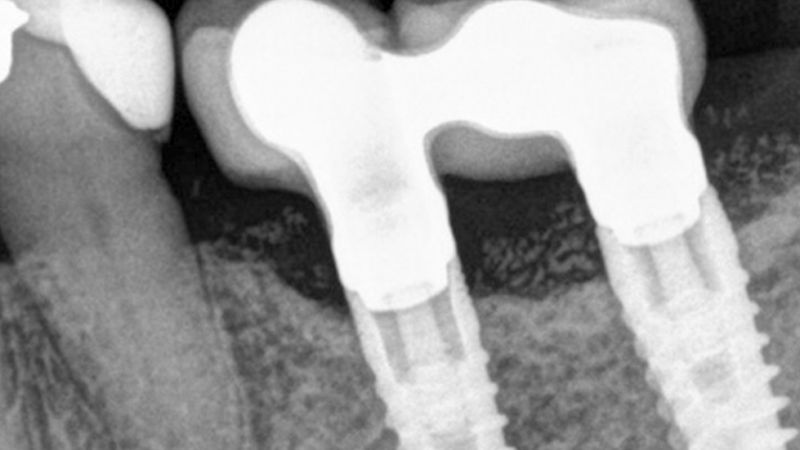
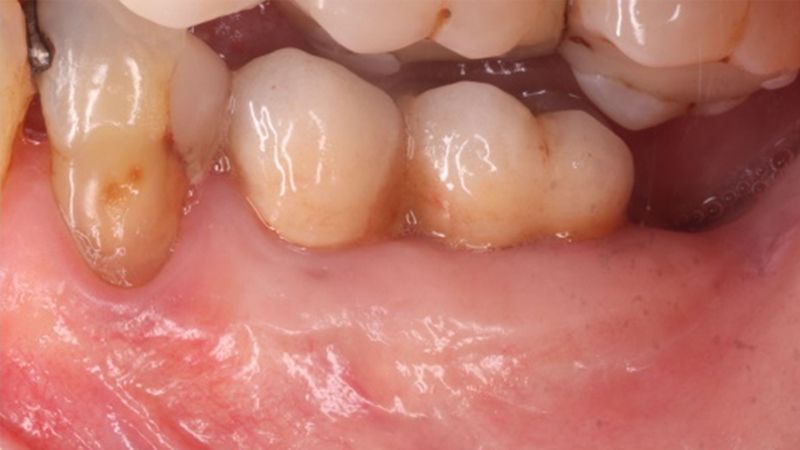
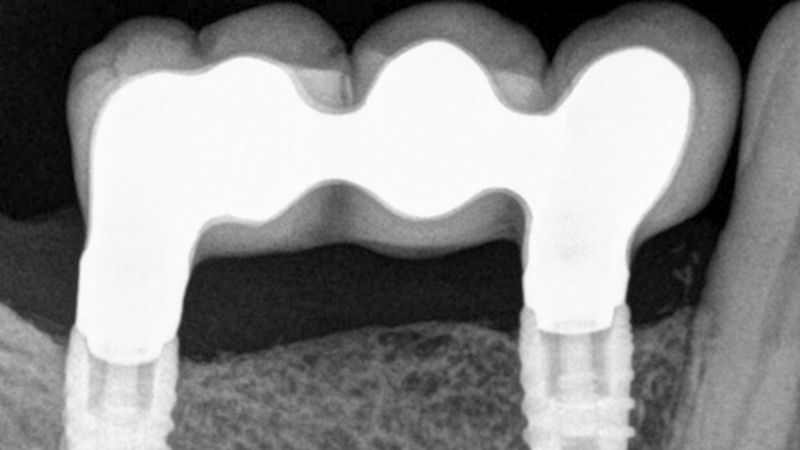
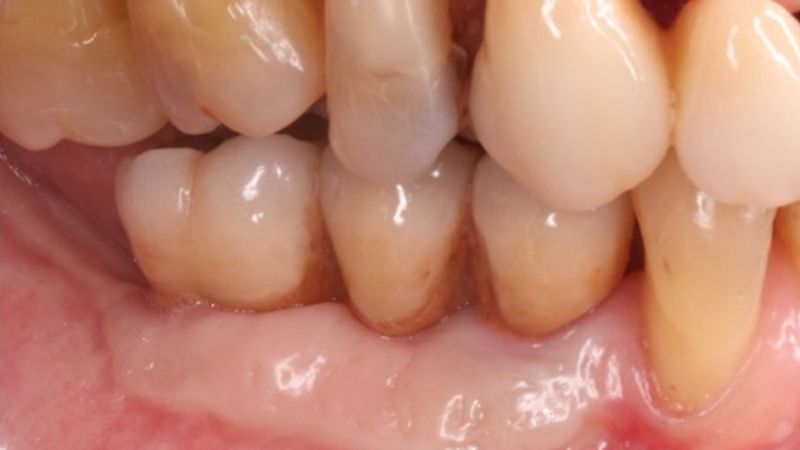
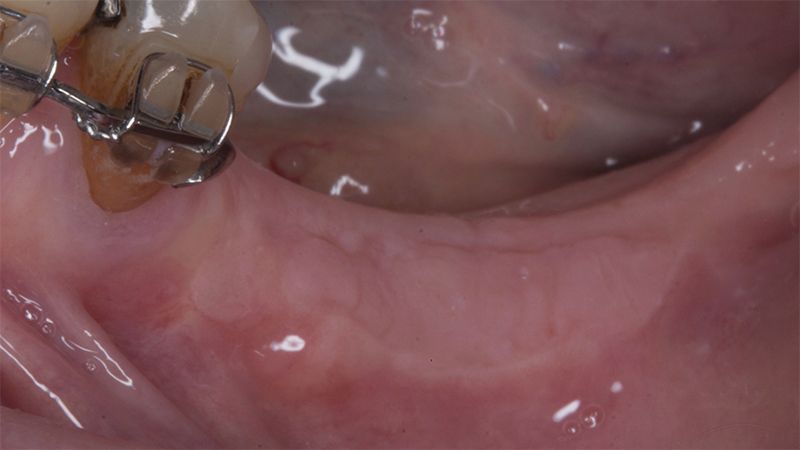
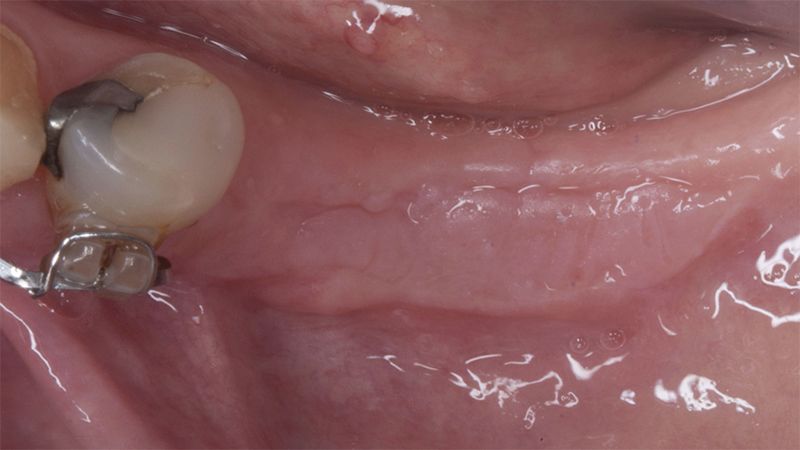
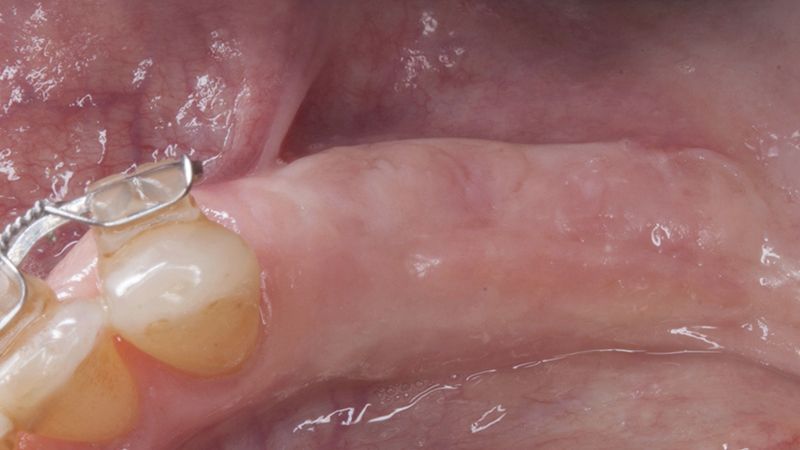
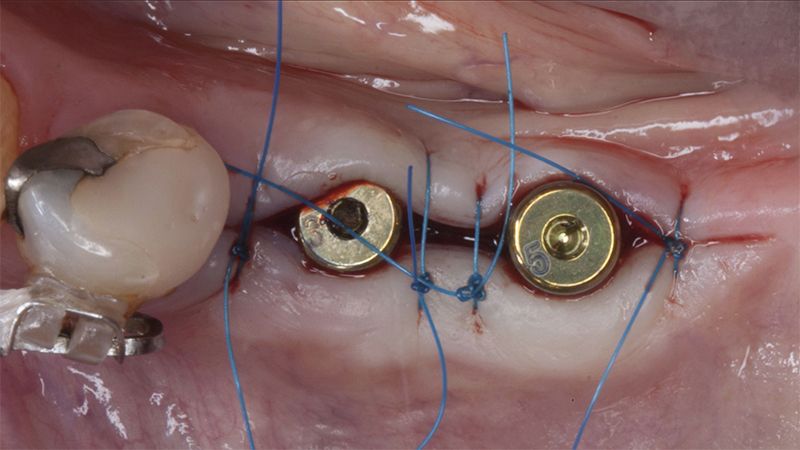
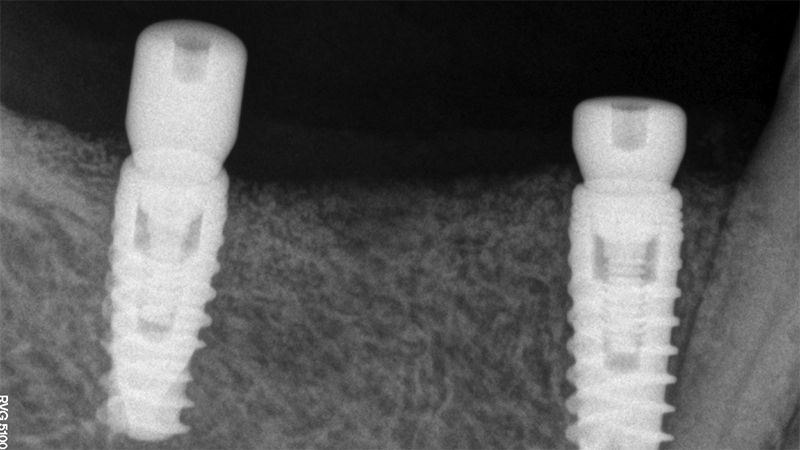
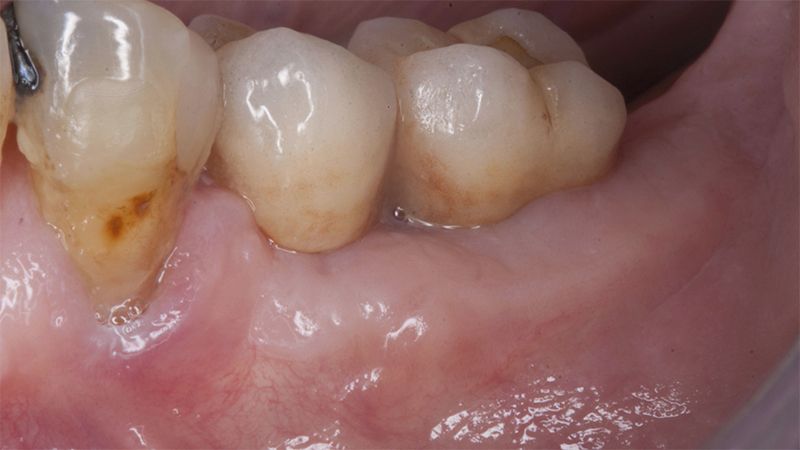
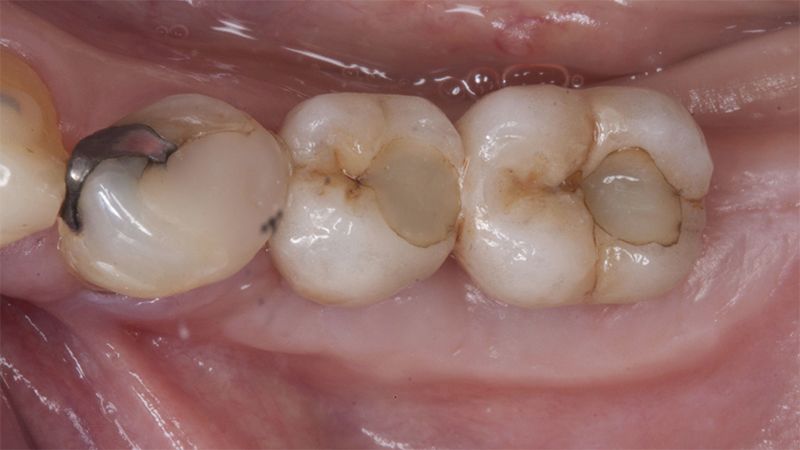
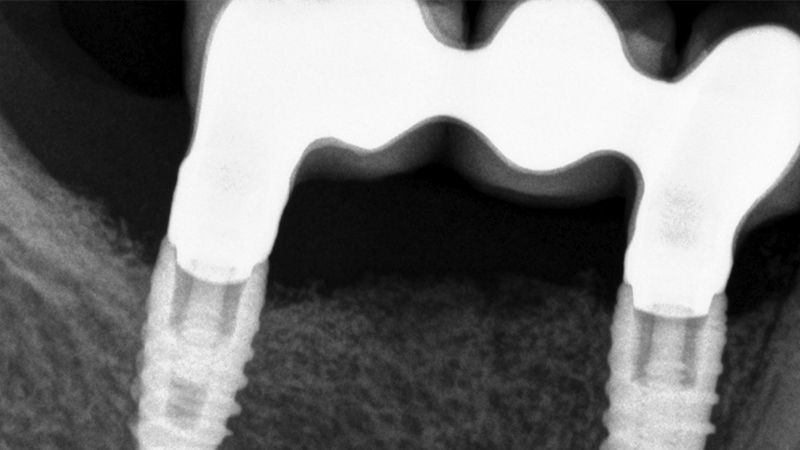
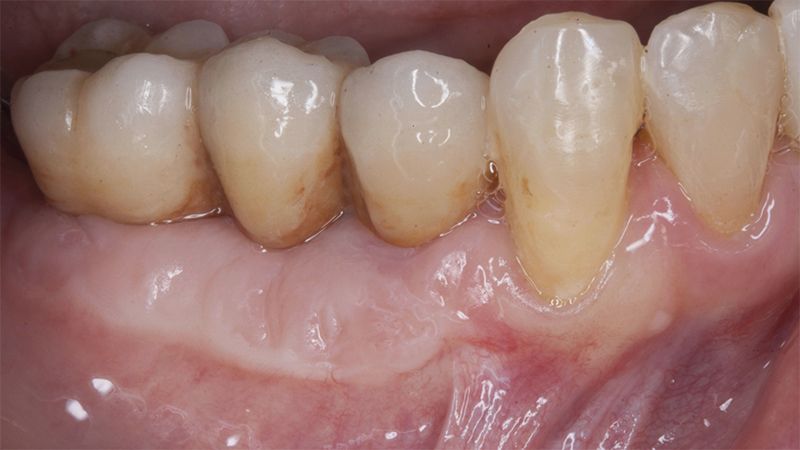
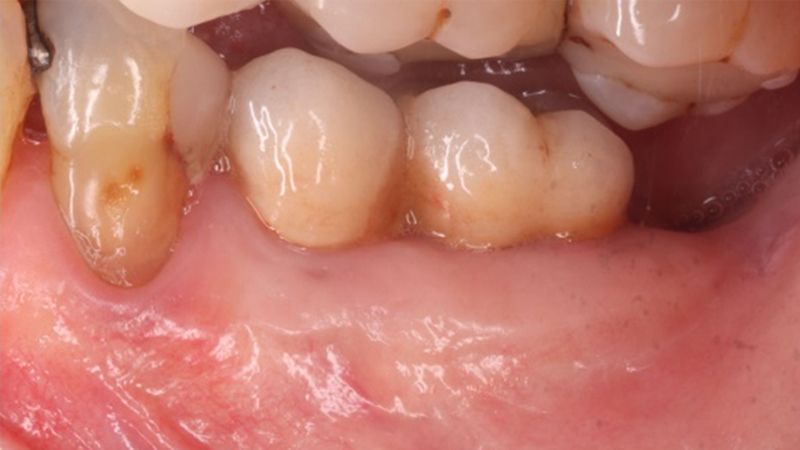
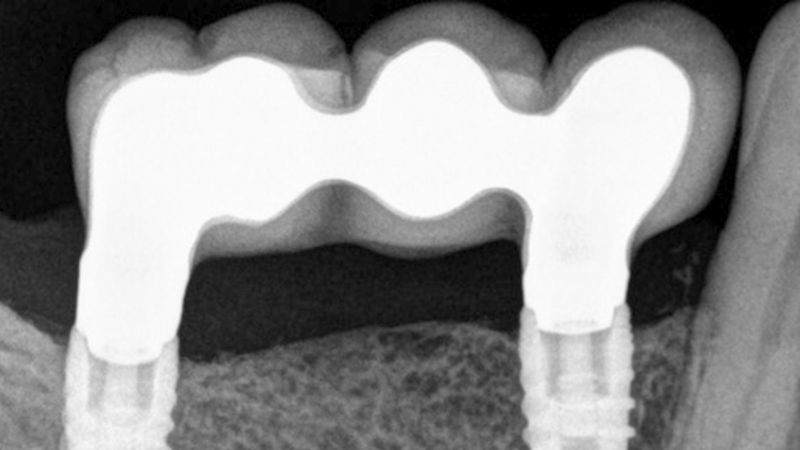
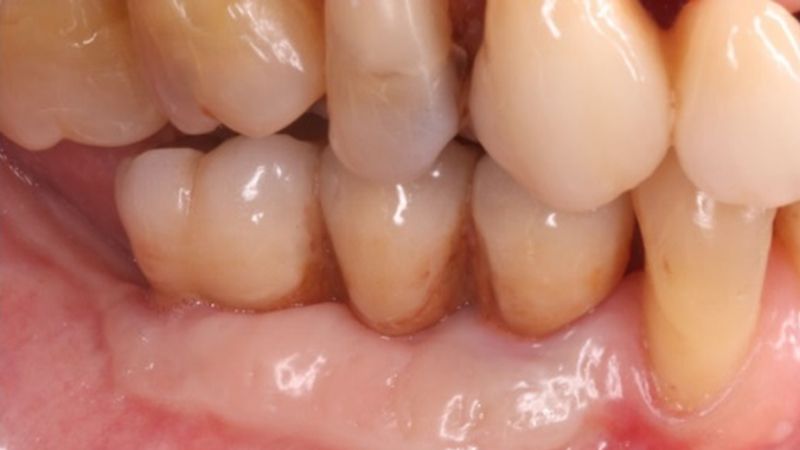
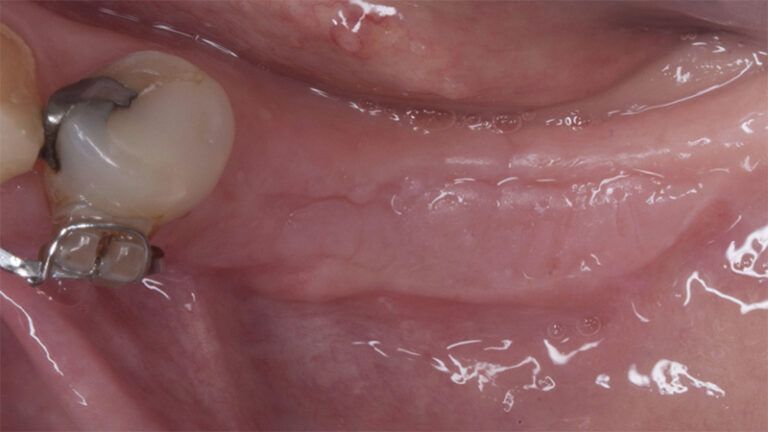
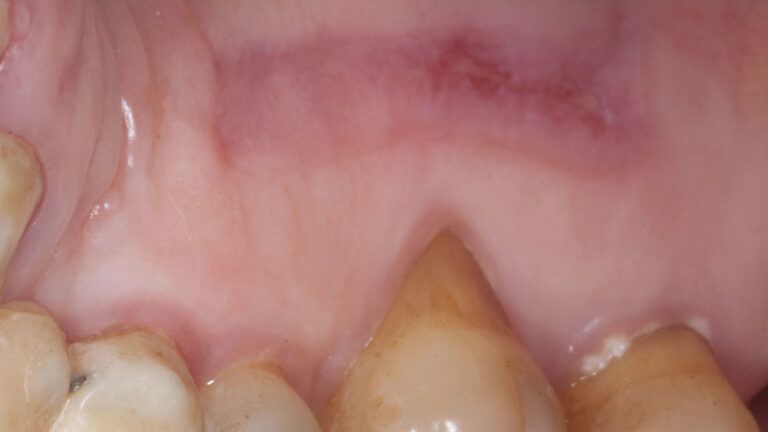
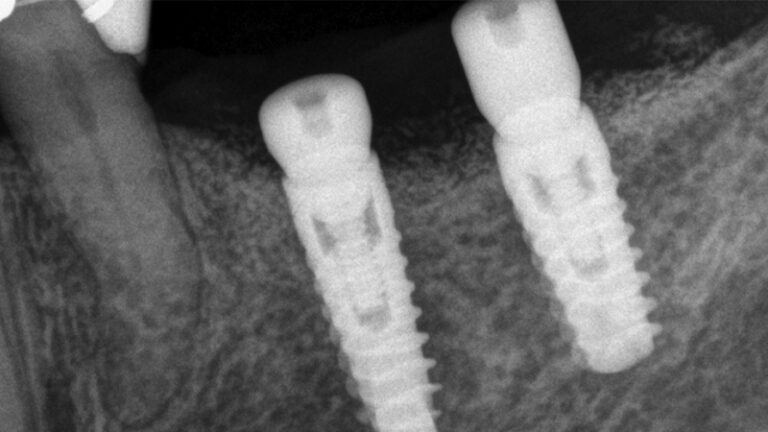
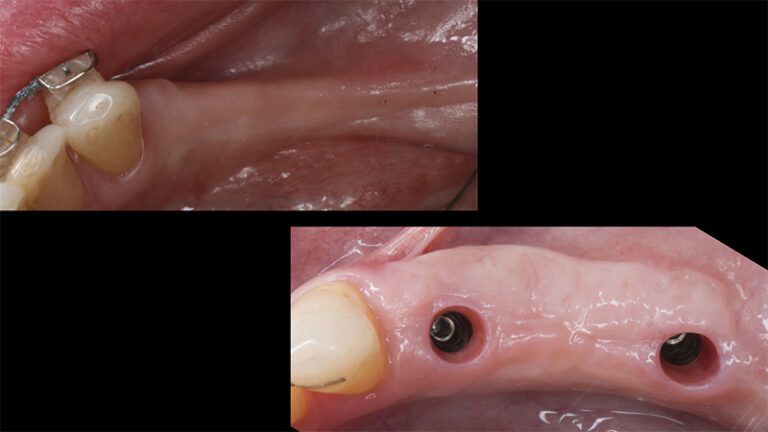
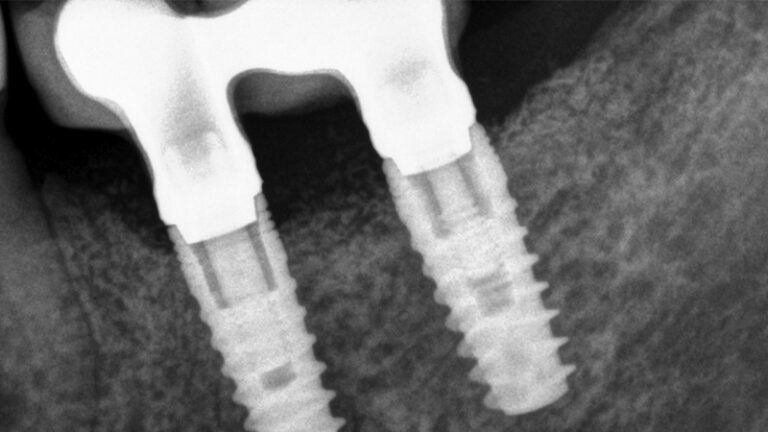
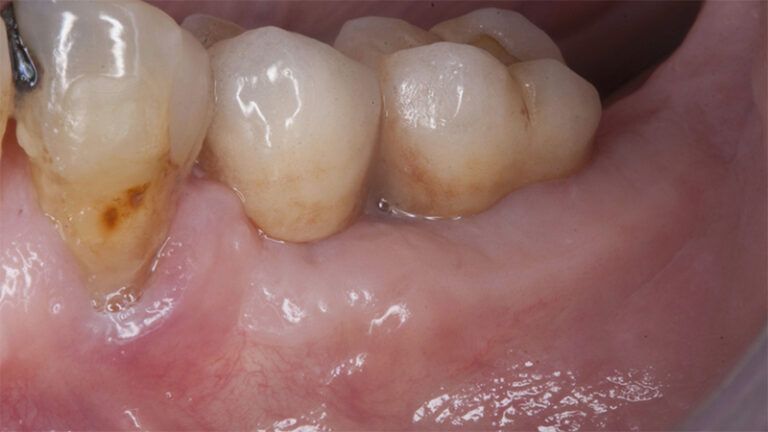
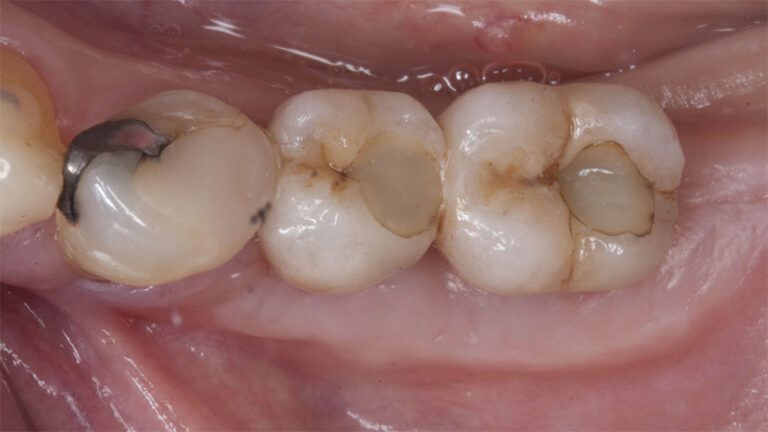
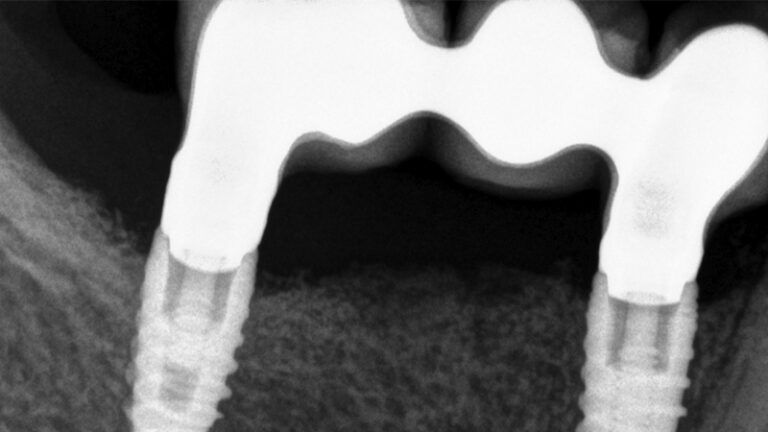
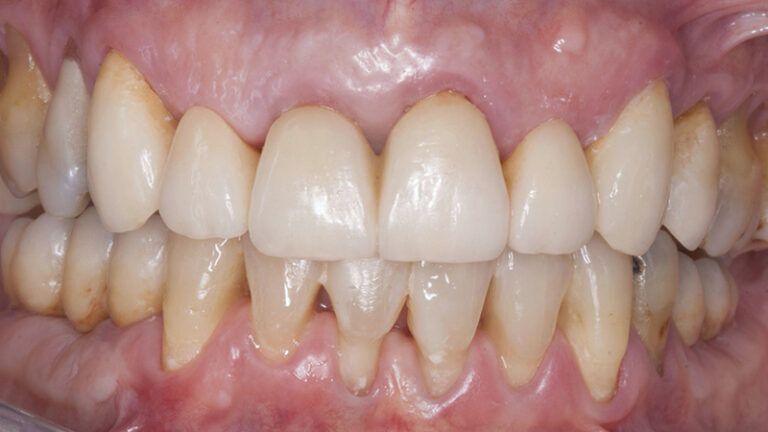
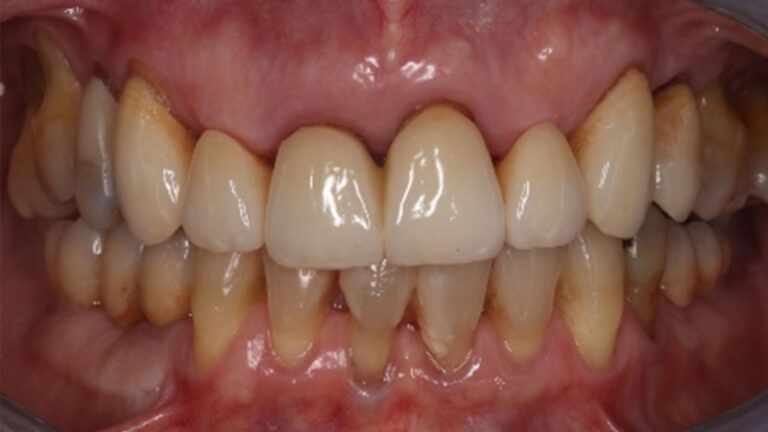
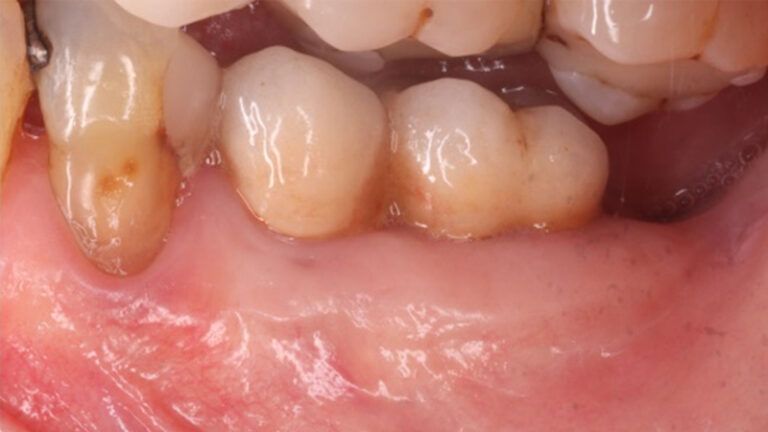
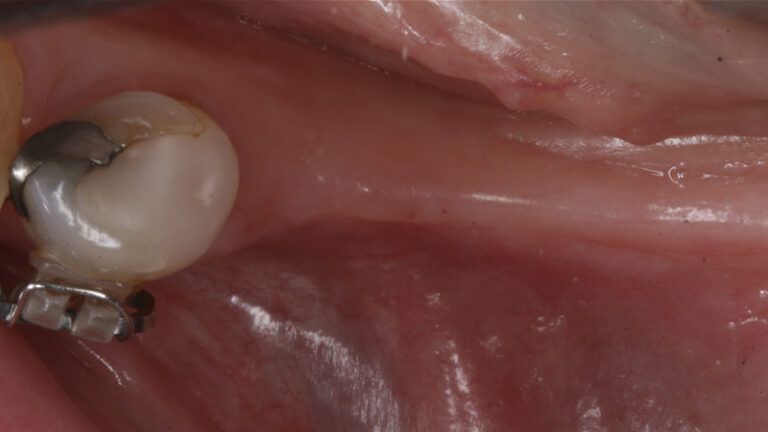
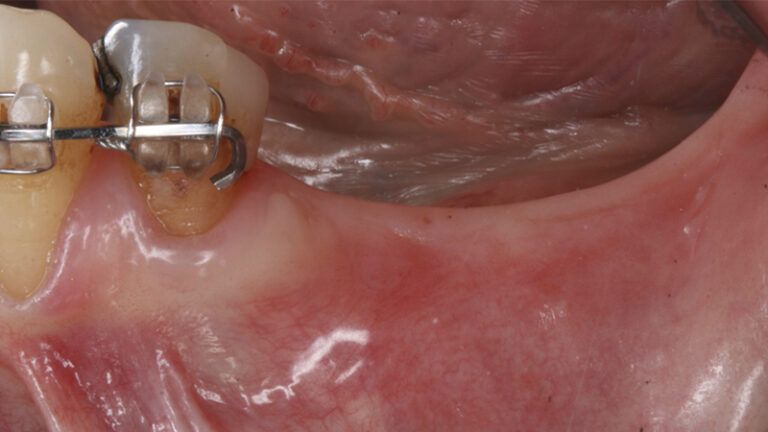
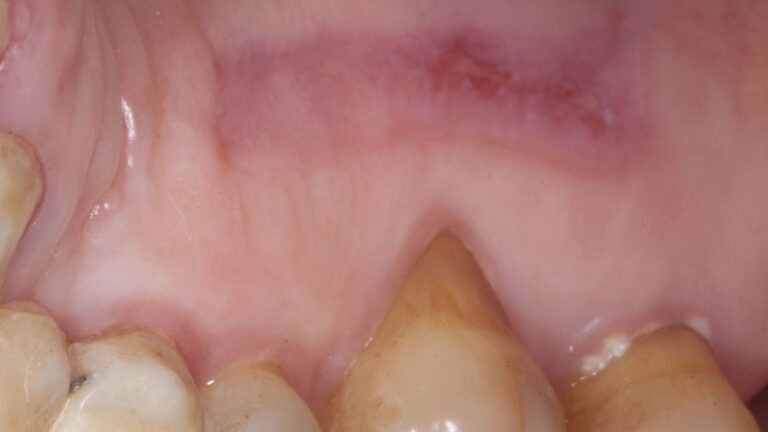
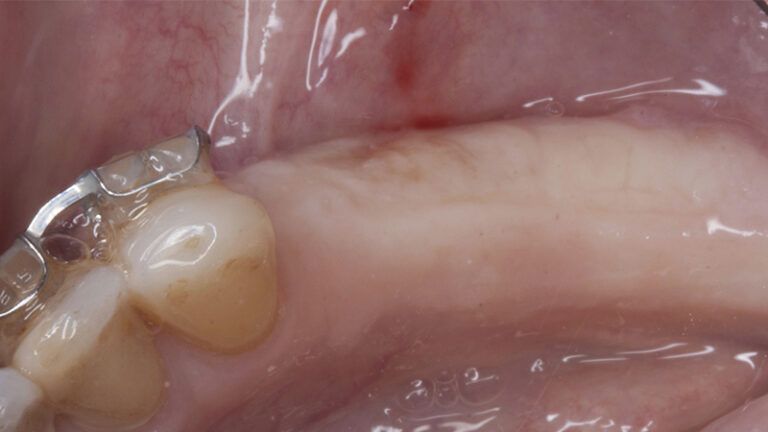
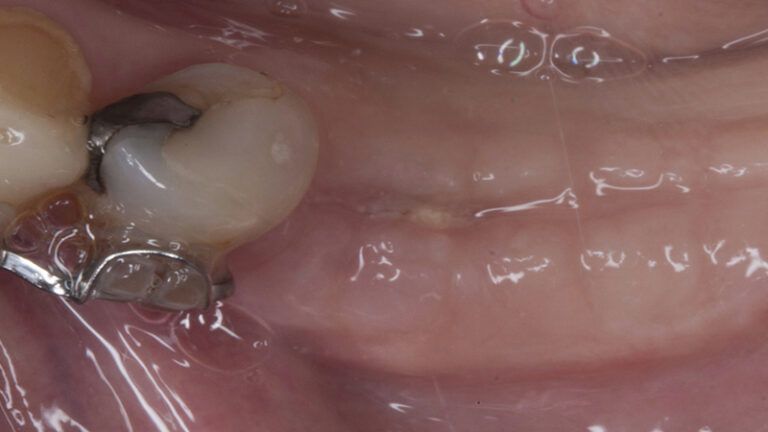
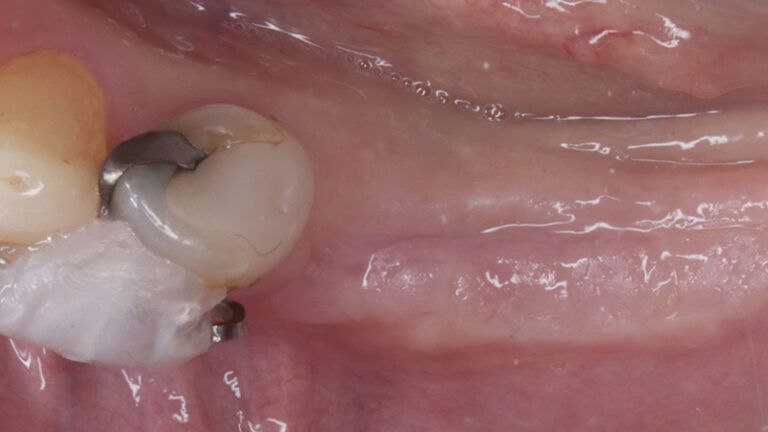
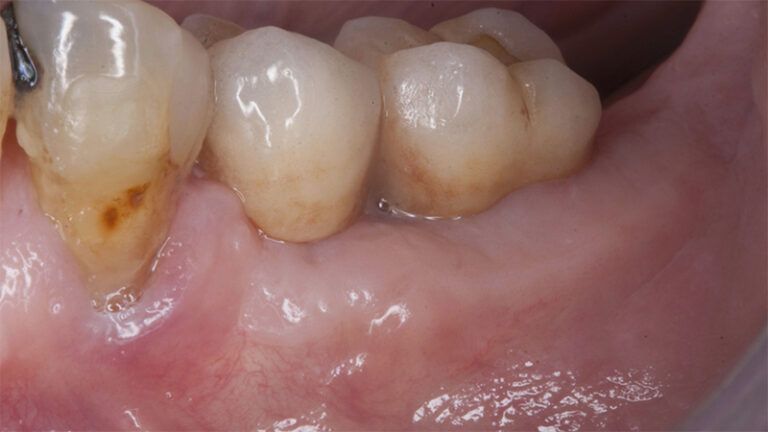
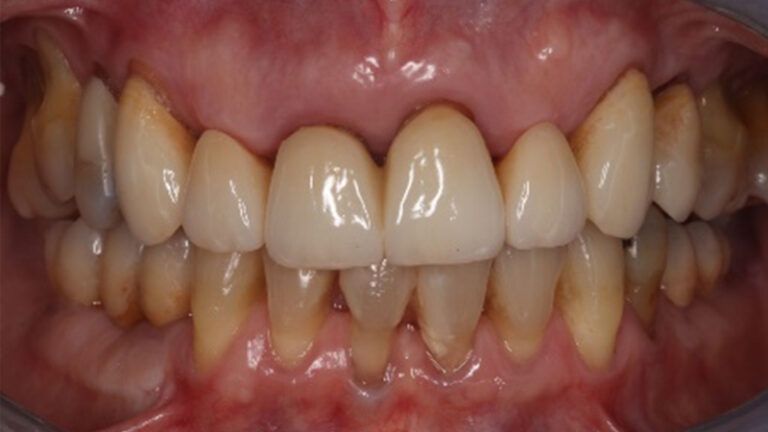
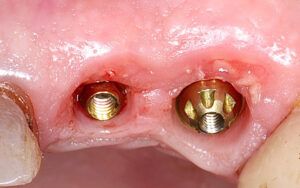
The clinical and x-ray controls 5 years after completing the treatment show complete stability of both hard and soft tissues.
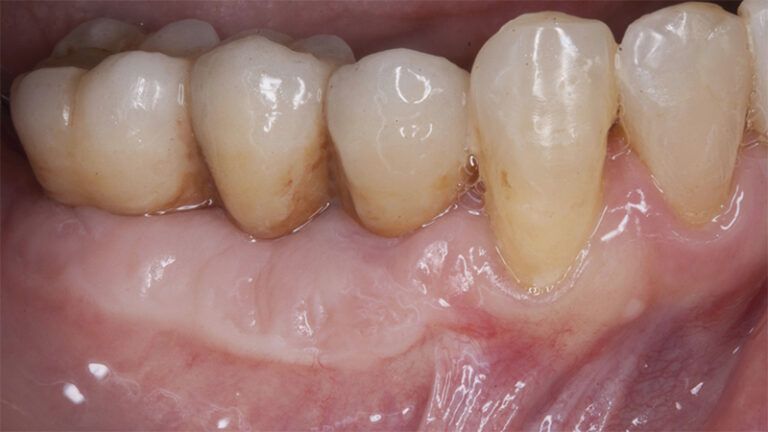
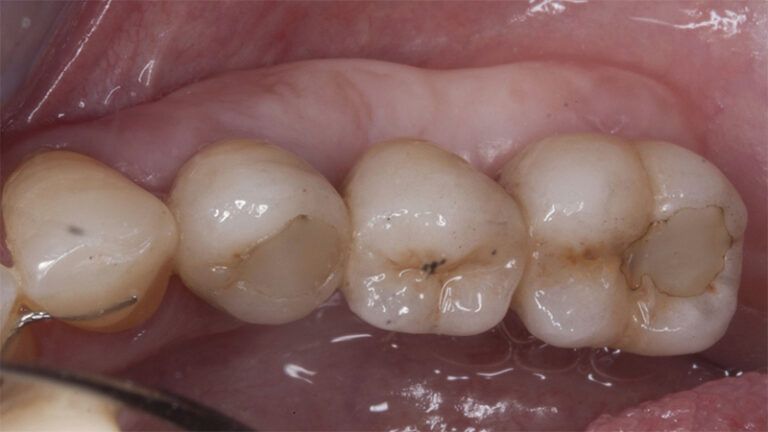
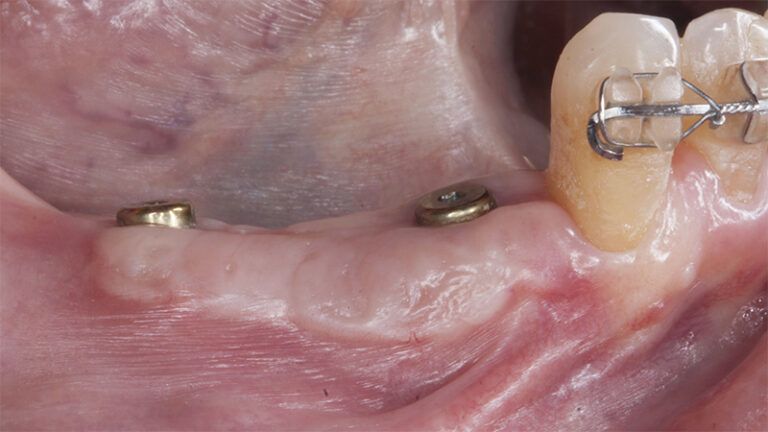
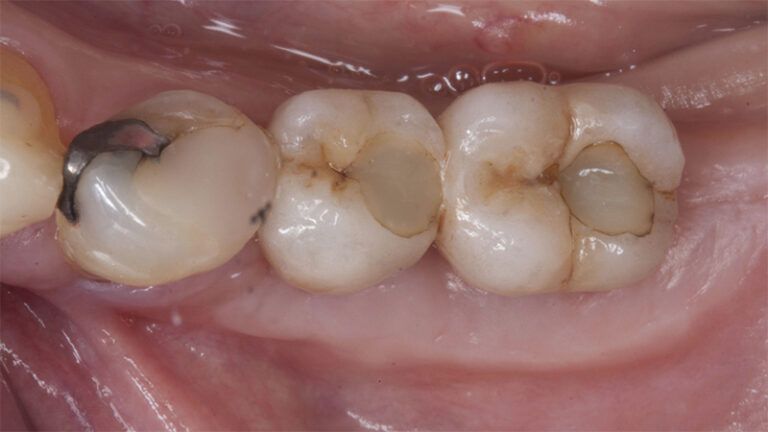
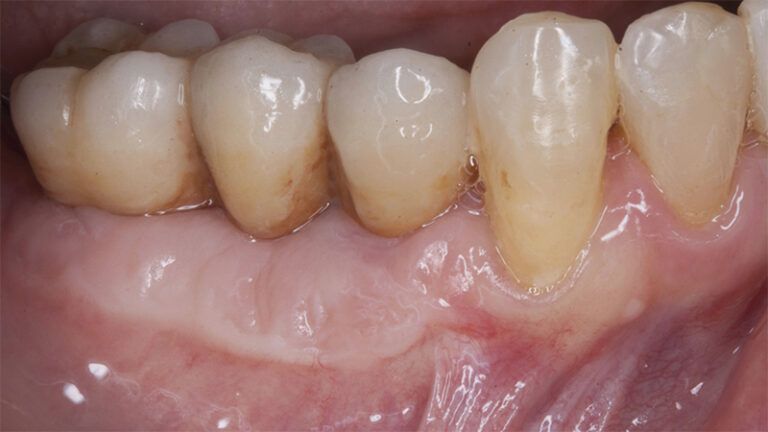
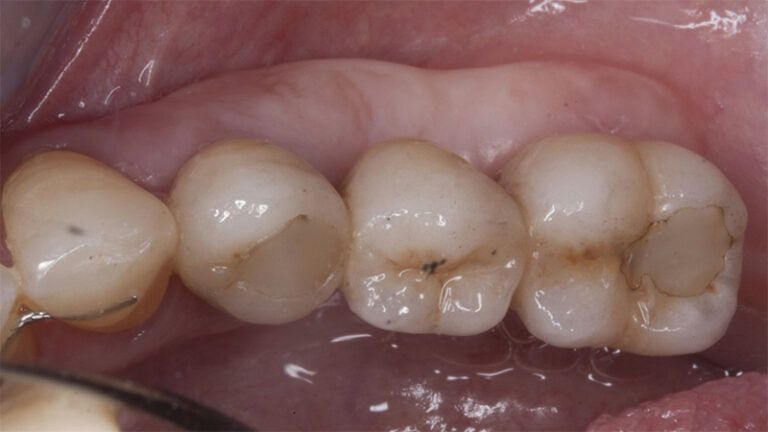
Control of the implants and prosthesis after 5 years in the third quadrant Control of the implants and prosthesis after 5 years in the third quadrant Control of the implants and prosthesis after 5 years in the third quadrant Control of the implants and prosthesis after 5 years in the third quadrant
Conclusion
There are more and more studies indicating that implants need an adequate band of keratinized gum to maintain a healthy situation in the long term, above all in patients with inadequate oral hygiene or that do not comply with the periodontal maintenance sessions.
In addition, according to the various studies, it is the posterior areas of the mandible that present less keratinized gum when placing our implants.
Therefore, in this case we can see how a simple Free Gingival Graft surgery can increase the band of keratinized gum around the implants placed and achieve a stable, inflammation-free result for at least 5 years.
Initial status of the case Initial situation of the implant area Initial situation of the implant area Preparation of the recipient bed for the graft in the 3rd quadrant Obtaining the free gingival graft of 20x7mm, with an approximate thickness of 1.5mm Details of the treatment of the donor area of the palate with hemostatic collagen sponges and cross sutures Checking the graft and its dimensions in the recipient bed Stabilizing the graft with simple stitches and compression sutures with 6-0 monofilament Stabilizing the graft with simple stitches and compression sutures with 6-0 monofilament Healing 15 days after surgery Lateral view of the complete revascularization and integration of the graft in the bed after 8 weeks Occlusal view of the keratinized tissue gained after 8 weeks Details of the recipient bed of the graft in the 4th quadrant Stabilization and suture of the graft Details of the donor area Healing of the graft after 15 days Healing of the donor area after 15 days Details of the increase in the band of keratinized gum after 8 weeks Placement sequence of the Avinent Biomimetic CC implants
Placement sequence of the Avinent Biomimetic CC implants
Placement sequence of the Avinent Biomimetic CC implantsGuided bone regeneration simultaneous to implant placement Guided bone regeneration simultaneous to implant placement Complete closure of the tissues after the bone regeneration Complete closure of the tissues after the bone regeneration Healing after 15 days Occlusal view of the volume gained after 4 months Lateral view of the tissues after 4 months Placement of the implants in the 4th quadrant with simultaneous regeneration Placement of the implants in the 4th quadrant with simultaneous regeneration Suture of the flaps without tension Details of the volume regenerated Placement of the healing abutments 5 months after the guided bone regeneration Placement of the healing abutments 5 months after the guided bone regeneration Healing after 15 days Initial situation and final appearance of the periimplant tissues Initial situation and final appearance of the periimplant tissues Reentry in the 4th quadrant after the regeneration Reentry in the 4th quadrant after the regeneration Placement of the healing abutments in the second phase Placement of the healing abutments in the second phase Suture of the flaps in the second surgery Healing after 15 days Initial and final appearance of the periimplant tissues Initial and final appearance of the periimplant tissues Fit of crowns 35 and 36 Definitive prosthesis in the mouth Definitive prosthesis in the mouth X-ray image of the prosthetic load Metal-ceramic prosthesis in the mouth Metal-ceramic prosthesis in the mouth Final image of the rehabilitated case Initial and final images of the patient Final image of the rehabilitated case The clinical and x-ray controls 5 years after completing the treatment show complete stability of both hard and soft tissues The clinical and x-ray controls 5 years after completing the treatment show complete stability of both hard and soft tissues
Control of the implants and prosthesis after 5 years in the third quadrant
Control of the implants and prosthesis after 5 years in the third quadrant